
Concept explainers
(a)
Give estimation on weight and area of a typical car.
(a)
Answer to Problem 40PQ
A typical car can have weight around
Explanation of Solution
The average of weight of car can be taken as two thousand pounds. Express two thousand pounds in kilogram.
Normally a car can have
Conclusion:
Therefore, a typical car can have weight around
(b)
Draw the graph of
(b)
Answer to Problem 40PQ
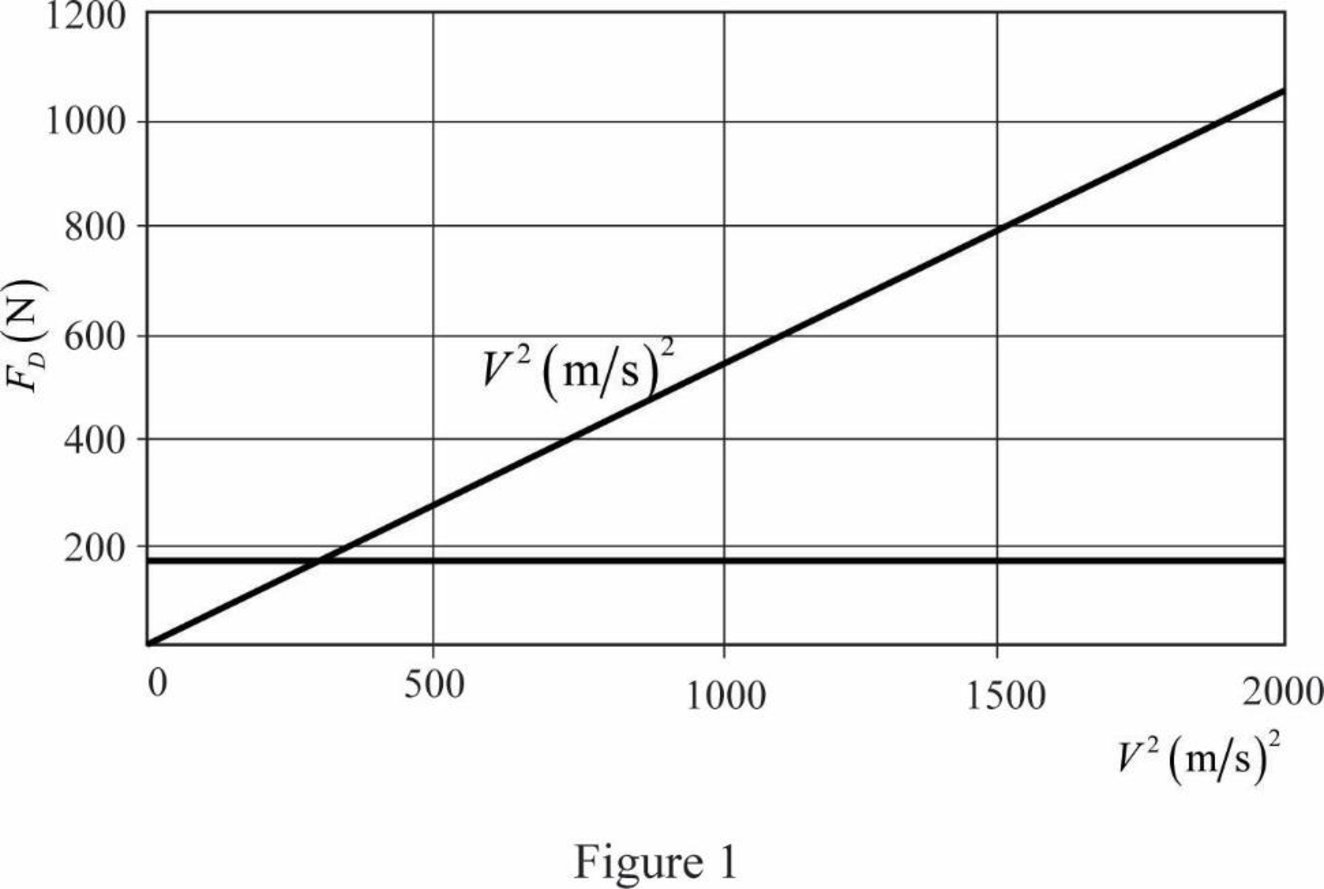
Graph of
Explanation of Solution
The graph of
Write the equation for drag force.
Here,
Substitute
The equation tells that the drag force is varying with the square of speed of car. It can be seen that the graph is also conveying the same result. Graph shows that
Conclusion:
Therefore, the graph of
(c)
The value of Rolling
(c)
Answer to Problem 40PQ
Rolling frictional force is
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation to find the rolling friction.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
It can be seen that
Therefore, the rolling frictional force is
(d)
The speed at which drag force equals rolling frictional force and the range of speed which the drag force can be neglected.
(d)
Answer to Problem 40PQ
The speed at which drag force equals rolling frictional force is
Explanation of Solution
Equate the right hand sides of equations (1) and (II).
Rewrite the above expression in terms of
It can be seen that lower speeds, drag force will be lesser than rolling frictional force. So drag force can be neglected at lower speed. It is better to limit the speed within
Conclusion:
Therefore, the speed at which drag force equals rolling frictional force is
(e)
The change in answer on the assumption that
(e)
Answer to Problem 40PQ
Explanation of Solution
Therefore, the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- Three charged particles are located at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure below (let q = 1.00 μC, and L = 0.850 m). Calculate the total electric force on the 7.00-μC charge. magnitude direction N ° (counterclockwise from the +x axis) y 7.00 με 9 L 60.0° x -4.00 μC ①arrow_forward(a) Calculate the number of electrons in a small, electrically neutral silver pin that has a mass of 9.0 g. Silver has 47 electrons per atom, and its molar mass is 107.87 g/mol. (b) Imagine adding electrons to the pin until the negative charge has the very large value 1.00 mC. How many electrons are added for every 109 electrons already present?arrow_forward(a) A physics lab instructor is working on a new demonstration. She attaches two identical copper spheres with mass m = 0.180 g to cords of length L as shown in the figure. A Both spheres have the same charge of 6.80 nC, and are in static equilibrium when 0 = 4.95°. What is L (in m)? Assume the cords are massless. 0.180 Draw a free-body diagram, apply Newton's second law for a particle in equilibrium to one of the spheres. Find an equation for the distance between the two spheres in terms of L and 0, and use this expression in your Coulomb force equation. m (b) What If? The charge on both spheres is increased until each cord makes an angle of 0 = 9.90° with the vertical. If both spheres have the same electric charge, what is the charge (in nC) on each sphere in this case? 9.60 Use the same reasoning as in part (a), only now, use the length found in part (a) and the new angle to solve for the charge. ncarrow_forward
- A proton moves at 5.20 x 105 m/s in the horizontal direction. It enters a uniform vertical electric field with a magnitude of 8.40 × 103 N/C. Ignore any gravitational effects. (a) Find the time interval required for the proton to travel 6.00 cm horizontally. 83.33 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. ns (b) Find its vertical displacement during the time interval in which it travels 6.00 cm horizontally. (Indicate direction with the sign of your answer.) 2.77 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. mm (c) Find the horizontal and vertical components of its velocity after it has traveled 6.00 cm horizontally. = 5.4e5 Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. I + 6.68e4 Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step…arrow_forward(a) A physics lab instructor is working on a new demonstration. She attaches two identical copper spheres with mass m = 0.180 g to cords of length L as shown in the figure. A Both spheres have the same charge of 6.80 nC, and are in static equilibrium when = 4.95°. What is L (in m)? Assume the cords are massless. 0.150 Draw a free-body diagram, apply Newton's second law for a particle in equilibrium to one of the spheres. Find an equation for the distance between the two spheres in terms of L and 0, and use this expression in your Coulomb force equation. m (b) What If? The charge on both spheres is increased until each cord makes an angle of 0 = 9.90° with the vertical. If both spheres have the same electric charge, what is the charge (in nC) on each sphere in this case? 13.6 ☑ Use the same reasoning as in part (a), only now, use the length found in part (a) and the new angle to solve for the charge. nCarrow_forwardA proton moves at 5.20 x 105 m/s in the horizontal direction. It enters a uniform vertical electric field with a magnitude of 8.40 × 10³ N/C. Ignore any gravitational effects. (a) Find the time interval required for the proton to travel 6.00 cm horizontally. 1.15e-7 ☑ Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. ns (b) Find its vertical displacement during the time interval in which it travels 6.00 cm horizontally. (Indicate direction with the sign of your answer.) 5.33e-3 ☑ Your response is off by a multiple of ten. mm (c) Find the horizontal and vertical components of its velocity after it has traveled 6.00 cm horizontally. | ↑ + jkm/sarrow_forward
- A proton moves at 5.20 105 m/s in the horizontal direction. It enters a uniform vertical electric field with a magnitude of 8.40 103 N/C. Ignore any gravitational effects. (a) Find the time interval required for the proton to travel 6.00 cm horizontally. (b) Find its vertical displacement during the time interval in which it travels 6.00 cm horizontally. (Indicate direction with the sign of your answer.)arrow_forwardThe figure below shows the electric field lines for two charged particles separated by a small distance. 92 91 (a) Determine the ratio 91/92. 1/3 × This is the correct magnitude for the ratio. (b) What are the signs of q₁ and 92? 91 positive 92 negative ×arrow_forwardPlease help me solve this one more detail, thanksarrow_forward
- A dielectric-filled parallel-plate capacitor has plate area A = 20.0 ccm2 , plate separaton d = 10.0 mm and dielectric constant k = 4.00. The capacitor is connected to a battery that creates a constant voltage V = 12.5 V . Throughout the problem, use ϵ0 = 8.85×10−12 C2/N⋅m2 . Find the energy U1 of the dielectric-filled capacitor. The dielectric plate is now slowly pulled out of the capacitor, which remains connected to the battery. Find the energy U2 of the capacitor at the moment when the capacitor is half-filled with the dielectric. The capacitor is now disconnected from the battery, and the dielectric plate is slowly removed the rest of the way out of the capacitor. Find the new energy of the capacitor, U3. In the process of removing the remaining portion of the dielectric from the disconnected capacitor, how much work W is done by the external agent acting on the dielectric?arrow_forwardIn (Figure 1) C1 = 6.00 μF, C2 = 6.00 μF, C3 = 12.0 μF, and C4 = 3.00 μF. The capacitor network is connected to an applied potential difference Vab. After the charges on the capacitors have reached their final values, the voltage across C3 is 40.0 V. What is the voltage across C4? What is the voltage Vab applied to the network? Please explain everything in steps.arrow_forwardI need help with these questions again. A step by step working out with diagrams that explains more clearlyarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





