
For the graph shown in Fig. 6-19,
a. find three different Hamilton circuits.
b. find a Hamilton path that starts at A and ends at B.
c. find a Hamilton path that starts at D and ends at F.
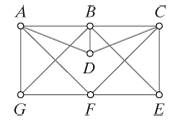
(a)
To find:
Three Hamilton circuits for given graph.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The Hamilton circuit are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is,
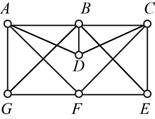
Approach:
A Hamilton circuit is the circuit that starts and ends at the same vertex and includes every other vertex of the graph only once.
Calculation:
Let’s start with vertex A the options to go forward are vertices B, D, F, and G, go to vertex B. From vertex B the options to move further are C, D, E, and G, go to vertex D. From vertex D the option to go forward is vertex C. From vertex C the option to move forward to is E. From vertex E the option to move forward to is F. From vertex F the option to move forward to is G. From vertex G the option to move forward to is A.
The Hamilton circuit is
Let’s start with vertex A the options to go forward are vertices B, D, F, and G, go forward with vertex G. From vertex G the options to move further are B and F, go forward with vertex B. From vertex B the options to go forward are vertices C, D, and E, go to vertex D. From vertex D the option to move forward to is C. From vertex C the option to move forward to is E. From vertex E the option to move forward to is F. From vertex F the option to move forward to is A.
The Hamilton circuit is
Let’s start with vertex A the options to go forward are vertices B, D, F, and G, go forward with vertex D. From vertex D the options to move further are B and C, go forward with vertex B. From vertex B the options to go forward are vertex C and E, go to vertex E. From vertex E the option to move forward to is C. From vertex C the option to move forward to is F. From vertex F the option to move forward to is G. From vertex G the option to move forward to is A.
The Hamilton circuit is
Conclusion:
Thus, the Hamilton circuits are
(b)
To find:
A Hamilton path that starts at A and ends at B.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
A Hamilton path that starts at A and ends at B is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is,
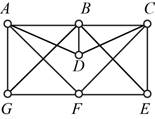
Approach:
A Hamilton path is the path that includes every other vertex of the graph only once.
Calculation:
Let’s start with vertex A the options to go forward are vertices B, D, F, and G, go forward with vertex G. From vertex G the options to move further are B and F, go forward with vertex F. From vertex F the options to go forward are vertex C, E, and G, go to vertex E. From vertex E the option to move forward to are B and C, go to vertex C. From vertex C the option to move forward to are B and D, go to vertex D. From vertex D the option to move forward to is B.
The Hamilton path is
Conclusion:
Thus, a Hamilton path that starts at A and ends at B is
(c)
To find:
A Hamilton path that starts at D and ends at F.
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
A Hamilton path that starts at D and ends at F is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is,
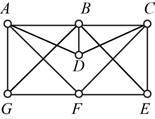
Approach:
A Hamilton path is the path that includes every other vertex of the graph only once.
Calculation:
Let’s start with vertex D the options to go forward are vertices A, B, C, go forward with vertex C. From vertex C the options to move further are B, E and F, go forward with vertex E. From vertex E the options to go forward are vertex B and F, go to vertex B. From vertex B the option to move forward to are A and G, go to vertex G. From vertex G the option to move forward to are A and F, go to vertex A. From vertex A the option to move forward to is F.
The Hamilton path is
Conclusion:
Thus, a Hamilton path that starts at D and ends at F is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Excursions in Modern Mathematics (9th Edition)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
University Calculus
Elementary Statistics: A Step By Step Approach
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences and Social Sciences
- please give the answerarrow_forwardNeed help with the following statistic problems.arrow_forwardom nearest tenth if necessary. milsum 3. છે. 9.3mm 3mm A 78-43-92 4-3) 11.7 of 72.04-11.7-= lygons 7.8 mi 60.94 blants" 9 om 6. 4.15-7 16- 32m 1.8m 4.5m % ose 4.5m as to 65m 14 represents 5 square meters.arrow_forward
- After a great deal of experimentation, two college senior physics majors determined that when a bottle of French champagne is shaken several times, held upright, and uncorked, its cork travels according to the function below, where s is its height (in feet) above the ground t seconds after being released. s(t)=-16t² + 30t+3 a. How high will it go? b. How long is it in the air?arrow_forward2PM Tue Mar 4 7 Dashboard Calendar To Do Notifications Inbox File Details a 25/SP-CIT-105-02 Statics for Technicians Q-7 Determine the resultant of the load system shown. Locate where the resultant intersects grade with respect to point A at the base of the structure. 40 N/m 2 m 1.5 m 50 N 100 N/m Fig.- Problem-7 4 m Gradearrow_forwardif δ ≥ 2, then it contains a cycle with length at least δ + 1.arrow_forward
 Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell

