
Concept explainers
a.
Identify the company which will report the highest amount of net income for 2014.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Net Income
Net income is the sum total of all the revenues generated in a particular accounting period after deducting cost of goods sold and expenses and losses, such as rent expense, depreciation of that particular accounting period.
Identify the company which will report the highest amount of net income for 2014:
| Net Income for 2014 | |||
| Company A (in $) | Company B (in $) | Company C (in $) | |
| Revenue | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 |
| Less: Depreciation expense | 12,000 | 25,600 | 14,500 |
| Net Income | $18,000 | $4,400 | $15,500 |
Table (1)
Working Note 1: Prepare depreciation schedule under straight-line method for Company A.
| Date | Depreciation Rate | Depreciation expense (in $) | |
| (A) | (B) | ||
| 2014 | 60,000 | 1/5 | 12,000 |
| 2015 | 60,000 | 1/5 | 12,000 |
| 2016 | 60,000 | 1/5 | 12,000 |
| 2017 | 60,000 | 1/5 | 12,000 |
| 2018 | 60,000 | 1/5 | 12,000 |
Table (2)
Calculate the depreciable cost:
Working Note 2: Prepare depreciation schedule under double-declining-balance (DDB) method for Company B.
| Date | Double-Declining-Balance Depreciation Rate | Book Value (Refer note) (in $) | Depreciation expense (in $) |
| (A) | (B) | ||
| 2014 | 0.40 | 64,000 | 25,600 |
| 2015 | 0.40 | 38,400 | 15,360 |
| 2016 | 0.40 | 23,040 | 9,216 |
| 2017 | 0.40 | 13,824 | 5,530 |
| 2018 | 0.40 | 8,294 | 4,294 |
Table (3)
Note: Book value:
The amount of acquisition cost of less
Formula for book value:
Accumulated depreciation:
The total amount of depreciation expense deducted, from the time asset acquired till date, as reported in the account as on a particular date, is referred to as accumulated depreciation.
Formula for accumulated depreciation:
Determine the depreciation rate applied each year:
Useful life = 5 years
Compute depreciation expense on 2018:
Working note 3: Prepare depreciation schedule under units-of-production method for Company C.
| Date | Depreciation per unit | Number of hours | Depreciation expense (in $) |
| (A) | (B) | ||
| 2014 | $0.30 | 50,000 | 15,000 |
| 2015 | $0.30 | 55,000 | 16,500 |
| 2016 | $0.30 | 40,000 | 12,000 |
| 2017 | $0.30 | 44,000 | 13,200 |
| 2018 | $0.30 | 31,000 | 3,300 |
Table (4)
Compute depreciation per unit:
Compute depreciation expense on 2018:
Hence, the company which will report the highest amount of net income for 2014 is Company A.
b.
Identify the company which will report the lowest amount of net income for 2016.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Net Income
Net income is the sum total of all the revenues generated in a particular accounting period after deducting cost of goods sold and expenses and losses, such as rent expense, depreciation of that particular accounting period.
Identify the company which will report the lowest amount of net income for 2016:
| Net Income for 2016 | |||
| Company A (in $) | Company B (in $) | Company C (in $) | |
| Revenue | 30,000 | 30,000 | 30,000 |
| Less: Depreciation expense | 12,000 | 9,216 | 12,000 |
| Net Income | $18,000 | $20,784 | $18,000 |
Table (5)
Working Note 4: Prepare depreciation schedule under straight-line method for Company A.
| Date | Depreciable Cost (in $) | Depreciation Rate | Depreciation expense (in $) |
| (A) | (B) | ||
| 2014 | 60,000 | 1/5 | 12,000 |
| 2015 | 60,000 | 1/5 | 12,000 |
| 2016 | 60,000 | 1/5 | 12,000 |
| 2017 | 60,000 | 1/5 | 12,000 |
| 2018 | 60,000 | 1/5 | 12,000 |
Table (6)
Calculate the depreciable cost:
Working Note 5: Prepare depreciation schedule under double-declining-balance (DDB) method for Company B.
| Date | Double-Declining-Balance Depreciation Rate | Book Value (Refer note) (in $) | Depreciation expense (in $) |
| (A) | (B) | ||
| 2014 | 0.40 | 64,000 | 25,600 |
| 2015 | 0.40 | 38,400 | 15,360 |
| 2016 | 0.40 | 23,040 | 9,216 |
| 2017 | 0.40 | 13,824 | 5,530 |
| 2018 | 0.40 | 8,294 | 4,294 |
Table (7)
Note:
Book value:
The amount of acquisition cost of less accumulated depreciation as on a particular date is referred to as book value.
Formula for book value:
Accumulated depreciation:
The total amount of depreciation expense deducted, from the time asset acquired till date, as reported in the account as on a particular date, is referred to as accumulated depreciation.
Formula for accumulated depreciation:
Determine the depreciation rate applied each year.
Useful life = 5 years
Compute depreciation expense on 2018:
Working Note 6: Prepare depreciation schedule under units-of-production method for Company C.
| Date | Depreciation per unit | Number of hours | Depreciation expense (in $) |
| (A) | (B) | ||
| 2014 | $0.30 | 50,000 | 15,000 |
| 2015 | $0.30 | 55,000 | 16,500 |
| 2016 | $0.30 | 40,000 | 12,000 |
| 2017 | $0.30 | 44,000 | 13,200 |
| 2018 | $0.30 | 31,000 | 3,300 |
Table (8)
Compute depreciation per unit.
Compute depreciation expense on 2018:
Hence, the company which will report the lowest amount of net income for 2016 is Company A and Company C.
c.
Identify the company which will report the highest book value on the December 31, 2016,
c.
Explanation of Solution
Book value:
The amount of acquisition cost of less accumulated depreciation as on a particular date is referred to as book value.
Formula for book value:
Identify the company which will report the highest book value on the December 31, 2016, balance sheet:
| Book value on December 31, 2016 | |||
| Company A (in $) | Company B (in $) | Company C (in $) | |
| Cost | 64,000 | 64,000 | 64,000 |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | 34,800 | 50,176 | 42,050 |
| Book value | $29,200 | $13,824 | $21,950 |
Table (9)
Working Note 7: Prepare depreciation schedule under straight-line method for Company A.
| Date | Depreciable Cost (in $) | Depreciation Rate | Depreciation expense (in $) | Accumulated depreciation (in $) |
| (A) | (B) | |||
| 2014 | 60,000 | 1/5 | 12,000 | 12,000 |
| 2015 | 60,000 | 1/5 | 12,000 | 24,000 |
| 2016 | 60,000 | 1/5 | 12,000 | 36,000 |
Table (10)
Calculate the depreciable cost:
Working Note 8: Prepare depreciation schedule under double-declining-balance (DDB) method for Company B.
| Date | Double-Declining-Balance Depreciation Rate | Book Value (Refer note) (in $) | Depreciation expense (in $) | Accumulated depreciation (in $) |
| (A) | (B) | |||
| 2014 | 0.40 | 64,000 | 25,600 | 25,600 |
| 2015 | 0.40 | 38,400 | 15,360 | 40,960 |
| 2016 | 0.40 | 23,040 | 9,216 | 50,176 |
Table (11)
Note:
Book value:
The amount of acquisition cost of less accumulated depreciation as on a particular date is referred to as book value.
Formula for book value:
Accumulated depreciation:
The total amount of depreciation expense deducted, from the time asset acquired till date, as reported in the account as on a particular date, is referred to as accumulated depreciation.
Formula for accumulated depreciation:
Determine the depreciation rate applied each year.
Useful life = 5 years
Working Note 9: Prepare depreciation schedule under units-of-production method for Company C.
| Date | Depreciation per unit (A) | Number of hours (B) | Depreciation expense (in $) | Accumulated depreciation (in $) |
| 2014 | $0.30 | 50,000 | 15,000 | 15,000 |
| 2015 | $0.30 | 55,000 | 16,500 | 31,500 |
| 2016 | $0.30 | 40,000 | 12,000 | 43,500 |
Table (12)
Compute depreciation per unit:
Hence, the company which will report the highest book value on the December 31, 2016, balance sheet is Company A.
d.
Identify the company which will report the highest amount of
d.
Explanation of Solution
Retained earnings:
The retained earnings statement is that financial statement which shows the amount of net income which is actually retained by the Company on a particular date. These earnings can be utilized by the Company for the reinvestment and to pay its debts.
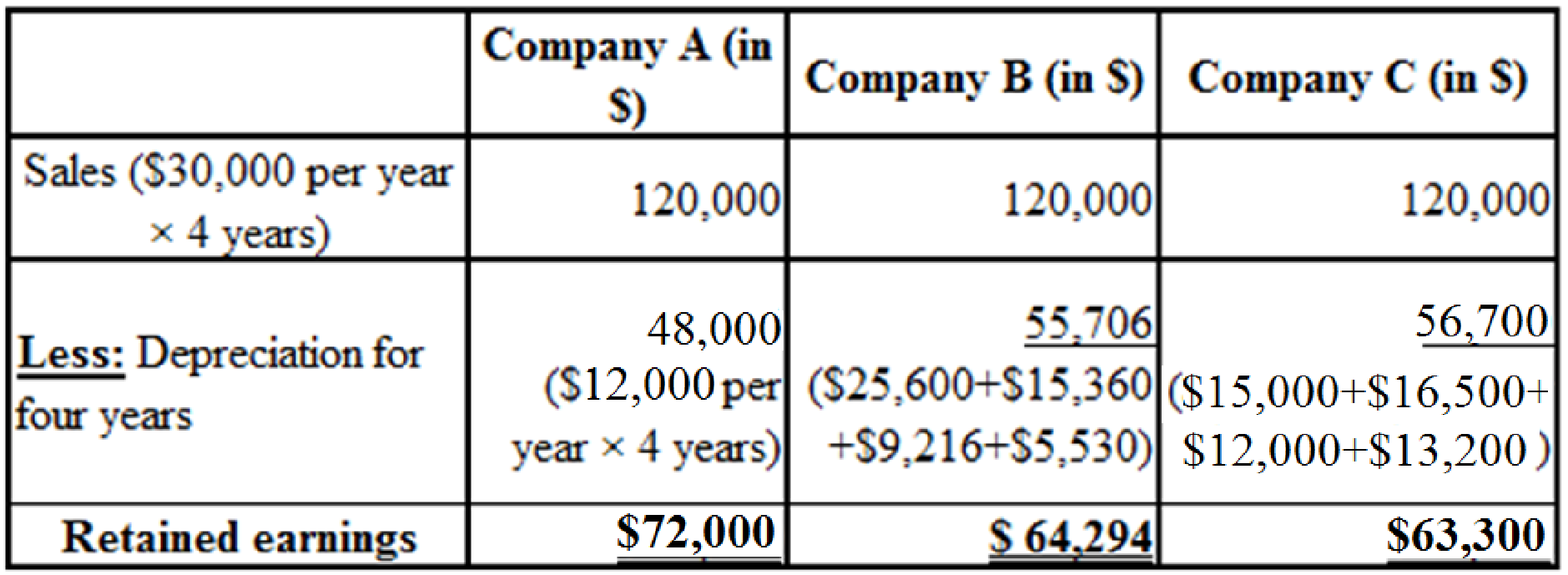
Table (13)
Hence, the company which will report the highest amount of retained earnings on the December 31, 2017, balance sheet is Company A. However, the retained earnings for all the companies will be the same at the end of the asset’s five-year life, as the total depreciation over the five year period is the same for all the three companies.
e.
Identify the company which will report the lowest amount of cash flow from operating activities on the 2016 statement of
e.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of cash flows:
This statement reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash, and result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period.
Cash flows from operating activities:
These refer to the cash received or cash paid in day-to-day operating activities of a company. In this direct method, cash flow from operating activities is computed by using all cash receipts and cash payments during the year.
Depreciation expense is not a
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Survey Of Accounting
- How much intrest bank collect?arrow_forwardRequired information Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]XYZ declared a $1 per share dividend on August 15. The date of record for the dividend was September 1 (the stock began selling ex-dividend on September 2). The dividend was paid on September 10. Ellis is a cash-method taxpayer. Determine if he must include the dividends in gross income under the following independent circumstances. b. Ellis bought 100 shares of XYZ stock on August 1 for $21 per share. Ellis sold his XYZ shares on September 5 for $23 per share. Ellis received the $100 dividend on September 10 (note that even though Ellis didn’t own the stock on September 10, he still received the dividend because he was the shareholder on the record date).arrow_forwardHow much overhead applied over this year?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





