
Physics, 11e WileyPLUS + Loose-leaf
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781119394112
Author: John D. Cutnell, Kenneth W. Johnson, David Young, Shane Stadler
Publisher: Wiley (WileyPLUS Products)
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 49P
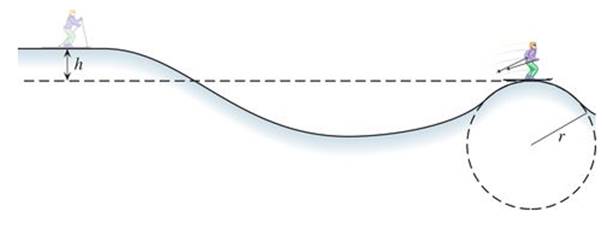
A skier starts from rest at the top of a hill. The skier coasts down the hill and up a second hill, as the drawing illustrates. The crest of the second hill is circular, with a radius of
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Use the following information to answer the next question.
Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of
42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below:
Incident
ray at A
Note: This diagram is not to
scale.
a
Air (n = 1.00)
Water (n = 1.34)
1) Determine the angle of refraction of the ray of light in the water.
B
Hi can u please solve
6. Bending a lens in OpticStudio or OSLO. In either package, create a BK7 singlet lens of 10 mm semi-diameter
and with 10 mm thickness. Set the wavelength to the (default) 0.55 microns and a single on-axis field point at
infinite object distance. Set the image distance to 200 mm. Make the first surface the stop insure that the lens
is fully filled (that is, that the entrance beam has a radius of 10 mm). Use the lens-maker's equation to
calculate initial glass curvatures assuming you want a symmetric, bi-convex lens with an effective focal length
of 200 mm. Get this working and examine the RMS spot size using the "Text" tab of the Spot Diagram analysis
tab (OpticStudio) or the Spd command of the text widnow (OSLO). You should find the lens is far from
diffraction limited, with a spot size of more than 100 microns.
Now let's optimize this lens. In OpticStudio, create a default merit function optimizing on spot size.Then insert
one extra line at the top of the merit function. Assign the…
Chapter 6 Solutions
Physics, 11e WileyPLUS + Loose-leaf
Ch. 6 - During a tug-of-war, team A pulls on team B by...Ch. 6 - You are moving into an apartment and take the...Ch. 6 - The brakes of a truck cause it to slow down by...Ch. 6 - A 75.0-kg man is riding an escalator in a shopping...Ch. 6 - Suppose in Figure 6.2 that +1.10103J of work is...Ch. 6 - A person pushes a 16.0-kg shopping cart at a...Ch. 6 - The drawing shows a plane diving toward the ground...Ch. 6 - A person pulls a toboggan for a distance of 35.0m...Ch. 6 - As a sailboat sails 47m due north, a breeze exerts...Ch. 6 - A 55-kg box is being pushed a distance of 7.0m...
Ch. 6 - A 1.00102kg crate is being pushed across a...Ch. 6 - A 1200-kg car is being driven up a 5.0 hill. The...Ch. 6 - A fighter jet is launched from an aircraft carrier...Ch. 6 - A golf club strikes a 0.045-kg golf ball in order...Ch. 6 - It takes 185kJ of work to accelerate a car from...Ch. 6 - Prob. 16PCh. 6 - Prob. 17PCh. 6 - Prob. 18PCh. 6 - Prob. 19PCh. 6 - Prob. 20PCh. 6 - Prob. 21PCh. 6 - Prob. 22PCh. 6 - Prob. 24PCh. 6 - Prob. 26PCh. 6 - Prob. 27PCh. 6 - A 75.0-kg skier rides a 2830-m-long lift to the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 30PCh. 6 - Prob. 31PCh. 6 - Prob. 32PCh. 6 - Prob. 33PCh. 6 - Prob. 34PCh. 6 - Prob. 35PCh. 6 - Prob. 36PCh. 6 - Prob. 37PCh. 6 - Prob. 38PCh. 6 - A slingshot fires a pebble from the top of a...Ch. 6 - The drawing shows two boxes resting on...Ch. 6 - Prob. 41PCh. 6 - Prob. 42PCh. 6 - The drawing shows a skateboarder moving at 5.4m/s...Ch. 6 - Prob. 44PCh. 6 - Prob. 46PCh. 6 - Prob. 47PCh. 6 - The drawing shows two frictionless inclines that...Ch. 6 - A skier starts from rest at the top of a hill. The...Ch. 6 - Prob. 50PCh. 6 - Prob. 51PCh. 6 - Prob. 52PCh. 6 - Starting from rest, a 93-kg firefighter slides...Ch. 6 - Prob. 54PCh. 6 - Prob. 55PCh. 6 - Prob. 56PCh. 6 - In attempting to pass the puck to a teammate, a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 59PCh. 6 - Prob. 60PCh. 6 - Prob. 62PCh. 6 - Prob. 63PCh. 6 - You are working out on a rowing machine. Each time...Ch. 6 - A car accelerates uniformly from rest to 20.0m/s...Ch. 6 - Prob. 66PCh. 6 - Prob. 67PCh. 6 - Prob. 68PCh. 6 - Prob. 72PCh. 6 - Prob. 74PCh. 6 - Prob. 75PCh. 6 - Prob. 76APCh. 6 - A 2.00-kg rock is released from rest at a height...Ch. 6 - Prob. 80APCh. 6 - Prob. 81APCh. 6 - Some gliders are launched from the ground by means...Ch. 6 - Prob. 84APCh. 6 - A water slide is constructed so that swimmers,...Ch. 6 - Prob. 88APCh. 6 - Prob. 89CCPCh. 6 - Prob. 90CCPCh. 6 - Prob. 91TPCh. 6 - Prob. 92TP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answer .arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: A Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) Barrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: A Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) Barrow_forward
- Good explanation it sure experts solve it.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Asaparrow_forwardA satellite has a mass of 100kg and is located at 2.00 x 10^6 m above the surface of the earth. a) What is the potential energy associated with the satellite at this loction? b) What is the magnitude of the gravitational force on the satellite?arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardCorrect answer No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardStatistical thermodynamics. The number of imaginary replicas of a system of N particlesa) cannot be greater than Avogadro's numberb) must always be greater than Avogadro's number.c) has no relation to Avogadro's number.arrow_forward
- Lab-Based Section Use the following information to answer the lab based scenario. A student performed an experiment in an attempt to determine the index of refraction of glass. The student used a laser and a protractor to measure a variety of angles of incidence and refraction through a semi-circular glass prism. The design of the experiment and the student's results are shown below. Angle of Incidence (°) Angle of Refraction (º) 20 11 30 19 40 26 50 31 60 36 70 38 2a) By hand (i.e., without using computer software), create a linear graph on graph paper using the student's data. Note: You will have to manipulate the data in order to achieve a linear function. 2b) Graphically determine the index of refraction of the semi-circular glass prism, rounding your answer to the nearest hundredth.arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next two questions. A laser is directed at a prism made of zircon (n = 1.92) at an incident angle of 35.0°, as shown in the diagram. 3a) Determine the critical angle of zircon. 35.0° 70° 55 55° 3b) Determine the angle of refraction when the laser beam leaves the prism.arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next two questions. A laser is directed at a prism made of zircon (n = 1.92) at an incident angle of 35.0°, as shown in the diagram. 3a) Determine the critical angle of zircon. 35.0° 70° 55 55° 3b) Determine the angle of refraction when the laser beam leaves the prism.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g7u6pIfUVy4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY