
Concept explainers
If you compare electron micrographs of a relaxed skeletal muscle fiber and a fully contracted muscle fiber, which would you see only in the relaxed fiber?
a. Z discs
b. Sarcomeres
c. I bands
d. A bands
e. H zones
Introduction:
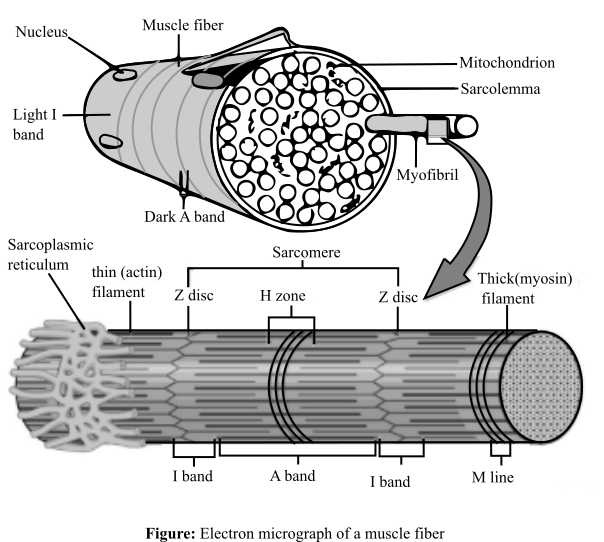
The skeletal muscle fibers are made of striated muscle tissues, which consists of alternating light (I) and dark bands (A). I-band consists of a dark region known as Z disc. On the other hand, A band consists of a light region known as H-zone. I-band consists only of thin actin filaments, while the A-band consists of both actin and myosin filaments. All these units of a muscle fiber makes sarcomere. The micrograph of a sarcomere is shown as below:
Answer to Problem 1MC
Correct answer:
I bands and the H zones of the skeletal muscle fiber will be visible only in the micrograph of the relaxed fiber.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation for the correct answer:
Option (c) and option (e) are given as I bands, and H zones, respectively. A sarcomere is basically a unit of the striated muscle tissue. Repeating units of Z lines are present in this and the actin molecules are bounded to these lines forming a border in the sarcomere. Alternating I which are light and A which are dark bands are present. When looking closer, I band comprises of a midline interruption which is known as Z disc while in the A band there is a lighter middle section known as H zone. During the muscle contraction, the actin filaments move over the myosin filaments according to the sliding filament theory. I-band and the H zone tends to overlap when a muscle is contracted. When they overlap it becomes difficult to observe I and H bands. Therefore, these will only be visible in the relaxed position. Hence, option (c) and option (e) are correct.
Explanation for the incorrect answers:
Option (a) is given as Z discs. The Z discs are dark stripes, which marks the ending of a sarcomere. These dark zones can be clearly seen in both the contracted and relaxed electron micrographs of the skeletal muscles. So, it is an incorrect option.
Option (b) is given as sarcomere. This is the part of the muscle composing of the thin and thick filaments. These thick and thin filaments forming the sarcomere are the basic unit of the muscle tissue present between the two Z discs. Therefore, sarcomere will be visible in both the contracted as well as a relaxed muscle fiber. So, it is an incorrect option.
Option (d) is given as A bands. These are the darker areas of the sarcomere. These bands do not shrink, when the muscle contracts, and hence, can be seen both in relaxed and contracted position. So, it is an incorrect option.
Hence, options (a), (b), and (d) are incorrect.
Thus, in a relaxed state, I-band and H-zone will be visible, which will disappear during contraction of the muscle.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology (12th Edition)
- A farmer has noticed that his soybean plants produce more beans in some years than others. He claims to always apply the same amount of fertilizer to the plants, but he suspects the difference in crop yield may have something to do with the amount of water the crops receive. The farmer has observed that the soybeans on his farm usually receive between 0 to 0.5 inches of water per day, but he is unsure of the optimal average daily amount of water with which to irrigate. 1. State a question that addresses the farmer’s problem 2. Conduct online research on “soybean crop irrigation" and record a brief summary of the findings 3. Construct a testable hypothesis and record i 4. Design an experiment to test the hypothesis and describe the procedures, variables, and data to be collectedarrow_forwardA pharmaceutical company has developed a new weight loss drug for adults. Preliminary tests show that the drug seems to be fairly effective in about 75% of test subjects. The drug company thinks that the drug might be most effective in overweight individuals, but they are unsure to whom they should market the product. Use the scientific method to address the pharmaceutical company’s needs: State a research question that addresses the pharmaceutical company's problem Conduct online research on “Body Mass Index” categories and record a brief summary Construct a testable hypothesis and record in Design an experiment to test the hypothesis and describe the procedures, variables, and data to be collected What is the purpose of a control group in an experiment? What would the control groups be for each of your designed experiments in this exercise? Describe the data that would be recorded in each of the experiments you designed. Would it be classified as quantitative or…arrow_forwardPatients with multiple sclerosis frequently suffer from blurred vision. Drug X was developed to reduce blurred vision in healthy patients, but the effectiveness had not been tested on those suffering from multiple sclerosis. A study was conducted to determine if Drug X is effective at reducing blurry vision in multiple sclerosis patients. To be considered effective, a drug must reduce blurred vision by more than 30% in patients. Researchers predicted that a 20 mg dose of the drug would be effective for treating blurred vision in multiple sclerosis patients by reducing blurred vision by more than 30%. Drug X was administered to groups of multiple sclerosis patients at three doses (10 mg/day, 20 mg/day, 30 mg/day) for three weeks. A fourth group of patients was given a placebo containing no drug X for the same length of time. Vision clarity was measured for each patient before and after the three-week period using a standard vision test. The results were analyzed and graphed (See Figure…arrow_forward
- Svp je voulais demander l aide pour mon exercicearrow_forwardImagine that you are a clinical geneticist. Your colleague is an oncologist who wants your help explaining the basics of genetics to their patient, who will be undergoing genetic testing in the coming weeks for possible acute myeloid leukemia (AML) induced by the radiation she had several years ago for breast cancer. Write a 1,050- to 1,225-word memo to your colleague. Include the following in your memo: An explanation of the molecular structure of DNA and RNA, highlighting both similarities and differences A description of the processes of transcription and translation An explanation of the differences between leading and lagging strands and how the DNA is replicated in each strand Reponses to the following common questions patients might ask about this type of genetic testing and genetic disorder: Does AML run in families? What genes are tested for?arrow_forwardRespond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: What are some potential consequences that could result if the processes of replication, transcription, and translation don’t function correctly? Provide an example of how you might explain these consequences in terms that patients might understand.arrow_forward
- answer questions 1-10arrow_forwardAnswer Question 1-9arrow_forwardEx: Mr. Mandarich wanted to see if the color of light shined on a planthad an effect on the number of leaves it had. He gathered a group ofthe same species of plants, gave them the same amount of water, anddid the test for the same amount of time. Only the color of light waschanged. IV:DV:Constants:Control Gr:arrow_forward
- ethical considerations in medical imagingarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward2. In one of the reactions of the citric acid cycle, malate is oxidized to oxaloacetate. When this reaction is considered in isolation, a small amount of malate remains and is not oxidized. The best term to explain this is a. enthalpy b. entropy c. equilibrium d. free energy e. loss of energyarrow_forward
 Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





