
Concept explainers
LO2 19 Interest Rate Risk. Both Bond Bill and Bond Ted have 6.2 percent coupons, make semiannual payments, and are priced at par value. Bond Bill has 5 years to maturity, whereas Bond Ted has 25 years to maturity. If interest rates suddenly rise by 2 percent, what is the percentage change in the price of Bond Bill? Of Bond Ted? Both bonds have a par value of $1,000. If rates were to suddenly fall by 2 percent instead, what would the percentage change in the price of Bond Bill be then? Of Bond Ted? Illustrate your answers by graphing
To determine: The percentage change in bond price.
Introduction:
A bond refers to the debt securities issued by the governments or corporations for raising capital. The borrower does not return the face value until maturity. However, the investor receives the coupons every year until the date of maturity.
Bond price or bond value refers to the present value of the future cash inflows of the bond after discounting at the required rate of return.
Answer to Problem 19QP
The percentage change in bond price is as follows:
| Yield to maturity | Bond B | Bond T |
| 4.2% | 8.94% | 30.77% |
| 8.2% | (8.071%) | (21.12%) |
The interest rate risk is high for a bond with longer maturity, and the interest rate risk is low for a bond with shorter maturity period. The maturity period of Bond B is 5 years, and the maturity period of Bond T is 25 years. Hence, the Bond T’s bond price fluctuates higher than the bond price of Bond B due to longer maturity.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
There are two bonds namely Bond B and Bond T. The coupon rate of both the bonds is 6.2 percent. The bonds pay the coupons semiannually. The price of the bond is equal to its par value. Assume that the par value of both the bonds is $1,000. Bond B will mature in 5 years, and Bond T will mature in 25 years.
Formulae:
The formula to calculate the bond value:
Where,
“C” refers to the coupon paid per period
“F” refers to the face value paid at maturity
“r” refers to the yield to maturity
“t” refers to the periods to maturity
The formula to calculate the percentage change in price:
Determine the current price of Bond B:
Bond B is selling at par. It means that the bond value is equal to the face value. It also indicates that the coupon rate of the bond is equal to the yield to maturity of the bond. As the par value is $1,000, the bond value or bond price of Bond B will be $1,000.
Hence, the current price of Bond B is $1,000.
Determine the current yield to maturity on Bond B:
As the bond is selling at its face value, the coupon rate will be equal to the yield to maturity of the bond. The coupon rate of Bond B is 6.2 percent.
Hence, the yield to maturity of Bond B is 6.2 percent.
Determine the current price of Bond T:
Bond T is selling at par. It means that the bond value is equal to the face value. It also indicates that the coupon rate of the bond is equal to the yield to maturity of the bond. As the par value is $1,000, the bond value or bond price of Bond T will be $1,000.
Hence, the current price of Bond T is $1,000.
Determine the current yield to maturity on Bond T:
As the bond is selling at its face value, the coupon rate will be equal to the yield to maturity of the bond. The coupon rate of Bond T is 6.2 percent.
Hence, the yield to maturity of Bond T is 6.2 percent.
The percentage change in the bond value of Bond B and Bond T when the interest rates rise by 2 percent:
Compute the new interest rate (yield to maturity) when the interest rates rise:
The interest rate refers to the yield to maturity of the bond. The initial yield to maturity of the bonds is 6.2 percent. If the interest rates rise by 2 percent, then the new interest rate or yield to maturity will be 8.2 percent
Compute the bond value when the yield to maturity of Bond B rises to 8.2 percent:
The coupon rate of Bond B is 6.2 percent, and its face value is $1,000. Hence, the annual coupon payment is $62
The yield to maturity is 8.2 percent. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity should also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual yield to maturity is 4.1 percent
The remaining time to maturity is 5 years. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 10
Hence, the bond price of Bond B will be $919.29 when the interest rises to 8.2 percent.
Compute the percentage change in the price of Bond B when the interest rates rise to 8.2 percent:
The new price after the increase in interest rate is $919.29. The initial price of the bond was $1,000.
Hence, the percentage decrease in the price of Bond B is (8.071 percent) when the interest rates rise to 8.2 percent.
Compute the bond value when the yield to maturity of Bond T rises to 8.2 percent:
The coupon rate of Bond T is 6.2 percent, and its face value is $1,000. Hence, the annual coupon payment is $62
The yield to maturity is 8.2 percent. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity should also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual yield to maturity is 4.1 percent
The remaining time to maturity is 25 years. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 50
Hence, the bond price of Bond T will be $788.8075 when the interest rises to 8.2 percent.
Compute the percentage change in the price of Bond T when the interest rates rise to 8.2 percent:
The new price after the increase in interest rate is $788.8075. The initial price of the bond was $1,000.
Hence, the percentage decrease in the price of Bond T is (21.12 percent) when the interest rates rise to 8.2 percent.
The percentage change in the bond value of Bond B and Bond T when the interest rates decline by 2 percent:
Compute the new interest rate (yield to maturity) when the interest rates decline:
The interest rate refers to the yield to maturity of the bond. The initial yield to maturity of the bonds is 6.2 percent. If the interest rates decline by 2 percent, then the new interest rate or yield to maturity will be 4.2 percent
Compute the bond value when the yield to maturity of Bond B declines to 4.2 percent:
The coupon rate of Bond B is 6.2 percent, and its face value is $1,000. Hence, the annual coupon payment is $62
The yield to maturity is 4.2 percent. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity should also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual yield to maturity is 2.1 percent
The remaining time to maturity is 5 years. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 10
Hence, the bond price of Bond B will be $1,089.36 when the interest declines to 4.2 percent.
Compute the percentage change in the price of Bond B when the interest rates decline to 4.2 percent:
The new price after the increase in interest rate is $1,089.36. The initial price of the bond was $1,000.
Hence, the percentage increase in the price of Bond B is 8.94 percent when the interest rates decline to 4.2 percent.
Compute the bond value when the yield to maturity of Bond T declines to 4.2 percent:
The coupon rate of Bond T is 6.2 percent, and its face value is $1,000. Hence, the annual coupon payment is $62
The yield to maturity is 4.2 percent. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity should also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual yield to maturity is 2.1 percent
The remaining time to maturity is 25 years. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 50
Hence, the bond price of Bond T will be $1,307.73 when the interest declines to 4.2 percent.
Compute the percentage change in the price of Bond T when the interest rates decline to 4.2 percent:
The new price after the increase in interest rate is $1,307.73. The initial price of the bond was $1,000.
Hence, the percentage increase in the price of Bond T is 30.77 percent when the interest rates decline to 4.2 percent.
A summary of the bond prices and yield to maturity of Bond B and Bond T:
Table 1
|
Yield to maturity |
Bond B | Bond T |
| 4.2% | $1,089.36 | $1,307.73 |
| 6.2% | $1,000.00 | $1,000.00 |
| 8.2% | $919.29 | $788.81 |
A graph indicating the relationship between bond prices and yield to maturity based on Table 1:
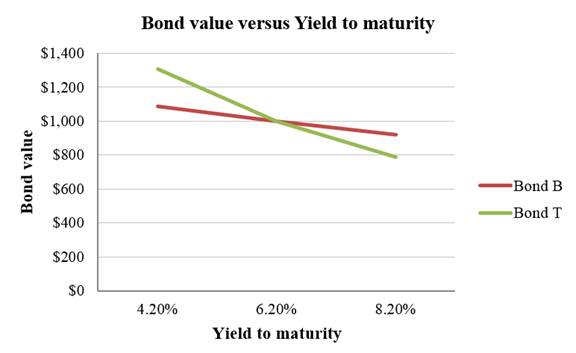
Interpretation of the graph:
The above graph indicates that the price fluctuation is higher in a bond with higher maturity. Bond T has a maturity period of 25 years. As its maturity period is longer, its price sensitivity to the interest rates is higher. Bond B has a maturity period of 5 years. As its maturity period is shorter, its price sensitivity to the interest rates is lower. Hence, a bond with longer maturity is subject to higher interest rate risk.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
ESSENTIALS CORPORATE FINANCE + CNCT A.
- No aiarrow_forwardList and discuss the various values for bonds discussed in the chapter. Additionally, explain in detail what is meant by "Yield to Maturity".arrow_forwardProvide Answer of This Financial Accounting Question And Please Don't Use Ai Becouse In all Ai give Wrong Answer. And Provide All Question Answer If you will use AI will give unhelpful.arrow_forward
- You plan to save $X per year for 6 years, with your first savings contribution in 1 year. You and your heirs then plan to withdraw $43,246 per year forever, with your first withdrawal expected in 7 years. What is X if the expected return per year is 18.15 percent per year? Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. 59 $arrow_forwardAre there assets for which a value might be considered to be hard to determine?arrow_forwardYou plan to save $X per year for 7 years, with your first savings contribution in 1 year. You and your heirs then plan to make annual withdrawals forever, with your first withdrawal expected in 8 years. The first withdrawal is expected to be $43,596 and all subsequent withdrawals are expected to increase annually by 1.84 percent forever. What is X if the expected return per year is 11.34 percent per year? Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. $arrow_forward
- You plan to save $41,274 per year for 4 years, with your first savings contribution later today. You then plan to make X withdrawals of $41,502 per year, with your first withdrawal expected in 4 years. What is X if the expected return per year is 8.28 percent per year? Input instructions: Round your answer to at least 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardYou plan to save $X per year for 10 years, with your first savings contribution in 1 year. You then plan to withdraw $58,052 per year for 9 years, with your first withdrawal expected in 10 years. What is X if the expected return is 7.41 percent per year? Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. 69 $arrow_forwardYou plan to save $X per year for 7 years, with your first savings contribution later today. You then plan to withdraw $30,818 per year for 5 years, with your first withdrawal expected in 8 years. What is X if the expected return per year is 6.64 percent per year? Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. $arrow_forward
- You plan to save $24,629 per year for 8 years, with your first savings contribution in 1 year. You then plan to withdraw $X per year for 7 years, with your first withdrawal expected in 8 years. What is X if the expected return per year is 5.70 percent per year? Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. $ SAarrow_forwardYou plan to save $15,268 per year for 7 years, with your first savings contribution later today. You then plan to withdraw $X per year for 9 years, with your first withdrawal expected in 8 years. What is X if the expected return per year is 10.66 percent per year? Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar. GA $arrow_forwardYou plan to save $19,051 per year for 5 years, with your first savings contribution in 1 year. You then plan to make X withdrawals of $30,608 per year, with your first withdrawal expected in 5 years. What is X if the expected return per year is 14.61 percent per year? Input instructions: Round your answer to at least 2 decimal places.arrow_forward
