
Concept explainers
Figure 6.4 Which of the following is the correct order of events in mitosis?
a. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore becomes attached to the initotic spindle. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides. The sister chromatids separate.
b. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. The sister chromatids separate. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides.
c. The kinetochore becomes attached to metaphase plate. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore breaks down and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides.
d. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. Sister chromatids line up at the
metaphase plate. The kinetochore breaks apart and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus re-forms and the cell divides.
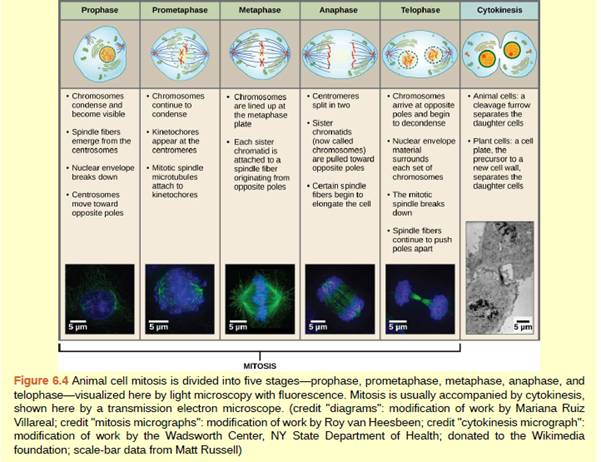
Introduction:
The mitosis is the process of the cell division, which takes place in all the somatic cells present in the body of a multicellular organism. The mitosis is divided into four phases, i.e., prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
In the prophase stage, the genetic material condenses to form the chromatids. These chromatids get lined up at the equator or the metaphase plate during metaphase and the spindle fibers bind to the kinetochore present at the center of the sister chromatids. In anaphase, the sister chromatids are pulled to the opposite poles, and in telophase, the chromatids are decondensed and nuclear envelope is formed which results in two nuclei in the dividing cell.
Answer to Problem 1ACQ
Correct answer:
The correct answer is option (d) − the kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. Cohesin proteins break down and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus reforms and the cell divides.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation/justification for the correct answer:
Option (d): During early metaphase, the kinetochore attaches to the spindle fibers. The sister chromatids of the dividing cells line up at the metaphase plate. After the alignment, the spindle fibers attach to the kinetochore. The sister chromatids are bound together with the help of cohesin. After the alignment of the sister chromatids at the metaphase plate, the cohesin breaks and the sister chromatid separate and move to the opposite poles. A nucleus is formed on each opposite pole and then the cytoplasmic division results in the formation of two new cells.
Explanation for the incorrect answer:
Option (a): In this option, the separation of sister chromatids is placed after the formation of a nucleus, but the formation of the nucleus takes place after the sister chromatids are separated and move to opposite poles. So, it is an incorrect option.
Option (b): In this option, the separation of the sister chromatids is placed before the lining of sister chromatids on the metaphase plate. The cohesin protein breaks after the sister chromatids are lined up on the metaphase plate, which causes the breaking of sister chromatids. So, it is an incorrect option.
Option (c): In this option, it is said that the kinetochore is attached to the cohesin protein, but the kinetochore actually gets attached to the spindle fibers. So, it is an incorrect answer.
During metaphase, the mitotic spindle binds to the kinetochore and causes the alignment of sister chromatids on metaphase plate and the cohesin breaks which results in separation of the sister chromatids. The sister chromatids are then pulled to the opposite pole, where the new nucleus is formed followed by cytokinesis. In this way the two new cells from one existing cell are formed. Hence, option (d) is the correct answer.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Concepts of Biology
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
- 22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forwardWhat is the label ?arrow_forwardCan you described the image? Can you explain the question as well their answer and how to get to an answer to an problem like this?arrow_forward
- Describe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardWhat are the functions of the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





