
A skier starts at the top of a hill. On which run does her gravitational potential energy change the most (a), (b), (c), or (d), or are they (e) all the same? On which run would her speed at the bottom be the fastest if the runs are icy and we assume no friction or air resistance? Recognizing that there is always some friction, answer the above two questions again. List your four answers now.
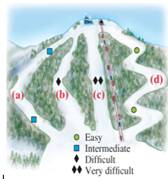
The path on which the gravitational potential energy changes the most when there is no friction and the skier will have the maximum speed.
Answer to Problem 1OQ
Solution:
All paths undergo the same amount of gravitational potential energy change. Skier will have same speed at the bottom for all the paths.
All paths undergo the same amount of gravitational potential energy change. Skier will have the greatest speed for the shortest path C.
Explanation of Solution
Force of gravity is a conservative force hence, the work done by force of gravity does not depend on the path but on the initial and final position, since in each path initial and final position is same. Hence, each path undergoes the same amount of gravitational potential energy change.
As the skier travels down, the potential energy converts to kinetic energy. Since the change in potential energy is same for each path, the change in kinetic energy is also same for each path. Hence, skier gains the same amount of speed through each path.
Force of gravity is a conservative force hence the work done by force of gravity does not depend on the path but on the initial and final position, since in each path they are same. Hence, each path undergoes the same amount of gravitational potential energy change.
As the skier travels down, the potential energy converts to kinetic energy and work done by frictional force. the change in potential energy is same for each path, but the work done by frictional force depends on the length of the path. Larger the length, larger is the energy lost to friction. So, only a small portion of potential energy converts to kinetic energy. smaller the length, smaller is the energy lost to friction. So, a large portion of potential energy converts to kinetic energy and skier gains larger speed.
Conclusion:
The change in gravitational potential energy for each path comes out to be same.
The speed at the bottom comes out to be same for each path.
The change in gravitational potential energy for each path comes out to be same.
The speed at the bottom comes out to be greatest for the shortest path C.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
PHYSICS:PRINCIPLES W/ APPLICATIONS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Microbiology: An Introduction
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
- 8. With the aid of a diagram draw the following electric circuit and use the resistor as the load, (a) Closed circuit (b) Open circuitarrow_forwardLab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation. I am having trouble with this part of the lab.arrow_forwardMick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





