
Concept explainers
Write a
Largest and Smallest numbers
Program Plan:
- Include the required headers.
- Define “main()” method.
- Declare the required “int” and “char” variables.
- Prompt the user for input file.
- Read the required input file.
- Create the object for “ifstream”.
- Open the required file.
- Check the file can be opened or not using “if” condition.
- If the file includes any error, print file “cannot be opened”.
- Initialize the input and check for largest and smallest numbers present in the file.
- Print the output using “cout”
- Return the required variable.
- Close the “main()” method.
The below C++ program describes about the displaying of largest and smallest values among the numbers present in a given file.
Explanation of Solution
Program:
//Include the needed headers
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
//main() Method
int main()
{
//Declaration of int variable sum
int sum = 0;
//Declaration of char variable file_name
char file_name [31];
//Declaration of input and index
int input, i = 0;
//Declaration of largest
int largest = -INT_MAX;
//Declaration of smallest
int smallest = INT_MAX;
//prompt the user for input file name
cout << "Enter a file name."
<< " This Program limits file names to"
<< endl
<< " a maximum of 30 characters. " << endl;
//read the input file name
cin >> file_name;
//creating object for ifstream
ifstream infile;
//a handle for opening the input file
infile.open(file_name);
//check the condition
if(!infile)
{
//display the error
cout << "Cannot open file " << file_name
<< " Aborting program " << endl;
//stop and exit
exit (1);
}
//initialize the input
infile >> input;
//start the loop
while(infile)
{
//check the condition
if(input > largest)
//get the largest value
largest = input;
//check the file
if(input < smallest)
//get the smallest value
smallest = input;
cout << input << " " << endl;
infile >> input;
}
//display the output
cout << "smallest in file = " << smallest
<< " largest in file = " << largest << endl;
getchar();
getchar();
//return the required value
return 0;
}
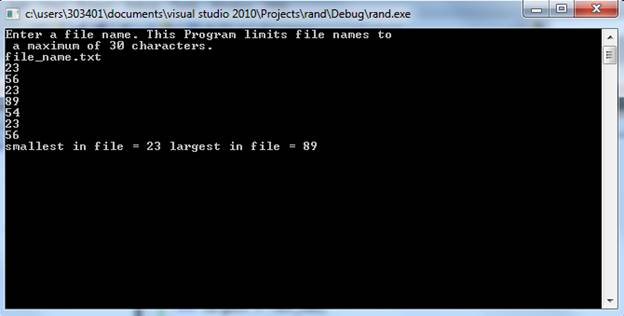
Output:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Problem Solving with C++ (9th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
- Describe three (3) Multiplexing techniques common for fiber optic linksarrow_forwardCould you help me to know features of the following concepts: - commercial CA - memory integrity - WMI filterarrow_forwardBriefly describe the issues involved in using ATM technology in Local Area Networksarrow_forward
- For this question you will perform two levels of quicksort on an array containing these numbers: 59 41 61 73 43 57 50 13 96 88 42 77 27 95 32 89 In the first blank, enter the array contents after the top level partition. In the second blank, enter the array contents after one more partition of the left-hand subarray resulting from the first partition. In the third blank, enter the array contents after one more partition of the right-hand subarray resulting from the first partition. Print the numbers with a single space between them. Use the algorithm we covered in class, in which the first element of the subarray is the partition value. Question 1 options: Blank # 1 Blank # 2 Blank # 3arrow_forward1. Transform the E-R diagram into a set of relations. Country_of Agent ID Agent H Holds Is_Reponsible_for Consignment Number $ Value May Contain Consignment Transports Container Destination Ф R Goes Off Container Number Size Vessel Voyage Registry Vessel ID Voyage_ID Tonnagearrow_forwardI want to solve 13.2 using matlab please helparrow_forward
- a) Show a possible trace of the OSPF algorithm for computing the routing table in Router 2 forthis network.b) Show the messages used by RIP to compute routing tables.arrow_forwardusing r language to answer question 4 Question 4: Obtain a 95% standard normal bootstrap confidence interval, a 95% basic bootstrap confidence interval, and a percentile confidence interval for the ρb12 in Question 3.arrow_forwardusing r language to answer question 4. Question 4: Obtain a 95% standard normal bootstrap confidence interval, a 95% basic bootstrap confidence interval, and a percentile confidence interval for the ρb12 in Question 3.arrow_forward
 EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage LearningProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage LearningProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning, C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology PtrCOMPREHENSIVE MICROSOFT OFFICE 365 EXCEComputer ScienceISBN:9780357392676Author:FREUND, StevenPublisher:CENGAGE L
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology PtrCOMPREHENSIVE MICROSOFT OFFICE 365 EXCEComputer ScienceISBN:9780357392676Author:FREUND, StevenPublisher:CENGAGE L





