
Concept explainers
To determine: The bond’s price at different periods.
Introduction:
A bond refers to the debt securities issued by the governments or corporations for raising capital. The borrower does not return the face value until maturity. However, the investor receives the coupons every year until the date of maturity.
Bond price or bond value refers to the present value of the future cash inflows of the bond after discounting at the required rate of return.
Answer to Problem 18QP
The price of the bond at different periods is as follows:
|
Time to maturity (Years) |
Bond X | Bond Y |
| 13 | $1,126.6776 | $883.3285 |
| 12 | $1,120.4378 | $888.5195 |
| 10 | $1,106.5930 | $900.2923 |
| 5 | $1,062.3745 | $939.9184 |
| 1 | $1,014.2477 | $985.9048 |
| 0 | $1,000.0000 | $1,000.0000 |
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Bond X is selling at a premium. The coupon rate of Bond X is 8.5 percent and its yield to maturity is 7 percent. The bond will mature in 13 years. Bond Y is selling at a discount. The coupon rate of Bond Y is 7 percent and its yield to maturity is 8.5 percent. The bond will mature in 13 years. Both the bonds make semiannual coupon payments. Assume that the face value of bonds is $1,000.
The formula to calculate annual coupon payment:
The formula to calculate the current price of the bond:
Where,
“C” refers to the coupon paid per period
“F” refers to the face value paid at maturity
“r” refers to the yield to maturity
“t” refers to the periods to maturity
Compute the bond price of Bond X at different maturities:
Compute the annual coupon payment of Bond X:
Hence, the annual coupon payment of Bond X is $85.
The bond value or the price of Bond X at present:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $85. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $42.50
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 13 years. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 26
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 3.50 percent
Hence, the current price of the bond is $1,126.6776.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after one year:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $85. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $42.50
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 12 years after one year from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 24
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 3.50 percent
Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,120.4378 after one year.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after 3 years:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $85. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $42.50
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 10 years after three years from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 20
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 3.50 percent
Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,106.5930 after three years.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after eight years:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $85. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $42.50
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 5 years after eight years from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 10
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 3.50 percent
Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,062.3745 after eight years.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after twelve years:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $85. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $42.50
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is one year after twelve years from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are two
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 7 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 3.50 percent
Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,014.2477 after twelve years.
The bond value or the price of Bond X after thirteen years:
The thirteenth year is the year of maturity for Bond X. In this year, the bondholder will receive the face value of the bond. Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,000 after thirteen years.
Compute the bond price of Bond Y at different maturities:
Compute the annual coupon payment of Bond Y:
Hence, the annual coupon payment of Bond Y is $70.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y at present:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $35
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 13 years. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 26
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 8.5 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 4.25 percent
Hence, the current price of the bond is $883.3285.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after one year:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $35
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 12 years after one year from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 24
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 8.5 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 4.25 percent
Hence, the price of the bond is $888.5195 after one year.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after three years:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $35
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 10 years after three years from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 20
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 8.5 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 4.25 percent
Hence, the price of the bond is $900.2923 after three years.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after eight years:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $35
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is 5 years after three years from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are 10
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 8.5 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 4.25 percent
Hence, the price of the bond is $939.9184 after eight years.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after twelve years:
The bond pays the coupons semiannually. The annual coupon payment is $70. However, the bondholder will receive the same is two equal installments. Hence, semiannual coupon payment or the 6-month coupon payment is $35
Secondly, the remaining time to maturity is one year after twelve years from now. As the coupon payment is semiannual, the semiannual periods to maturity are two
Thirdly, the yield to maturity is 8.5 percent per year. As the calculations are semiannual, the yield to maturity must also be semiannual. Hence, the semiannual or 6-month yield to maturity is 4.25 percent
Hence, the price of the bond is $985.9048 after twelve years.
The bond value or the price of Bond Y after thirteen years:
The thirteenth year is the year of maturity for Bond Y. In this year, the bondholder will receive the face value of the bond. Hence, the price of the bond will be $1,000 after thirteen years.
Table indicating the bond prices of Bond X and Bond Y at different maturities:
Table 1
|
Time to maturity (Years) |
Bond X | Bond Y |
| 13 | $1,126.6776 | $883.3285 |
| 12 | $1,120.4378 | $888.5195 |
| 10 | $1,106.5930 | $900.2923 |
| 5 | $1,062.3745 | $939.9184 |
| 1 | $1,014.2477 | $985.9048 |
| 0 | $1,000.0000 | $1,000.0000 |
Graphical representation of the bond prices of Bond X and Bond Y from Table 1:
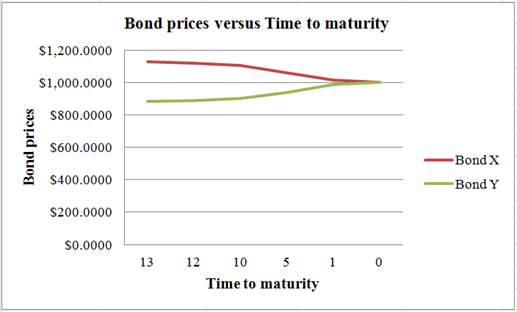
Explanation of the graph:
The graph indicates a “pull to par” effect on the prices of the bonds. The face value of both the bonds is $1,000. Although Bond X is at a premium and Bond Y is at a discount, both the bonds will reach their par values at the time of maturity. The effect of reaching the face value or par value from a discount or premium is known as “pull to par”.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Essentials of Corporate Finance (Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
- if image is blurr or data is not clear in image please comment i will write data or upload new image. Don't use chatgpt. confirm i will give unhelpful if answer with using incorrect data .arrow_forwardBright wood Seating sells reclining chairs for $55.00 per unit. The variable cost is 322 per unit. Each reclining chair requires 5 direct labor hours and 3 machine hours to produce. atribution margin pegmachine home* Wrightwood Manufacturing has a break-even point of 1,500 units. The sales price per unit is $18, and the variable cost per u 13. If the company sells 3,500 units, what will its net income be? Creatwood Industries provides the following budget data for its Processing Department for the year 2022: ⚫ Manufacturing Overhead Costs=$250,400 . Direct Labor Costs $1,234,500 Determine the manufacturing overhead application rate underthe base of Direct Labor Costs. Modesto Accessories manufactures two types of wallets leather and canvas. The company allocates manufacturing overhead using a single plant wide rate with direct labor cost as the allocation base. $48 Estimated Overhead Costs = 30,600 Direct Labor Cost per Leather Wallet Direct Labor Cost per Canvas Wallet = $52 Number of…arrow_forwardPlease don't use AI . Chatgpt giving wrong answer . confirm i will give unhelpharrow_forward
- Anti-Pandemic Pharma Co. Ltd. reports the following information inits income statement:Sales = $5,250,000;Costs = $2, 173,000;Other expenses = $187,400;Depreciation expense = $79,000;Interest expense= $53,555;Taxes = $76,000;Dividends = $69,000.$136,700 worth of new shares were also issued during the year andlong-term debt worth $65,300 was redeemed.a) Compute the cash flow from assetsb) Compute the net change in working capital Show all calculations. Please no spreadsheet so that I can clearly understandarrow_forwardAnswer this question Using the Google drive liink below it hhas the case study In the scenario, Sharp’s employer has been putting more emphasis on controlling costsfor the various businesses. With the slowing of overall spending in the construction sector,Travolta had ordered managers to closely monitor expenses. He had sold several companiesand has given vice presidents greater responsibility for statements of financial positions. Whatpositive and negative consequences might this pose to the company in future fraud prevention?Outline at least three of each type. Please use sources and insert intext citiations Apa 7 format in the answer and provide the links and references below. https://docs.google.com/document/d/1MpthrFl3eAnMKR-EprYRP9sMo8Ll0WtbhxhpGtLbdcw/edit?usp=sharingarrow_forwardfile:///C:/Users/rafan/Downloads/Assignment%201%20Paving%20Company%20Case%20S2%202024%20to%202025.pdf Using the link for the fraud case answer only this question below. b) As discussed in units 1 to 4, all frauds involve key elements. Identify and describe usingexamples, the elements of Sharp’s fraud.arrow_forward
- Option should be match experts are giving incorrect answer they are using AI /Chatgpt that is generating wrong answer. i will give unhelpful if answer will not match in option. dont use AI alsoarrow_forwardOption should be match. please don't use ai if option will not match means answer is incorrect . Ai giving incorrect answerarrow_forwardOption should be match. please don't use ai if option will not match means answer is incorrect . Ai giving incorrect answerarrow_forward
- all frauds involve key elements. Identify and describe usingexamples the elements of fraudarrow_forwardSolve for maturity value, discount period, bank discount, and proceeds. Assume a bank discount rate of 9%. Use the ordinary interest method. (Use Days in a year table.) Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to the nearest cent. face value(principal) $50000rate interest:11%length of note: 95 days maturity value: ?date of note: june 10date note discounted: July 18discount period:?bank discount:?proceeds:?arrow_forwardWhat are the different types of audits and different types of auditors? WHat is an example of each type of audit? What is the significance of each from the perspective of different stakeholders?arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





