
For the graph shown in Fig. 6-19,
a. find three different Hamilton circuits.
b. find a Hamilton path that starts at A and ends at B.
c. find a Hamilton path that starts at D and ends at F.
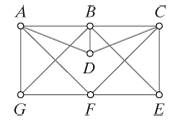
(a)
To find:
Three Hamilton circuits for given graph.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The Hamilton circuit are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is,
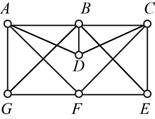
Approach:
A Hamilton circuit is the circuit that starts and ends at the same vertex and includes every other vertex of the graph only once.
Calculation:
Let’s start with vertex A the options to go forward are vertices B, D, F, and G, go to vertex B. From vertex B the options to move further are C, D, E, and G, go to vertex D. From vertex D the option to go forward is vertex C. From vertex C the option to move forward to is E. From vertex E the option to move forward to is F. From vertex F the option to move forward to is G. From vertex G the option to move forward to is A.
The Hamilton circuit is
Let’s start with vertex A the options to go forward are vertices B, D, F, and G, go forward with vertex G. From vertex G the options to move further are B and F, go forward with vertex B. From vertex B the options to go forward are vertices C, D, and E, go to vertex D. From vertex D the option to move forward to is C. From vertex C the option to move forward to is E. From vertex E the option to move forward to is F. From vertex F the option to move forward to is A.
The Hamilton circuit is
Let’s start with vertex A the options to go forward are vertices B, D, F, and G, go forward with vertex D. From vertex D the options to move further are B and C, go forward with vertex B. From vertex B the options to go forward are vertex C and E, go to vertex E. From vertex E the option to move forward to is C. From vertex C the option to move forward to is F. From vertex F the option to move forward to is G. From vertex G the option to move forward to is A.
The Hamilton circuit is
Conclusion:
Thus, the Hamilton circuits are
(b)
To find:
A Hamilton path that starts at A and ends at B.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
A Hamilton path that starts at A and ends at B is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is,
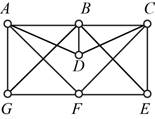
Approach:
A Hamilton path is the path that includes every other vertex of the graph only once.
Calculation:
Let’s start with vertex A the options to go forward are vertices B, D, F, and G, go forward with vertex G. From vertex G the options to move further are B and F, go forward with vertex F. From vertex F the options to go forward are vertex C, E, and G, go to vertex E. From vertex E the option to move forward to are B and C, go to vertex C. From vertex C the option to move forward to are B and D, go to vertex D. From vertex D the option to move forward to is B.
The Hamilton path is
Conclusion:
Thus, a Hamilton path that starts at A and ends at B is
(c)
To find:
A Hamilton path that starts at D and ends at F.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
A Hamilton path that starts at D and ends at F is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is,
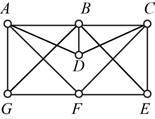
Approach:
A Hamilton path is the path that includes every other vertex of the graph only once.
Calculation:
Let’s start with vertex D the options to go forward are vertices A, B, C, go forward with vertex C. From vertex C the options to move further are B, E and F, go forward with vertex E. From vertex E the options to go forward are vertex B and F, go to vertex B. From vertex B the option to move forward to are A and G, go to vertex G. From vertex G the option to move forward to are A and F, go to vertex A. From vertex A the option to move forward to is F.
The Hamilton path is
Conclusion:
Thus, a Hamilton path that starts at D and ends at F is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Excursions In Modern Mathematics, 9th Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
University Calculus
Elementary Statistics: A Step By Step Approach
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences and Social Sciences
- Consider the hypothesis test Ho: = 622 against H₁: 6 > 62. Suppose that the sample sizes are n₁ = 20 and n₂ = 8, and that = 4.5; s=2.3. Use a = 0.01. (a) Test the hypothesis. Round your answers to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76). The test statistic is fo = i The critical value is f = Conclusion: i the null hypothesis at a = 0.01. (b) Construct the confidence interval on 02/022 which can be used to test the hypothesis: (Round your answer to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76).) iarrow_forwardConjecture Let x and y be integers. If x is even and y is odd, then xy is even. Try some examples. Does the conjecture seem to be true or false?arrow_forwardFind the general solution to the differential equationarrow_forward
- 3. A room has a large circular table with ten seats, numbered 1 to 10, such that to the right of seat number i is seat number i + 1 for all i ∈ {1, . . . , 9} and to the right of seat 10 is seat 1. We want to assign seats to 10 people, 6 of them only speak Slovene, 1 of them only speaks English, and the remaining 3 speak both Slovene and English, by giving out numbered place cards. In how many ways can we do that so that everyone sits next to at least one person who speaks a common language?arrow_forwardcharity savings Budget for May travel food Peter earned $700 during May. The graph shows how the money was used. What fraction was clothes? O Search Submit clothes leisurearrow_forwardExercise 11.3 A slope field is given for the equation y' = 4y+4. (a) Sketch the particular solution that corresponds to y(0) = −2 (b) Find the constant solution (c) For what initial conditions y(0) is the solution increasing? (d) For what initial conditions y(0) is the solution decreasing? (e) Verify these results using only the differential equation y' = 4y+4.arrow_forward
- SOLVE ONLY FOR (L) (M) AND (O)arrow_forwardAphids are discovered in a pear orchard. The Department of Agriculture has determined that the population of aphids t hours after the orchard has been sprayed is approximated by N(t)=1800−3tln(0.17t)+t where 0<t≤1000. Step 1 of 2: Find N(63). Round to the nearest whole number.arrow_forward1. A telegraph can transmit two different signals: a dot and a dash. We want to encode the 26 letters of the English alphabet and the ten digits 0, 1, 2, . . . , 9 using sequences of these two symbols. What is the smallest integer n such that we can encode all these letters and digits with sequences of length at most n and length at least 1?arrow_forward
- Use the graph of y = f(x) to answer the following. 3- 2 -4 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 -1 2 m -3- + (d) Find all x for which f(x) = -2. If there is more than one value, separate them with commas or write your answer in interval notation, if necessary. Select "None", if applicable. Value(s) of x for which f(x)=-2: | (0,0) (0,0) (0,0) (0,0) 0,0... -00 None (h) Determine the range of f. The range is (0,0) Garrow_forwardFile Preview A gardener has ten different potted plants, and they are spraying the plants with doses of Tertizers. Plants can receive zero or more doses in a session. In the following, we count each possible number of doses the ten plants can receive (the order of spraying in a session does not matter). (a) How many ways are there if there were twelve total doses of a single type of fertilizer? (b) How many ways are there if there are six total doses of a single type of fertilizer, each plant receives no more than one dose? (c) How many ways are there if is was one dose of each of six types of fertilizers? (d) How many ways are there if there are four doses of fertilizer #1 and eight doses of fertilizer #2? (e) How many ways are there if there are four doses of fertilizer #1 and eight doses of fertilizer #2, and each plant receives no more than one dose of fertilizer #1? (f) How many ways are there to do two sessions of spraying, where each plant receives at most two doses total?arrow_forward3. [-/3 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SCALCET8 7.4.032. ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER Evaluate the integral. X + 4x + 13 Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER dxarrow_forward
 Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell

