
Concept explainers
MATHEMATICAL The enzyme
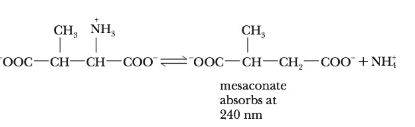
[V. Williams and J. Selbin, J. Biol. Chem. 239, 1636 (1964)]. The
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
In an enzymatic reaction,
To determine
To draw this plot, substrate concentration
The
Answer to Problem 28RE
Plotting the data gives the following straight line:
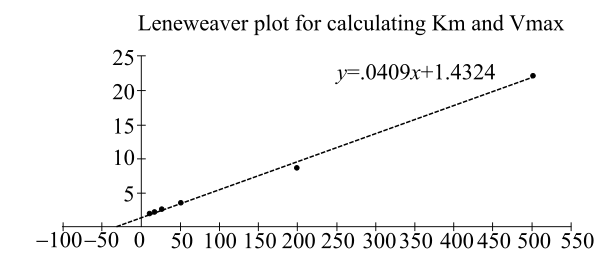
From this straight-line graph, the value of
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Following data containing substrate concentrations and velocity of the reaction at that substrate concentration, is given.
In enzyme kinetics, to determine
But
Modification of the equation is
This equation can be plotted on the graph,
The enzyme, b-methyl aspartate, catalyzes the deamination of b-methyl aspartate. By plotting the given data into a Lineweaver–Burk plot, Km for this reaction is 2.86 × 10-2 mole. Although in this case, concentration cannot be determined directly. Absorbance values were used instead, as a matter of convenience.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
BIOCHEMISTRY (LOOSELEAF) >CUSTOM PKG<
- The following data were recorded for the enzyme catalyzed conversion of S -> P. Question: Estimate the Vmax and Km. What would be the rate at 2.5 and 5.0 x 10-5 M [S] ?arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forwardThe following data were recorded for the enzyme catalyzed conversion of S -> P Question: what would the rate be at 5.0 x 10-5 M [S] and the enzyme concentration was doubled? Also, the rate given in the table is from product accumulation after 10 minuets of reaction time. Verify these rates represent a true initial rate (less than 5% turnover). Please helparrow_forward
- The following data was obtained on isocitrate lyase from an algal species. Identify the reaction catalyzed by this enzyme, deduce the KM and Vmax , and determine the nature of the inhibition by oxaloacetate. Please helparrow_forwardIn the table below, there are sketches of four crystals made of positively-charged cations and negatively-charged anions. Rank these crystals in decreasing order of stability (or equivalently increasing order of energy). That is, select "1" below the most stable (lowest energy) crystal. Select "2" below the next most stable (next lowest energy) crystal, and so forth. A B 鹽 (Choose one) +2 C +2 +2 (Choose one) D 鹽雞 (Choose one) (Choose one)arrow_forward1. Draw the structures for the fats A. 16:2: w-3 and B. 18:3:49,12,15 2. Name each of the molecules below (image attached)arrow_forward
- draw the structures for the fats A. 16:2:w-3 B 18:3:9,12,15arrow_forward1. Below is a template strand of DNA. Show the mRNA and protein that would result. label the ends of the molecules ( refer to attached image)arrow_forwardAttach the followina labels to the diagram below: helicase, single stranded binding proteins, lagging strand, leading strand, DNA polymerase, primase, 5' ends (3), 3' ends (3) (image attached)arrow_forward
- 1. How much energy in terms of ATP can be obtained from tristearin (stearate is 18:0) Show steps pleasearrow_forwardMultiple choice urgent!!arrow_forward1. Write the transamination reaction for alanine. Indicate what happens next to each of the molecules in the reaction, and under what conditions it happens. 2.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
