
Concept explainers
Heat lamps are commonly used to maintain foods at about 50°C for as long as 12 hours in cafeteria serving lines. The following experiment was conducted to determine whether this practice poses a potential health hazard.
Beef cubes were surface-inoculated with 500,000 bacterial cells and incubated at 43–53°C to establish temperature limits for bacterial growth. The following results were obtained from heterotrophic plate counts performed on beef cubes at 6 and 12 hours after inoculation:
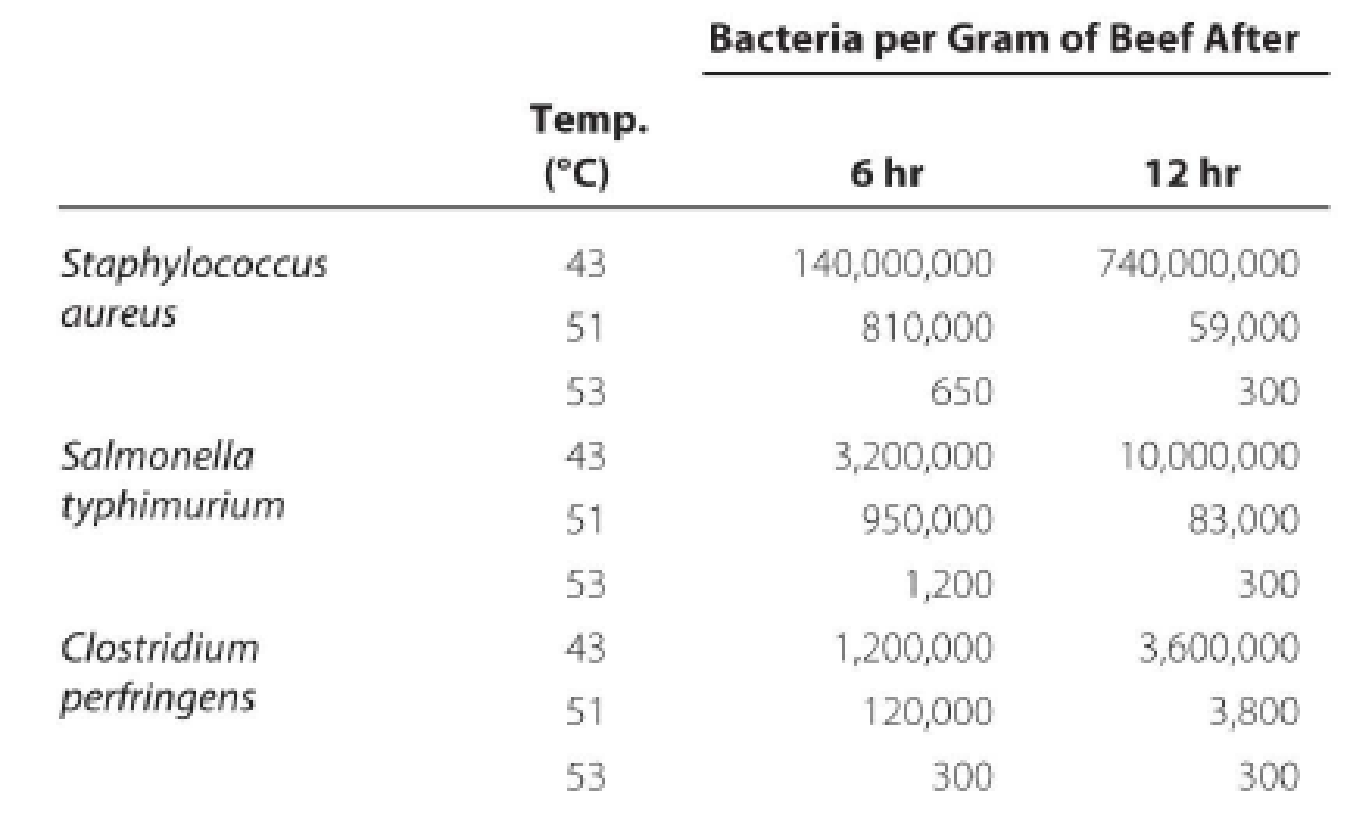
Draw the growth curves for each organism. What holding temperature would you recommend? Assuming that cooking kills bacteria in foods, how could these bacteria contaminate the cooked foods? What disease does each organism cause? (Hint: See Chapter 25.)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
MICROBIOLOGY-ACCESS >CUSTOM<
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
- 1. Match each vocabulary term to its best descriptor A. affinity B. efficacy C. inert D. mimic E. how drugs move through body F. how drugs bind Kd Bmax Agonist Antagonist Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamicsarrow_forward50 mg dose of a drug is given orally to a patient. The bioavailability of the drug is 0.2. What is the volume of distribution of the drug if the plasma concentration is 1 mg/L? Be sure to provide units.arrow_forwardDetermine Kd and Bmax from the following Scatchard plot. Make sure to include units.arrow_forward
- Choose a catecholamine neurotransmitter and describe/draw the components of the synapse important for its signaling including synthesis, packaging into vesicles, receptors, transporters/degradative enzymes. Describe 2 drugs that can act on this system.arrow_forwardThe following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. a) Which has a higher potency? b) Which is has a higher efficacy? c) What is the approximate Kd of capsaicin in uM? (you can round to the nearest power of 10)arrow_forwardWhat is the rate-limiting-step for serotonin synthesis?arrow_forward
 Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781111306663Author:Margaret Rodriguez, Paul PricePublisher:Cengage Learning
Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781111306663Author:Margaret Rodriguez, Paul PricePublisher:Cengage Learning Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage Learning





