
For the weighted graph shown in
a. The nearest-neighbor tour with starting vertex B
b. The nearest-neighbor tour with starting vertex C
c. The nearest-neighbor tour with starting vertex D
d. The nearest-neighbor tour with starting vertex E
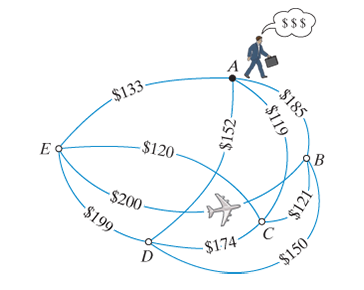
Figure 6-41
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
EXCURSIONS IN MOD.MATH W/ACCESS >BI<
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics Using The Ti-83/84 Plus Calculator, Books A La Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Beginning and Intermediate Algebra
Precalculus: A Unit Circle Approach (3rd Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences and Social Sciences
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- T={(−7,1),(1,−1),(6,−8),(2,8)}. Find the inverse. Express your answer as a set of ordered pairs.arrow_forwardStarting with the finished version of Example 6.2, attached, change the decision criterion to "maximize expected utility," using an exponential utility function with risk tolerance $5,000,000. Display certainty equivalents on the tree. a. Keep doubling the risk tolerance until the company's best strategy is the same as with the EMV criterion—continue with development and then market if successful. The risk tolerance must reach $ 160,000,000 before the risk averse company acts the same as the EMV-maximizing company. b. With a risk tolerance of $320,000,000, the company views the optimal strategy as equivalent to receiving a sure $____________ , even though the EMV from the original strategy (with no risk tolerance) is $ 59,200.arrow_forwardComplete solutions need handwriting. For all only sure experts solve it correct complete solutionsarrow_forward
- The graph below shows the U.S. federal expenses for 2012. A) estimate the fraction of the total expenses that were spent on Medicare. Write your answer as the closest fraction whose denominator is 100. B) estimate the fraction of the total expenses that were spent on Medicare and Medicaid. Write your answer as the closest fraction, whose denominator is 100.arrow_forwardStarting with the finished version of Example 6.2, attached, change the decision criterion to "maximize expected utility," using an exponential utility function with risk tolerance $5,000,000. Display certainty equivalents on the tree. a. Keep doubling the risk tolerance until the company's best strategy is the same as with the EMV criterion—continue with development and then market if successful. The risk tolerance must reach $ ____________ before the risk averse company acts the same as the EMV-maximizing company. b. With a risk tolerance of $320,000,000, the company views the optimal strategy as equivalent to receiving a sure $____________ , even though the EMV from the original strategy (with no risk tolerance) is $ ___________ .arrow_forward2.8.1arrow_forward
- Do not use the Residue Theorem. Thank you.arrow_forwardA television network earns an average of $14 million each season from a hit program and loses an average of $8 million each season on a program that turns out to be a flop. Of all programs picked up by this network in recent years, 25% turn out to be hits and 75% turn out to be flops. At a cost of C dollars, a market research firm will analyze a pilot episode of a prospective program and issue a report predicting whether the given program will end up being a hit. If the program is actually going to be a hit, there is a 75% chance that the market researchers will predict the program to be a hit. If the program is actually going to be a flop, there is only a 30% chance that the market researchers will predict the program to be a hit. What is the maximum value of C that the network should be willing to pay the market research firm? Enter your answer in dollars, not in million dollars. $ __________ Calculate EVPI for this decision problem. Enter your answer in dollars, not in million…arrow_forwardEvaluate the line integral sin z dz, So sin where C is the portion of the curve y = x² from 0 to −1 + i.arrow_forward
- Let f(z) be complex differentiable everywhere in C. Fix two distinct complex numbers a and b and a circle C of radius R with |a| < R,|b| < R traversed in the counter-clockwise direction. Evaluate the integral Sc − f(z)dz (z - a)(z – b) in terms of a, b and the values of f at those points.arrow_forward| Let C be a circle (with a positive radius) such that z = 1 lies in its interior. Evaluate the contour integral So Tz zez (z - 1)³ = where C is traversed in the clockwise direction. dzarrow_forwardquestion 8arrow_forward
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Algebra for College StudentsAlgebraISBN:9781285195780Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra for College StudentsAlgebraISBN:9781285195780Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning





