
(a)
Interpretation:
Bond-dissociation energy should be identified for the red line bond in the given structure.
Concept introduction:
Bond-dissociation energy (
Bond-dissociation energy is mainly depends on the hybridization of the carbon atom and substitution on the carbon atom
It is also determined by the electronegativity of the molecule and polarization of the molecule to which carbon atom bonded with.
Sigma bond: A covalent bond formation is mainly due to end to end overlap of atomic orbitals.
Pi bond: A covalent bond formation is mainly due to side to side overlap of atomic orbitals
Electronegativity: The ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself.
Polarization: A partial charge separation between the carbon and an other heteroatom due to its electronegativity difference.
(a)
Answer to Problem 20PP
Answer
The bond dissociation energy of the bonds in red line of the molecule (a) is given below
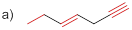
Carbon - carbon triple bond has more dissociation energy
Carbon - carbon triple bond has more dissociation energy than the carbon – carbon double bond and Carbon – carbon double bond more dissociation than the carbon – carbon single bond.
Explanation of Solution
To find: Bond-dissociation energy of the given compounds.
Draw the given molecule and analyze the nature of C-C bonds present in it.
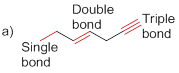
The given molecule is drawn and it has three types of C-C bonds. They are
Carbon – Carbon Single bond has less dissociation energy than carbon – carbon double bond and triple bond. Carbon – carbon triple bond (sp hybridization) has more dissociation energy because it consists of three bonds (two pi bonds and one sigma bond) so it requires more energy to break the bonds than the other carbon- carbon double bonds (one pi bonds and one sigma bond) and carbon – carbon single bond (only one sigma bond).
(b)
Interpretation:
Bond-dissociation energy should be identified for the red line bond in the given structure.
Concept introduction:
Bond-dissociation energy (BDE) is determined from the strength of a single chemical bond.
Bond-dissociation energy is mainly depends on the hybridization of the carbon atom and substitution on the carbon atom
It is also determined by the electronegativity of the molecule and polarization of the molecule to which carbon atom bonded with.
Sigma bond: A covalent bond formation is mainly due to end to end overlap of atomic orbitals.
Pi bond: A covalent bond formation is mainly due to side to side overlap of atomic orbitals
Electronegativity: The ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself.
Polarization: A partial charge separation between the carbon and an other heteroatom due to its electronegativity difference.
(b)
Answer to Problem 20PP
Answer
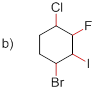
C-F bond has more dissociation energy
Explanation of Solution
To find: Bond-dissociation energy of the given compounds.
Draw the given molecule and analyze the nature of C-C bonds present in it.

The given molecule is drawn and it has four types of C-C bonds. They are
Bond dissociation energy depends on the electronegativity of the molecule and polarization of the molecule. If the molecule has high electronegativity (less polarizability) the dissociation energy of the molecule is high.
The electronegativity order in the halogen series given below
C-F has more Bond dissociation energy in the given molecule since it has more electronegativity than the other halogen atoms.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Binder Ready Version
- How many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forwardIdentify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forward
- H H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forward
- choose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forwardWhy isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forward
- OH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





