
Concept explainers
The Number of Ending Inventory Units.
Explanation of Solution
The ending Inventory units is a difference between units of goods available for sale and units sold and has been computed as under:
| Ending Inventory Units | |
| | UNITS |
| Units Available for sale | 1800 |
| Purchase | |
| 15-Mar | 800 |
| 10-Sep | 600 |
| Ending Inventory Units | 400 |
Requirement 3-a:
First in First Out:
The first in first out method of assigning the cost to goods sold is based on the principle that the goods that are entered first in the store room shall be issued first for sale and hence the cost shall be recorded at its initial prices of goods entered in store room. The periodic Inventory system means the records are maintained only at the end of period.
The Cost assigned to ending Inventory under FIFO.
Explanation of Solution
The FIFO method of period inventory suggests that the goods issued for sale on a particular date shall be assigned cost on the basis of cost of oldest material lies in the store during the end of period.
The Ending Inventory shall be computed as under:
| STATEMENT SHOWING INVENTORY RECORD UNDER PERIODIC FIFO METHOD | |||||||||
| | RECIEPTS | COST OF GOODS GOODS SOLD | BALANCE | ||||||
| DATE | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ |
| Balance Oct1 | 600 | 45 | 27000 | 600 | 45 | 27000 | | | |
| Purchase | | | | | | | | | |
| 10-Feb | 400 | 42 | 16800 | 400 | 42 | 16800 | | | |
| 13-Mar | 200 | 27 | 5400 | 200 | 27 | 5400 | | | |
| 21-Aug | 100 | 50 | 5000 | 100 | 50 | 5000 | | | |
| 5-Sep | 500 | 46 | 23000 | 100 | 46 | 4600 | 400 | 46 | 18400 |
| TOTAL | 1800 | | 77200 | 1400 | | 58800 | 400 | | 18400 |
Therefore, Ending Inventory is 400 units of $18400.
Requirement 3-b:
Last in First Out:
The Last in first out method of assigning the cost to goods sold is based on the principle that the goods that are entered recently in the store room shall be issued first for sale and hence the cost shall be recorded at its recent prices of goods entered in store room. The periodic Inventory system means the records are maintained at the end of period.
The Cost assigned to ending Inventory under LIFO.
Explanation of Solution
The LIFO method of periodic inventory suggests that the goods issued for sale on a particular date shall be assigned cost on the basis of cost of newest material lies in the store at the end of period.
The Ending Inventory shall be computed as under:
| STATEMENT SHOWING INVENTORY RECORD UNDER PERIODIC LIFO METHOD | |||||||||
| | RECIEPTS | COST OF GOODS GOODS SOLD | BALANCE | ||||||
| DATE | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ |
| Balance Oct1 | 600 | 45 | 27000 | 200 | 45 | 9000 | 400 | 45 | 18000 |
| Purchase | | | | | | | | | |
| 10-Feb | 400 | 42 | 16800 | 400 | 42 | 16800 | | | |
| 13-Mar | 200 | 27 | 5400 | 200 | 27 | 5400 | | | |
| 21-Aug | 100 | 50 | 5000 | 100 | 50 | 5000 | | | |
| 5-Sep | 500 | 46 | 23000 | 500 | 46 | 23000 | | | |
| TOTAL | 1800 | | 77200 | 1400 | | 59200 | 400 | 45 | 18000 |
Therefore, Ending Inventory is 400 units of $18000.
Requirement 3-c:
Weighted Average:
The Weighted Average method of issuing inventory is based on principle that the goods shall be issued at an average of prices of goods which are lying in the store room at the end of period. The periodic Inventory system means the records are maintained at the end of period.
The Cost assigned to ending Inventory under Weighted average.
Explanation of Solution
The Weighted Average method of periodic inventory suggests that the goods issued for sale on a particular date shall be assigned cost on the basis of average cost of material lies in the store during the period.
The Ending Inventory shall be computed as under:
| STATEMENT SHOWING INVENTORY RECORD UNDER PERIODIC WEIGHTED AVERAGE METHOD | |||||||||
| | RECIEPTS | COST OF GOODS GOODS SOLD | BALANCE | ||||||
| DATE | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ |
| Balance Oct1 | 600 | 45 | 27000 | | | | | | |
| Purchase | | | | | | | | | |
| 10-Feb | 400 | 42 | 16800 | | | | | | |
| 13-Mar | 200 | 27 | 5400 | | | | | | |
| 21-Aug | 100 | 50 | 5000 | | | | | | |
| 5-Sep | 500 | 46 | 23000 | | | | | | |
| TOTAL | 1800 | 42.89 | 77200 | 1400 | 42.89 | 60046 | 400 | 42.89 | 17156 |
Therefore, Ending Inventory is 400 units of $17156.
Requirement 3-d:
Specific Identification:
Specific Identification method of assigning the cost to goods sold is based on the principle that the goods that have been issued for sale has been specifically identified to be issued from the particular lot of material. Therefore, the cost of that particular lot shall be assigned on the same. The periodic Inventory system means the records are maintained at the end of period.
The Cost assigned to ending Inventory under Specific Identification.
Explanation of Solution
The Specific Identification method of periodic inventory suggests that the goods issued for sale on a particular date shall be assigned cost on the basis of cost of material specifically identified as issued from the store at the end of period.
The Ending Inventory shall be computed as under:
| STATEMENT SHOWING INVENTORY RECORD UNDER PERIODIC SPECIFIC IDENTIFICATION METHOD | |||||||||
| | RECIEPTS | COST OF GOODS GOODS SOLD | BALANCE | ||||||
| DATE | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ |
| Balance Oct1 | 600 | 45 | 27000 | 600 | 45 | 27000 | | | |
| Purchase | | | | | | | | | |
| 10-Feb | 400 | 42 | 16800 | 300 | 42 | 12600 | 100 | 42 | 4200 |
| 13-Mar | 200 | 27 | 5400 | 200 | 27 | 5400 | | | |
| 21-Aug | 100 | 50 | 5000 | 50 | 50 | 2500 | 50 | 50 | 2500 |
| 5-Sep | 500 | 46 | 23000 | 250 | 46 | 11500 | 250 | 46 | 11500 |
| TOTAL | 1800 | | 77200 | 1400 | | 59000 | 400 | | 18200 |
Therefore, Ending Inventory is 400 units of $18200.
Requirement 4:
Gross Profits:
Gross Profits means excess of sales revenue over the cost of goods sold.
Gross profits earned by the company under various methods.
Explanation of Solution
The Gross profits is computed as a difference between the sales revenue and cost of goods sold as assigned under various methods and has been computed as under:
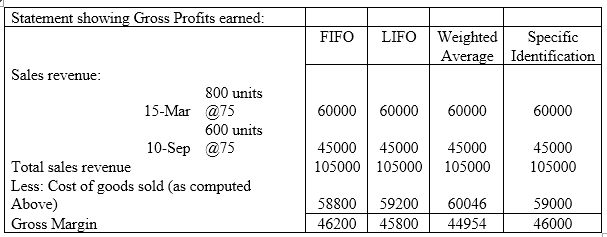
Requirement 5:
The Method to be preferred so as to generate higher bonus.
Explanation of Solution
As the bonus is based on gross profit, the method shall be preferred which will give provide lowest cost of goods sold. Therefore, as per above computations, the FIFO method shall be followed as its gives the lowest cost of goods sold and resultant higher gross profit.
The FIFO method of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
FUNDAMENTAL ACCT PRIN CONNECT ACCESS
- Read The company events occured during the first half of the year and answer the following questions: 1)Determine the importance of the company having property, plant, and equipment as part of the long-term assets on its balance sheet. 2)What are the costs for determining what is included in the acquisition of property, plant, and equipment? 3)What are the methods you can use to calculate depreciation? Which method makes the most sense for this company? 4)Taking into account the disposal of property, plant, and equipment, what is the correct way to record a disposal?arrow_forwardCan you guide me through solving this financial accounting problem using proper techniques?arrow_forwardRead The company events occured during the first half of the year and answer the following questions: 1)Determine the importance of the company having goodwill or intangibles as part of the long-term assets on its balance sheet. 2)How do companies acquire goodwill? 3)What are examples of intangible assets and how are they amortized?arrow_forward
- Can you demonstrate the accurate method for solving this financial accounting question?arrow_forwardComputer Zone sells laptops. During August 2023, it sold 320 laptops at a $1,850 average price each. The August 2023 budget included sales of 350 laptops at an average price of $1,750 each. Compute the sales price variance and the sales volume variance for August 2023.arrow_forwardThe standard cost of Product ZZ includes 3 hours of direct labor at $16 per hour. The predetermined overhead rate is $28 per direct labor hour. During September, the company incurred 3,600 hours of direct labor at an average rate of $15.75 per hour and $94,200 of manufacturing overhead costs. It produced 1,200 units. Compute the total overhead variance.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





