
Physics (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780321976444
Author: James S. Walker
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 38PCE
Find the acceleration of the masses shown in Figure 6-53, given that m1 = 1.0kg, m2 = 2.0kg, and m3 = 3.0 kg. Assume the table is frictionless and the masses move freely.
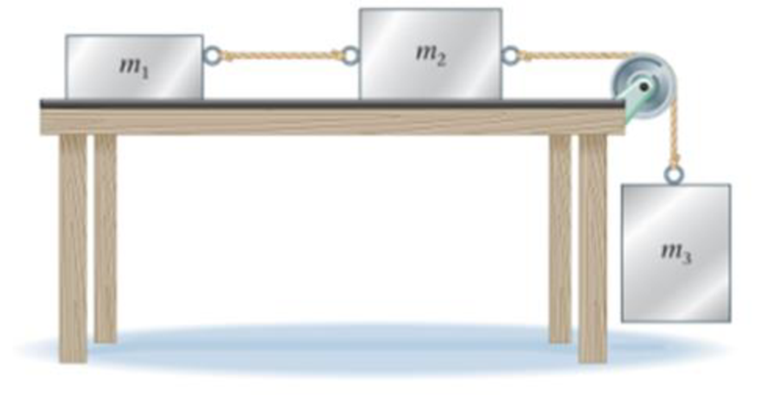
Figure 6-53
Problem 38
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A parachutist whose mass is 75 kg drops from a helicopter hovering 1000 m above the ground and falls toward the ground under the influence of gravity. Assume that the force due to air resistance is
proportional to the velocity of the parachutist, with the proportionality constant b, 30 N-secim when the chute is closed and by 100 N-secim when the chule is open if the chute does not open
until the velocity of the parachutist reaches 20 m/sec, after how many seconds will the parachutist reach the ground? Assume that the acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/sec
The parachutist will reach the ground after
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
seconds.
CHE
The 20-1b cabinet is subjected to the force F= (3-2t) Ib, where t is in seconds. If the cabinet is initially moving down the plane with a speed of 6 ft's,
determine how long for the force to bring the cabinet to rest. F is parallel to the plane.
A parachutist whose mass is 80 kg drops from a helicopter hovering 1000 m above the ground and falls toward the ground under the influence of gravity. Assume that the force due to air
resistance is proportional to the velocity of the parachutist, with the proportionality constant b, = 30 N-sec/m when the chute is closed and b, = 90 N-sec/m when the chute is open. If the chute
does not open until the velocity of the parachutist reaches 20 m/sec, after how many seconds will the parachutist reach the ground? Assume that the acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/ sec.
Chapter 6 Solutions
Physics (5th Edition)
Ch. 6.1 - A block rests on a rough, horizontal surface, as...Ch. 6.2 - When a mass is attached to a certain spring, the...Ch. 6.3 - Suppose the tension in the clothesline in Quick...Ch. 6.4 - Three boxes are connected by ropes and pulled...Ch. 6.5 - A system consists of an object with mass m and...Ch. 6 - A clothesline always sags a little, even if...Ch. 6 - In the Jurassic Park sequel, The Lost World, a man...Ch. 6 - When a traffic accident is investigated, it is...Ch. 6 - In a car with rear-wheel drive, the maximum...Ch. 6 - A train typically requires a much greater distance...
Ch. 6 - Give some everyday examples of situations in which...Ch. 6 - At the local farm, you buy a flat of strawberries...Ch. 6 - It is possible to spin a bucket of water in a...Ch. 6 - Water sprays off a rapidly turning bicycle wheel....Ch. 6 - Can an object be in translational equilibrium if...Ch. 6 - Prob. 11CQCh. 6 - The gravitational attraction of the Earth is only...Ch. 6 - A popular carnival ride has passengers stand with...Ch. 6 - Referring to Question 13, after the cylinder...Ch. 6 - Your car is stuck on an icy side street. Some...Ch. 6 - The parking brake on a car causes the rear wheels...Ch. 6 - BIO The foot of your average gecko is covered with...Ch. 6 - Discuss the physics involved in the spin cycle of...Ch. 6 - The gas pedal and the brake pedal are capable of...Ch. 6 - In the movie 2001: A Space Odyssey, a rotating...Ch. 6 - When rounding a corner on a bicycle or a...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain You push two identical bricks...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain Two drivers traveling side-by-side...Ch. 6 - A 1.8-kg block slides on a horizontal surface with...Ch. 6 - A child goes down a playground slide with an...Ch. 6 - What is the minimum horizontal force F needed to...Ch. 6 - What is the minimum horizontal force F needed to...Ch. 6 - The three identical boxes shown in Figure 6-33...Ch. 6 - To move a large crate across a rough floor, you...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 37-kg crate is placed on an...Ch. 6 - Coffee To Go A person places a cup of coffee on...Ch. 6 - A mug rests on an inclined surface, as shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Force Times Distance At the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 13PCECh. 6 - A certain spring has a force constant k. (a) If...Ch. 6 - A certain spring has a force constant k. (a) If...Ch. 6 - Pulling up on a rope you lift a 7.27-kg bucket of...Ch. 6 - When a 9.09-kg mass is placed on top of a vertical...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A backpack full of books...Ch. 6 - Two springs, with force constants k1= 150N/m and...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Illinois Jones is being pulled...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A spring with a force constant...Ch. 6 - A spring is suspended vertically from the ceiling...Ch. 6 - Mechanical Advantage The pulley system shown in...Ch. 6 - Pulling the string on a bow back with a force of...Ch. 6 - In Figure 6-42 we see two blocks connected by a...Ch. 6 - BIO Traction After a skiing accident, your leg is...Ch. 6 - Two blocks are connected by a string, as shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate The system shown in Figure 6-45...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain (a) Referring to the hanging...Ch. 6 - BIO Spiderweb Forces An orb-weaver spider sits in...Ch. 6 - A 0.15-kg ball is placed in a shallow wedge with...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A picture hangs on the wall...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate You want to nail a 1.6-kg board...Ch. 6 - Prob. 34PCECh. 6 - In Example 6-13 (Connected Blocks), suppose m1 and...Ch. 6 - Predict/Explain Suppose m1 and m2 in Example 6-14...Ch. 6 - Three boxes of masses m, 2m, and 3m are connected...Ch. 6 - Find the acceleration of the masses shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate (a) If the hanging mass m3 in...Ch. 6 - Two blocks are connected by a string, as shown in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 3 50-kg block on a smooth...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 7.7-N force pulls horizontally...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate (a) Find the magnitude of the...Ch. 6 - A car drives with constant speed on an elliptical...Ch. 6 - A puck attached to a string undergoes circular...Ch. 6 - BIO Bubble Net Fishing Humpback whales sometimes...Ch. 6 - When you take your 1900-kg car out for a spin, you...Ch. 6 - BIO A Human Centrifuge To test the effects of high...Ch. 6 - A car goes around a curve on a road that is banked...Ch. 6 - Clearview Screen Large ships often have circular...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate (a) As you ride on a Ferris...Ch. 6 - Driving in your car with a constant speed of v =...Ch. 6 - CE If you weigh yourself on a bathroom scale at...Ch. 6 - CE BIO Maneuvering a Jet Humans lose consciousness...Ch. 6 - CE BIO Gravitropism As plants grow, they tend to...Ch. 6 - BIO Human-Powered Centrifuge One of the hazards of...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 9 3-kg box slides across the...Ch. 6 - A child goes down a playground slide that is...Ch. 6 - Spin-Dry Dragonflies Some dragonflies splash down...Ch. 6 - The da Vinci Code Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519) is...Ch. 6 - A 4 5-kg sled is pulled with constant speed across...Ch. 6 - A 0 045-kg golf ball hangs by a string from the...Ch. 6 - A physics textbook weighing 22 N rests on a desk....Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate The blocks shown in Figure 6-64...Ch. 6 - A Conical Pendulum A 0 075-kg toy airplane is tied...Ch. 6 - A tugboat tows a barge at constant speed with a...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Two blocks, stacked one on top...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate In a daring rescue by helicopter...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A light spring with a fore...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate The blocks in Figure 6-69 have...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Playing a Violin The tension in...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A 9 8-kg monkey hangs from a...Ch. 6 - As your plane circles an airport, it moves in a...Ch. 6 - At a playground, a 22-kg child sits on a spinning...Ch. 6 - A 2.0-kg box rests on a plank that is inclined at...Ch. 6 - A wood block of mass m rests on a larger wood...Ch. 6 - A hockey puck of mass m is attached to a string...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate A popular ride at amusement...Ch. 6 - A Conveyor Belt A box is placed on a conveyor belt...Ch. 6 - As part of a circus act, a person drives a...Ch. 6 - On the straight-line segment II in Figure 6-76 (b)...Ch. 6 - 82. Rank the straight segments I, II, and III in...Ch. 6 - In use on a typical human nose, the end-to-end...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 6-3 Suppose...Ch. 6 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 6-3 The...Ch. 6 - Referring to Example 6-13 Suppose that the mass on...Ch. 6 - Referring to Example 6-15 (a) At what speed will...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
Equation 33.5a transforms the velocity u of an object moving in the x-directionthe same direction as the relati...
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Use your knowledge of the velocities and changes in velocities to construct momentum vectors and change in mome...
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Do you think these differences in distance between locations at the same latitude in the Northern and Southern ...
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Q23.21 When a thunderstorm is approaching, sailors at sea sometimes observe a phenomenon called “St. Elmo’s fir...
University Physics (14th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Gggarrow_forwardA boy who normally weighs 300 N on a bathroom scale crouches on the scale and suddenly jumps upward. His companion notices that the scale reading momentarily jumps up to 400 N as the boy springs upward. Estimate the boy’s maximum acceleration in this process.arrow_forwardTwo boxes are connected by a rope that passes over a pulley (Figure 6-31). Box #1 is on a ramp inclined at 35° to the horizontal, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and ramp is 0.54. The masses of the boxes are m1 5 2.5 kg and m2 5 5.5 kg. Neglecting the motion of the pulley and assuming that the velocity of each box is in the same direction as its acceleration, what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the boxes?arrow_forward
- The tolerance is 2% While two forces act on it, a particle is to move at the constant velocity= (3.86 m/s) î- (-3.30 m/s) 7. One of the forces is F₁ = (1.52 N) î+ (-5.14 N) 7. What is the other force? Number î+ ĴUnitsarrow_forwardA parachutist whose mass is 85 kg drops from a helicopter hovering 2000 m above the ground and falls toward the ground under the influence of gravity. Assume that the force due to air resistance is proportional to the velocity of the parachutist, with the proportionality constant b 1 = 20 N - sec/m when the chute is closed and b 2 = 90 N - sec/m when the chute is open. If the chute does not open until the velocity of the parachutist reaches 35 m/sec, after how many seconds will the parachutist reach the ground? Assume that the acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/ sec ^2arrow_forwardA city planner is working on the redesign of a hilly portion of a city. An important consideration is how steep the roads can be so that even low-powered cars can get up the hills without slowing down. A particular small car, with a mass of 920 kg, can accelerate on a level road from rest to 21m/s(75Km/h) in 12.5 s. Using these data, calculate the maximum steepness of a hill.arrow_forward
- An 8 kg block rests on a horizontal surface whose coefficients of friction are: s = 0.4 and k = 0.2. The maximum force that can be applied to the block so that it does not move is?arrow_forwardTwo masses of 8kg and 2kg are suspended from a light inextensible cord passing over a pulley. The pulley exerts a constant friction on the cord that is equivalent to the force of 3N at the circumference. When the masses are released, the 8kg mass drops while the 2kg mass is pulled up by the cord towards the pulley. Determine the acceleration of the massesarrow_forward1) In Figure, a block with mass m = 1 kg is released from height h, friction until it reaches the path with first length d,= 3 m, where the friction force between B and C is f, = 9 N, and until it reaches the path, where the friction force between E and F is f, = 7 N. The height is h, = 1 m, and second horizontal length is d,= 1 m. The block continues its motion after the point F. (a) Find the velocity at the point A. (b) Find the velocity at the point D. (c) Find the height h if the velocity of m is v= 9 m/s at the point F.(sin45=0.7 g=9.8 m/s²) 11 m. Its path is without 1 m (F d,=1 m h h, = 11 m D 45° E d,=3 m h,=1 m A Вarrow_forward
- Two masses are connected by a string which goes over an ideal pulley as shown in Figure 6-6. Block A has a mass of 3.0 kg and can slide along a smooth plane inclined 30°to the horizontal. What is the mass of block B if the system is in equilibrium? 3.5 kg 3.0 kg 2.6 kg 1.5 kgarrow_forwardPlease Asaparrow_forward1. Given that sinθ = 2/3 and cosθ = √5/3, find the cotθ, and tanθ. 2. To move a large crate across a rough floor, you push on it with a force F at an angle of 21° below the horizontal, as shown in Figure 6–18. Find the force necessary to start the crate moving, given that the mass of the crate is 32 kg and the coefficient of static friction between the crate and the floor is 0.57. Find the acceleration of the crate if the applied force is 330 N and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.45.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's Second Law of Motion: F = ma; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzA6IBWUEDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY