
In addition to the key words, you should also be able to define each of the following terms:
descriptive research strategy
linear relationship
curvilinear relationship
positive relationship
correlational research strategy
experimental research strategy
quasi-experimental research strategy
nonexperimental research strategy
selection bias
volunteer bias
novelty effect
multiple treatment interference
sensitization, or assessment sensitization, or pretest
sensitization
participant variables
time-related variables
fatigue
practice
artifact
experimenter bias
single-blind
double-blind
demand characteristics
reactivity
laboratory
field
To define:
The following terms:
- Descriptive Research Strategy
- Linear relationship
- Curvilinear Relationship
- Positive Relationship
- Negative Relationship
- Correlational Research Strategy
- Experimental Research Strategy
- Quasi-Experimental Research Strategy
- Non-Experimental Research Strategy
- Selection Bias
- Volunteer Bias
- Novelty Effect
- Multiple Treatment Interference
- Sensitization/Assessment Sensitization/ Pretest Sensitization
- Participant Variable
- Time-Related Variable
- Fatigue
- Practice
- Artifact
- Experimenter Bias
- Single-Blind
- Double-Blind
- Demand Characteristics
- Reactivity
- Laboratory
- Field
Explanation of Solution
Descriptive Research Strategy:
This strategy gives the description of single variable, that is, how it is varying according to time or situation. In other words, one can say that this is a strategy which is used in research to describe the variables. This strategy is used to know the behaviour of any variable and does not work for the causes behind the variation in it.
Linear relationship:
A linear relationship between any two variables can be defined as the relationship which can be represented by a line on a graph. Mathematically, a relationship between the variables x and y which satisfies the equation-
Where m is a slope and c represents intercept.
Curvilinear Relationship:
If the linear relationship does not exist between two variables then there would be another relationship, known as a curvilinear relationship, that is, the relationship except the linear relationship between the two variables is known as curvilinear relationship.
Positive Relationship:
In statistics, a positive relationship or positive correlation is defined as the relationship between two variables in which, increment (decrement) in one variable results in increment(decrement) of other variable (not necessarily in same ratio). In other words, positive relationship is the relationship between the two variables in which both variable moves in same direction.
For example, increment in RAM results in increment in price of mobile. The positive relationship can also be seen graphically through scatter plot.
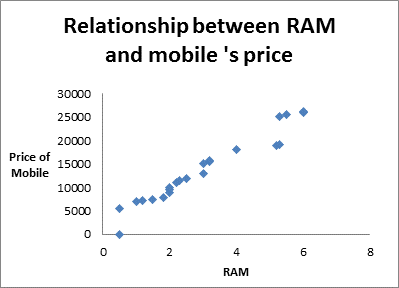
Negative Relationship:
In statistical terms, a negative relationship or negative correlation is defined as the relationship between two variables in which both the variables move in opposite direction, that is, increment(decrement) in the value of one variable results in decrement (increment) of other.
For example, on increasing the temperature of microwave, the time taken by water to boil is decreased.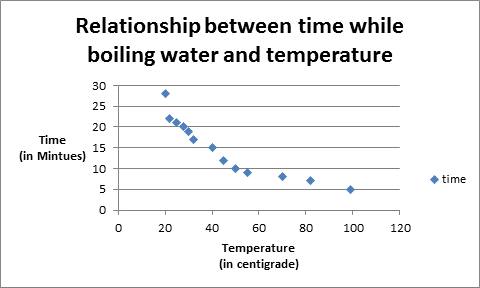
Correlational Research Strategy:
The research strategy used to find the relationship between two variables is known as correlational research strategy. It tells whether the relationship exists or not and if exists then which kind of relationship exists, that is, the nature of relationship. It can be seen by scatter plot which is a graphical representation of variables. Correlation is not same as causation.
Experimental Research Strategy:
The research study which gives the cause and effect relationship between the two variables is known as experimental research strategy. In this type of study, one does changes in a variable which is known as independent variable and the dependent variable is measured at different levels of the independent variable and the remaining variables are known as extraneous variables. Here, manipulation in independent variable is used to determine the direction of a relationship and comparison of dependent variable is done at each level of treatment and one controls the effect of extraneous variables as much as possible through randomization technique.
Quasi-Experimental Research Strategy:
A quasi-experimental research strategy is not a true experimental research strategy but it is between correlational and experimental research strategy. In this strategy, the problem of controlling extraneous variable is not eliminated but the problem of directionality is solved. In this, participants are not randomly assigned to experimental groups.
Non-Experimental Research Strategy:
A research strategy in which independent variable cannot be manipulated or random assignment is not possible is known as non-experimental research strategy. In this type of study, sometimes one has to deal with a problem of single variable or the problem of non causal relationship between variables or the problem may be about a particular experience. Some kinds of non-experimental research are correlational research, quasi-experimental research, single-variable research and qualitative research.
Selection Bias:
As the name 'selection bias' sounds that it is the bias in selection, that is, when the selection of units is not done randomly then it is not a good representative of population and it affects the analysis. So, the main purpose of analysis is not fulfilled when the units in the sample are not chosen randomly. For example, sometimes in interviews, the interviewer do bias in selecting candidates.
Volunteer Bias:
A volunteer bias occurs when the when sample members are self-selected. For example, if teacher asks to students to participate in sports event, then some of the students come to teacher and tell that they want to participate in sports event then they are volunteers and here randomization does not play any role so this type of bias is known as selection bias.
Novelty Effect:
Novelty effect arises due to something new which means that when there is an effect of any new thing occurs or changes in environment then people get boosted for some time and there will be novelty effect. For example, when the online shopping apps came into our lives then suddenly people love to use those apps because of saving of time and some other reasons. The people got attract to online shopping and this was the change for them. So, here the novelty effect kicked in.
Multiple Treatment Interference:
When the multiple treatments are given to the same subjects and effect of one treatment may be influenced by other treatment, this process is known as multiple treatment interference.
Sensitization/Assessment Sensitization/ Pretest Sensitization:
Sensitization is the process of making someone react to something that previously had no effect or in other words, the process of being sensitive towards any specific event.
When the participants involved in the experiment are pretested then there is a risk that they will be sensitive towards the variables which is measured by pretesting and that will affect their post-test scores, this is pretest sensitization.
Participant Variable:
Participant variables are the extraneous variables which describe the individual's characteristics that may impact how he or she responds such as age, anxiety, awareness or intelligence etc. These are known as extraneous variables because these variables can affect the experiment but the experimenter may not consider it.
Time-Related Variable:
It is clear by the name 'time-related variable' that the variables which varies with the time such as price of mobiles, temperature over a day etc. These types of variables are very useful in time-series analysis and in research study too.
Fatigue:
Fatigue means extreme tiredness which occurs without taking rest over a period of time whether from physical or mental illness. Fatigue is a process that has a degree of randomness and is influenced by variety of factors. The most common distributions in data analysis which works against fatigue are Weibull distribution, lognormal distribution and extreme value distribution.
Practice:
It is a threat to internal validity that occurs when prior participation in a measurement provides additional skills that influence their performance on subsequent measurements.
Artifact:
In statistics, artifact is a noise or error which occurs during data manipulation or in the case of selection of faulty choice of variables. It threats the validity of measurement and is an external factor.
Experimenter Bias:
During an experiment, the thoughts of a researcher affect the experiment and it can occur at any phase of research. This is known as experimenter bias. It is very difficult to leave subjectivity completely for anyone because of which this bias arises.
Single-Blind:
When a researcher gives any treatment or medication to a subject and that subject is not aware about the treatment or medication which he/she is receiving is known as single-blind study.
Double-Blind:
When a subject as well as researcher is not aware of the treatment then the study is called as double-blind study. This type of study is used to remove the bias by keeping both the persons unaware about what is being tested.
Demand Characteristics:
In research, demand characteristics are artifact which occurs when the subject is aware about the treatment which they are receiving and then they change their behaviour which affects the outcome of the research.
Reactivity:
Reactivity refers to the behaviour of subject which changes during the experiment when they get affected by any instrument during experiment and this may create bias.
Laboratory:
Laboratory term refers to observing the behaviour of the subject that is observed in controlled atmosphere. For example, a teacher can observe a student in a classroom which is controlled atmosphere and also in playground during holidays which is an uncontrolled atmosphere. So, as a teacher, she/he can get nearly accurate result about student in a class.
Field:
In statistics, field can be defined as the place from where one can collect primary data by using various methods such as personal interview, direct investigation etc.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
RESEARCH METHODS-W/ACCESS >CUSTOM<
- Examine the Variables: Carefully review and note the names of all variables in the dataset. Examples of these variables include: Mileage (mpg) Number of Cylinders (cyl) Displacement (disp) Horsepower (hp) Research: Google to understand these variables. Statistical Analysis: Select mpg variable, and perform the following statistical tests. Once you are done with these tests using mpg variable, repeat the same with hp Mean Median First Quartile (Q1) Second Quartile (Q2) Third Quartile (Q3) Fourth Quartile (Q4) 10th Percentile 70th Percentile Skewness Kurtosis Document Your Results: In RStudio: Before running each statistical test, provide a heading in the format shown at the bottom. “# Mean of mileage – Your name’s command” In Microsoft Word: Once you've completed all tests, take a screenshot of your results in RStudio and paste it into a Microsoft Word document. Make sure that snapshots are very clear. You will need multiple snapshots. Also transfer these results to the…arrow_forwardExamine the Variables: Carefully review and note the names of all variables in the dataset. Examples of these variables include: Mileage (mpg) Number of Cylinders (cyl) Displacement (disp) Horsepower (hp) Research: Google to understand these variables. Statistical Analysis: Select mpg variable, and perform the following statistical tests. Once you are done with these tests using mpg variable, repeat the same with hp Mean Median First Quartile (Q1) Second Quartile (Q2) Third Quartile (Q3) Fourth Quartile (Q4) 10th Percentile 70th Percentile Skewness Kurtosis Document Your Results: In RStudio: Before running each statistical test, provide a heading in the format shown at the bottom. “# Mean of mileage – Your name’s command” In Microsoft Word: Once you've completed all tests, take a screenshot of your results in RStudio and paste it into a Microsoft Word document. Make sure that snapshots are very clear. You will need multiple snapshots. Also transfer these results to the…arrow_forwardExamine the Variables: Carefully review and note the names of all variables in the dataset. Examples of these variables include: Mileage (mpg) Number of Cylinders (cyl) Displacement (disp) Horsepower (hp) Research: Google to understand these variables. Statistical Analysis: Select mpg variable, and perform the following statistical tests. Once you are done with these tests using mpg variable, repeat the same with hp Mean Median First Quartile (Q1) Second Quartile (Q2) Third Quartile (Q3) Fourth Quartile (Q4) 10th Percentile 70th Percentile Skewness Kurtosis Document Your Results: In RStudio: Before running each statistical test, provide a heading in the format shown at the bottom. “# Mean of mileage – Your name’s command” In Microsoft Word: Once you've completed all tests, take a screenshot of your results in RStudio and paste it into a Microsoft Word document. Make sure that snapshots are very clear. You will need multiple snapshots. Also transfer these results to the…arrow_forward
- 2 (VaR and ES) Suppose X1 are independent. Prove that ~ Unif[-0.5, 0.5] and X2 VaRa (X1X2) < VaRa(X1) + VaRa (X2). ~ Unif[-0.5, 0.5]arrow_forward8 (Correlation and Diversification) Assume we have two stocks, A and B, show that a particular combination of the two stocks produce a risk-free portfolio when the correlation between the return of A and B is -1.arrow_forward9 (Portfolio allocation) Suppose R₁ and R2 are returns of 2 assets and with expected return and variance respectively r₁ and 72 and variance-covariance σ2, 0%½ and σ12. Find −∞ ≤ w ≤ ∞ such that the portfolio wR₁ + (1 - w) R₂ has the smallest risk.arrow_forward
- 7 (Multivariate random variable) Suppose X, €1, €2, €3 are IID N(0, 1) and Y2 Y₁ = 0.2 0.8X + €1, Y₂ = 0.3 +0.7X+ €2, Y3 = 0.2 + 0.9X + €3. = (In models like this, X is called the common factors of Y₁, Y₂, Y3.) Y = (Y1, Y2, Y3). (a) Find E(Y) and cov(Y). (b) What can you observe from cov(Y). Writearrow_forward1 (VaR and ES) Suppose X ~ f(x) with 1+x, if 0> x > −1 f(x) = 1−x if 1 x > 0 Find VaRo.05 (X) and ES0.05 (X).arrow_forwardJoy is making Christmas gifts. She has 6 1/12 feet of yarn and will need 4 1/4 to complete our project. How much yarn will she have left over compute this solution in two different ways arrow_forward
- Solve for X. Explain each step. 2^2x • 2^-4=8arrow_forwardOne hundred people were surveyed, and one question pertained to their educational background. The results of this question and their genders are given in the following table. Female (F) Male (F′) Total College degree (D) 30 20 50 No college degree (D′) 30 20 50 Total 60 40 100 If a person is selected at random from those surveyed, find the probability of each of the following events.1. The person is female or has a college degree. Answer: equation editor Equation Editor 2. The person is male or does not have a college degree. Answer: equation editor Equation Editor 3. The person is female or does not have a college degree.arrow_forwardneed help with part barrow_forward
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill


