
A space probe, initially at rest, undergoes an internal mechanical malfunction and breaks into three pieces. One piece of mass ml = 48.0 kg travels in the positive x-direction at 12.0 m/s, and a second piece of mass m2 = 62.0 kg travels in the xy-plane at an angle of 105° at 15.0 m/s. The third piece has mass m3 = 112 kg. (a) Sketch a diagram of the situation, labeling the different masses and their velocities, (b) Write the general expression for conservation of momentum in the x- and y-directions in terms of m1, m2, m3, v1, v2 and v3 and the sines and cosines of the angles, taking θ to be the unknown angle, (c) Calculate the final x-components of the momenta of m1 and m2. (d) Calculate the final y-components of the momenta of m1 and m2. (e) Substitute the known momentum components into the general equations of momentum for the x- and y-directions, along with the known mass m3. (f) Solve the two momentum equations for v3 cos θ and v3 sin θ, respectively, and use the identity cos2 θ + sin2 θ = 1 to obtain v3. (g) Divide the equation for v3 sin θ by that for v3 cos θ to obtain tan θ, then obtain the angle by taking the inverse tangent of both sides, (h) In general, would three such pieces necessarily have to move in the same plane? Why?
a)
Answer to Problem 46P
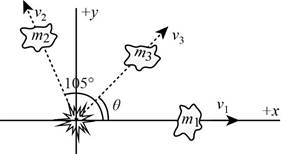
Explanation of Solution
The diagram of the breakage is,
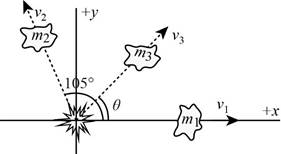
The numerical values of the masses and velocities are,
The numerical values of the masses and velocities are,
Conclusion:
Thus, the diagram of the breakage is,
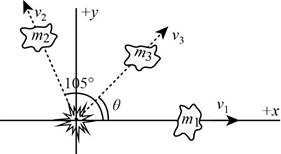
(b)
Answer to Problem 46P
Explanation of Solution
The general expression for the conservation of momentum in x-direction is,
The general expression for the conservation of momentum in y-direction is,
Conclusion:
Thus, the general expression for the conservation of momentum in x-direction is
(c)
Answer to Problem 46P
Explanation of Solution
The final x-component of the momenta of the mass
Substitute
The final x-component of the momenta of the mass
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the final x-component of the momenta of the mass
(d)
Answer to Problem 46P
Explanation of Solution
The final y-component of the momenta of the mass
Substitute
The final y-component of the momenta of the mass
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the final y-component of the momenta of the mass
(e)
Answer to Problem 46P
Explanation of Solution
The final x-component of the momenta of mass
The final y-component of the momenta of mass
Conclusion:
Thus, the final x and y-components of the momenta of mass
(f)
Answer to Problem 46P
Explanation of Solution
In the x-direction,
In the y-direction,
Squaring and adding the equations,
Conclusion:
Thus, the velocity
(g)
Answer to Problem 46P
Explanation of Solution
The tangent of the angle is,
Thus, the angle is,
The angle must be in third quadrant. So, angle
Conclusion:
Thus, the angle
(h)
Answer to Problem 46P
Explanation of Solution
The momentum of the third fragment must be equal in magnitude and must be in the opposite direction to the resultant of the other two fragments momenta. So, all three pieces have to move in the same plane.
Conclusion:
Thus, all three pieces have to move in the same plane.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
College Physics 11E Global Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
MARINE BIOLOGY
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
- 20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on thesearrow_forward
- pls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward19. Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, has a peak of 8849 m above sea level. Assume that sea level defines the height of Earth's surface. (re = 6.38 × 106 m, ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, G = 6.67 × 10 -11 Nm²/kg²) a. Calculate the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point at the peak of Mount Everest. b. What is the ratio of the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point 644416m below the surface of the Earth to a point at the top of Mount Everest? C. A tourist watching the sunrise on top of Mount Everest observes a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude 3580 km above his position. Determine the speed of the satellite.arrow_forward
- pls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





