
Concept explainers
The Number of Ending Inventory Units.
Explanation of Solution
The ending Inventory units is a difference between units of goods available for sale and units sold and has been computed as under:
| Ending Inventory Units: | |
| | UNITS |
| Units available for sale | 820 |
| Less: Units sold | |
| Mar-9 Sales | 420 |
| Mar-29 Sales | 160 |
| Ending Inventory Units: | 240 |
Requirement 3-a:
First in First Out:
The first in first out method of assigning the cost to goods sold is based on the principle that the goods that are entered first in the store room shall be issued first for sale and hence the cost shall be recorded at its initial prices of goods entered in store room. The periodic Inventory system means the records are maintained only at the end of period.
The Cost assigned to ending Inventory under FIFO.
Explanation of Solution
The FIFO method of period inventory suggests that the goods issued for sale on a particular date shall be assigned cost on the basis of cost of oldest material lies in the store during the end of period.
The Ending Inventory shall be computed as under:
| STATEMENT SHOWING INVENTORY RECORD UNDER PERIODIC FIFO METHOD | |||||||||
| | RECIEPTS | COST OF GOODS SOLD | BALANCE | ||||||
| DATE | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ |
| Balance Oct1 | 100 | 50 | 5000 | 100 | 50 | 5000 | | | |
| Purchase | | | | | | | | | |
| 5-Mar | 400 | 55 | 22000 | 400 | 55 | 22000 | | | |
| 18-Mar | 120 | 60 | 7200 | 80 | 60 | 4800 | 40 | 60 | 2400 |
| 25-Mar | 200 | 62 | 12400 | | | | 200 | 62 | 12400 |
| TOTAL | 820 | | 46600 | 580 | | 31800 | 240 | | 14800 |
Therefore, Ending Inventory is 240 units of $14800.
Requirement 3-b:
Last in First Out:
The Last in first out method of assigning the cost to goods sold is based on the principle that the goods that are entered recently in the store room shall be issued first for sale and hence the cost shall be recorded at its recent prices of goods entered in store room. The periodic Inventory system means the records are maintained at the end of period.
The Cost assigned to ending Inventory under LIFO.
Explanation of Solution
The LIFO method of periodic inventory suggests that the goods issued for sale on a particular date shall be assigned cost on the basis of cost of newest material lies in the store at the end of period.
The Ending Inventory shall be computed as under:
| STATEMENT SHOWING INVENTORY RECORD UNDER PERIODIC LIFO METHOD | |||||||||
| | RECIEPTS | COST OF GOODS SOLD | BALANCE | ||||||
| DATE | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ |
| Balance Oct1 | 100 | 50 | 5000 | | | | 100 | 50 | 5000 |
| Purchase | | | | | | | | | |
| 5-Mar | 400 | 55 | 22000 | 260 | 55 | 14300 | 140 | 55 | 7700 |
| 18-Mar | 120 | 60 | 7200 | 120 | 60 | 7200 | | | |
| 25-Mar | 200 | 62 | 12400 | 200 | 62 | 12400 | | | |
| TOTAL | 820 | | 46600 | 580 | | 33900 | 240 | | 12700 |
Therefore, Ending Inventory is 240 units of $12700.
Requirement 3-c:
Weighted Average:
The Weighted Average method of issuing inventory is based on principle that the goods shall be issued at an average of prices of goods which are lying in the store room at the end of period. The periodic Inventory system means the records are maintained at the end of period.
The Cost assigned to ending Inventory under Weighted average.
Explanation of Solution
The Weighted Average method of periodic inventory suggests that the goods issued for sale on a particular date shall be assigned cost on the basis of average cost of material lies in the store during the period.
The Ending Inventory shall be computed as under:
| STATEMENT SHOWING INVENTORY RECORD UNDER PERIODIC WEIGHTED AVERAGE METHOD | |||||||||
| | RECIEPTS | COST OF GOODS SOLD | BALANCE | ||||||
| DATE | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ |
| Balance Oct1 | 100 | 50 | 5000 | | | | | | |
| Purchase | | | | | | | | | |
| 5-Mar | 400 | 55 | 22000 | | | | | | |
| 18-Mar | 120 | 60 | 7200 | | | | | | |
| 25-Mar | 200 | 62 | 12400 | | | | | | |
| TOTAL | 820 | 56.83 | 46600 | 580 | 56.83 | 32961 | 240 | 56.83 | 13639 |
Therefore, Ending Inventory is 240 units of $13639.
Requirement 3-d:
Specific Identification:
Specific Identification method of assigning the cost to goods sold is based on the principle that the goods that have been issued for sale has been specifically identified to be issued from the particular lot of material. Therefore, the cost of that particular lot shall be assigned on the same. The periodic Inventory system means the records are maintained at the end of period.
The Cost assigned to ending Inventory under Specific Identification.
Explanation of Solution
The Specific Identification method of periodic inventory suggests that the goods issued for sale on a particular date shall be assigned cost on the basis of cost of material specifically identified as issued from the store at the end of period.
The Ending Inventory shall be computed as under:
| STATEMENT SHOWING INVENTORY RECORD UNDER PERIODIC SPECIFIC IDENTIFICATION METHOD | |||||||||
| | RECIEPTS | COST OF GOODS SOLD | BALANCE | ||||||
| DATE | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ |
| Balance Oct1 | 100 | 50 | 5000 | 80 | 50 | 4000 | 20 | 50 | 1000 |
| Purchase | | | | | | | | | |
| 5-Mar | 400 | 55 | 22000 | 340 | 55 | 18700 | 60 | 55 | 3300 |
| 18-Mar | 120 | 60 | 7200 | 40 | 60 | 2400 | 80 | 60 | 4800 |
| 25-Mar | 200 | 62 | 12400 | 120 | 62 | 7440 | 80 | 62 | 4960 |
| TOTAL | 820 | | 46600 | 580 | | 32540 | 2400 | | 14060 |
Therefore, Ending Inventory is 240 units of $14060.
Requirement 4:
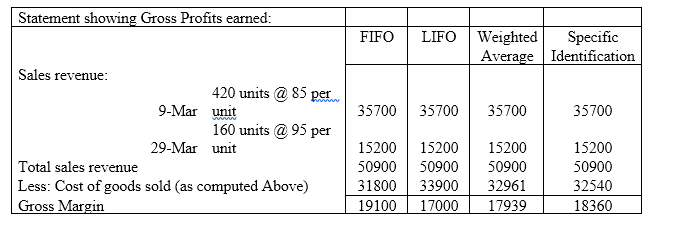
Gross Profits:
Gross Profits means excess of sales revenue over the cost of goods sold.
Gross profits earned by the company under various methods.
Explanation of Solution
The Gross profits is computed as a difference between the sales revenue and cost of goods sold as assigned under various methods and has been computed as under:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
FUNDAMENTAL ACCT PRIN CONNECT ACCESS
- Please give me true answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardcritically analyze the effectiveness of the tax system in Jamaica with a brief history of the tax system highlight the different types of taxes used in the country and identify and discuss 4 problems with the Jamaican tax system.arrow_forwardSolve my problemarrow_forward
- Solution of all problemsarrow_forwardJones Manufacturing Co. Ltd. makes a product by way of three consecutive processes. Inspection takes place during the processing operation, at which point bad units are separated from good units and sold as scrap at $20 each. Normal losses are estimated to be 5% of input during the period. The following data relates to process 2 for the month of October. During October, 20,000 units valued at $400,000 were transferred from process 1 to process 2. Other costs incurred during the month were: Direct material added Direct labour Production overheads $272,000 $254,000 $ 120,400 At inspection, 3000 units were rejected as scrap. These units had reached the following degree of completion: Transfer from process 1 Direct material added Conversion costs 100% 80% 50% Work-in-progress at the end of October was 4,000 units and had reached the following degree of completion: Transfer from process 1 Direct material added 100% 60% 40% Conversion costs There were no unfinished goods in process 2 at the…arrow_forwardIf you answered with incorrect data then will give unhelpful. If image is not clear commentarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





