
Concept explainers
Recording Cash Sales, Credit Sales, Sales Returns, and Sales Allowances and Analyzing Gross Profit Percentage
Campus Stop, Inc., is a student co-op. Campus Stop uses a perpetual inventory system. The following transactions (summarized) have been selected for analysis:
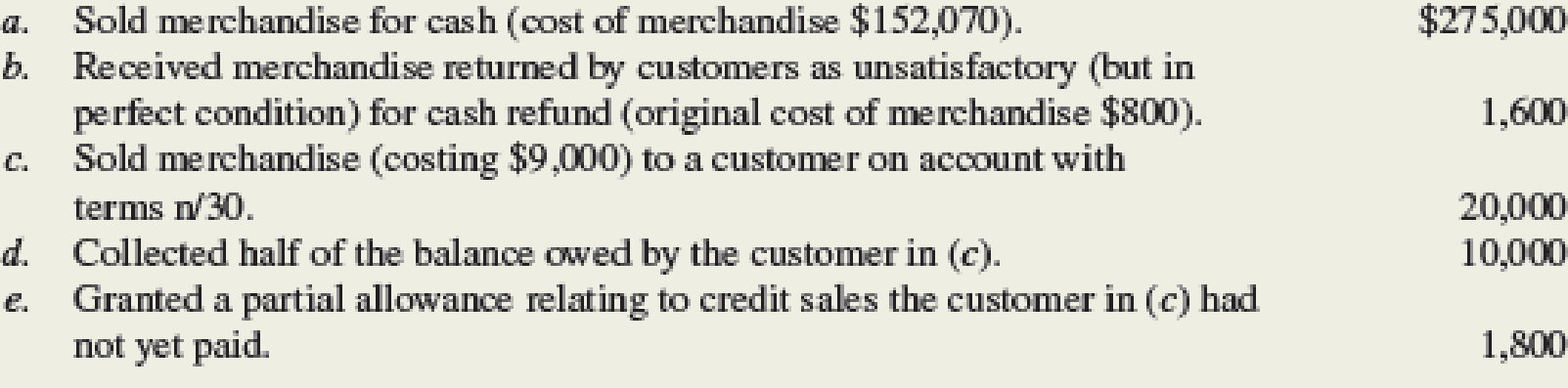
Required:
- 1. Compute Net Sales and Gross Profit for Campus Stop. No additional sales returns/allowances are expected.
- 2. Compute the gross profit percentage (using the formula shown in this chapter and rounding to one decimal place).
- 3. Prepare
journal entries to record transactions (a)–(e). - 4. Campus Stop is considering a contract to sell merchandise to a campus organization for $15,000. This merchandise will cost Campus Stop $12,000. Would this contract increase (or decrease) Campus Stop’s dollars of gross profit and its gross profit percentage (round to one decimal place)?
TIP: The impact on gross profit dollars may differ from the impact on gross profit percentage.
1.
Calculate the net sales and gross profit of Company C.
Explanation of Solution
Net sales:
Net sales is the balance of remaining amount that is arrived after subtracting sales discounts, allowances for damaged goods and return of goods from sales.
Gross Profit:
Gross Profit is the difference between the net sales, and the cost of goods sold. Gross profit usually appears on the income statement of the company.
Calculate the net sales and gross profit of Company C as follows:
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| Sales Revenue (1) | 295,000 |
| Less: Sales Returns and Allowances(2) | (3,400) |
| Net Sales | 291,400 |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold (3) | 160,270 |
| Gross Profit | 131,130 |
Table (1)
Working note 1:
Calculate the value of sales revenue:
Working note 2:
Calculate the sales returns and allowances
Working note 3:
Calculate the cost of goods sold
Therefore, the net sales and gross profit of Company C are $291,600 and $131,330 respectively.
2.
Compute the gross profit percentage of Company C.
Explanation of Solution
Gross Profit Percentage:
Gross profit is the financial ratio that shows the relationship between the gross profit and net sales. It represents gross profit as a percentage of net sales. Gross Profit is the difference between the net sales revenue, and the cost of goods sold. It can be calculated by dividing gross profit and net sales.
Compute the gross profit percentage of Company C as follows:
Thus, the gross profit percentage of Company C is 45.0%
3.
Prepare the journal entries to record transaction from (a) to (e).
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entries to record transaction from (a) to (e) as follows:
a. Record the sales revenue and cost of goods sold:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Cash | 275,000 | ||
| Sales Revenue | 275,000 | ||
| (To record the sales revenue recognized in cash ) |
Table (1)
- Cash is an asset and it increases the value of assets. Therefore, debit cash by $275,000
- Sales revenue is component of stockholders’ equity and it increases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, credit sales revenue by $275,000
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Cost of goods sold | 152,070 | ||
| Inventory | 152,070 | ||
| (To record the cost of goods sold incurred during the year) |
Table (2)
- Cost of goods sold is a component of stockholders’ equity and it is decreases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, debit cost of goods sold by $152,070.
- Inventory is an asset and it decreases the value of asset. Therefore, credit inventory account by $152,070.
b. Record the sales return and the cost of inventory used for production.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Sales revenue | 1,600 | ||
| Cash | 1,600 | ||
| (To record the sales returns from customer) |
Table (3)
- Sales revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity and it increases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, debit sales revenue by $1,600
- Cash is an asset and it decreases the value of assets. Therefore, credit cash by $1,600
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Inventory | 800 | ||
| Cost of goods sold | 800 | ||
| (To record the cost of inventory used for production) |
Table (4)
- Inventory is an asset and it increases the value of assets. Therefore, debit inventory by $800.
- Cost of goods sold is a component of stockholders’ equity and it decreases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, credit cost of goods sold by $800.
c. Record the sale of merchandise on account and put back of inventory from production:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Accounts Receivable | 20,000 | ||
| Sales Revenue | 20,000 | ||
| (To record the sales made on account) |
Table (5)
- Accounts receivable is an asset and it increases the value of assets. Therefore, debit accounts receivable by $20,000.
- Sales revenue is component of stockholders’ equity and it increases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, credit sales revenue by $20,000.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Cost of goods sold | 9,000 | ||
| Inventory | 9,000 | ||
| (To record the cost of inventory return) |
Table (6)
- Cost of goods sold is a component of stockholders’ equity and it decreases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, debit cost of goods sold by $9,000.
- Inventory is an asset and it decreases the value of asset. Therefore, credit inventory by $9,000.
d. Record the cash received from credit customer.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Cash | 10,000 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 10,000 | ||
| (To record the cash received from the credit customer) |
Table (7)
- Cash is an asset and it increases the value of assets. Therefore, debit cash by $10,000.
- Accounts receivable is an asset and it decreases the value of assets. Therefore, credit accounts receivable by $10,000.
e. Record the sales return and allowances:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Sales revenue | 1,800 | ||
| Accounts receivable | 1,800 | ||
| (To record the sales returns and allowances ) |
Table (8)
- Sales revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity and it decreases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, debit sales returns and allowances by $1,800
- Accounts receivable is an asset and it decreases the value of assets. Therefore, credit accounts receivable by $1,800
4.
Describe whether the given contract would increase the gross profit and gross profit percentage of Company C.
Explanation of Solution
Describe whether the given contract would increase the gross profit and gross profit percentage of Company C as follows:
In this case, the gross profit percentage is decreased from 45% to 43.8% (refer working note 5), because of the sale of contract.
Working note 4:
Calculate the gross profit for sale of contract:
Working note 5:
Calculate the gross profit percentage of Company after the sale of contract.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
- provide correct answerarrow_forwardsubject-general accountingarrow_forwardayco Inc. started its operations in 2022. Its sales during 2022, all on account, totalled $700,000. The company collected $500,000 in cash from customers during the year and wrote off $8,000 in uncollectible accounts. The company set up an allowance for doubtful accounts at December 31, 2022, its fiscal year-end, and determined the account balance to be $14,000. The unadjusted balances of selected accounts at December 31, 2023 are as follows: Accounts receivable $ 300,000 Allowance for doubtful accounts (debit) 10,000 Sales revenue (including 80 percent in sales on account) 800,000 Aging of the accounts receivable on December 31, 2023, resulted in an estimate of $11,000 in potentially uncollectible accounts. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entries to record all the transactions during 2022 and post them to appropriate T-accounts. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.)…arrow_forward
- Calculate the sample size based on the specifications in Buhi's contract. Make sure it is within budget, reasonable to obtain, and that you use appropriate inputs relative to market research best practices. Use the calculator to adjust the sample size statement. Use the agreed-upon sample size in Buhi's contract: 996. In your secondary research, find the target population size (an estimate of those in the United States looking to purchase luggage in the category in the next two years). You will use this target population size for each sample size estimate. Adjust the provided sample size calculator inputs to find the rest of the figures that get you to the agreed-upon sample size. The caveats from Buhi are that you must: Use the market research standard for your confidence level. Use a confidence interval that is better than the market research standard for your confidence interval.arrow_forwardThe partnership of Keenan and Kludlow paid the following wages during this year: Line Item Description Amount M. Keenan (partner) $108,000 S. Kludlow (partner) 96,000 N. Perry (supervisor) 54,700 T. Lee (factory worker) 35,100 R. Rolf (factory worker) 27,200 D. Broch (factory worker) 6,300 S. Ruiz (bookkeeper) 26,000 C. Rudolph (maintenance) 5,200 In addition, the partnership owed $250 to Rudolph for work he performed during December. However, payment for this work will not be made until January of the following year. The state unemployment tax rate for the company is 2.95% on the first $9,000 of each employee's earnings. Compute the following: ound your answers to the nearest cent. a. Net FUTA tax for the partnership for this year b. SUTA tax for this yeararrow_forwardGiven answer financial accounting questionarrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax CollegePrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning


