
Concept explainers
(a).
To label: The photomicrographs in figure 6.3.
Introduction: The epithelial tissue is formed by joining the epithelial cells in the body. The epithelial cells have important functions like protecting the tissue layers and hence they are always found on the surface of the organs and tissues. The epithelial cells also act as a barrier to control the movement of molecules in-between the glands.
(a).
Answer to Problem 1.3BGL
Pictorial representation:
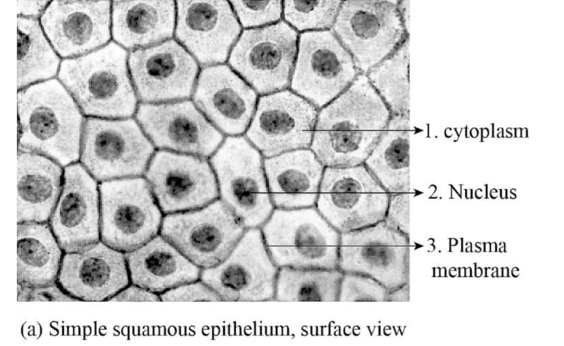
Fig.1: The figure showing simple squamous epithelial cell.
Explanation of Solution
Simple squamous epithelial cells: The simple squamous epithelial cells are a single layer of epithelial cells that are found in the alveoli in the lungs, glomerular capsule; as endothelium in the inner lining of capillaries, as mesothelium in the peritoneal cavity and mediastinum. These epithelial cells have a specific function of gaseous exchange by diffusion, secretion, filtration, absorption. The presence of single layer allows easy passage of the gases in-between the cells.
(b).
To label: The photomicrographs in figure 6.4.
(b).
Answer to Problem 1.3BGL
Pictorial representation:
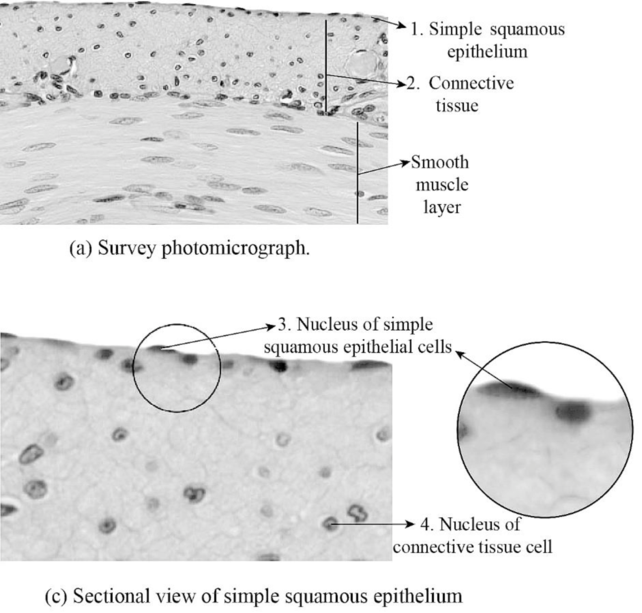
Fig.2: The figure showing sectional view of simple squamous epithelial cell.
Explanation of Solution
The cross section image of the simple squamous epithelial cells shows, smooth muscle are covered by the epithelial cells. The connective tissue forms the basement membrane for the epithelial cells to form a single layer of simple squamous epithelial cell over the smooth muscle.
(c).
To label: The photomicrographs in figure 6.5.
(c).
Answer to Problem 1.3BGL
Pictorial representation:
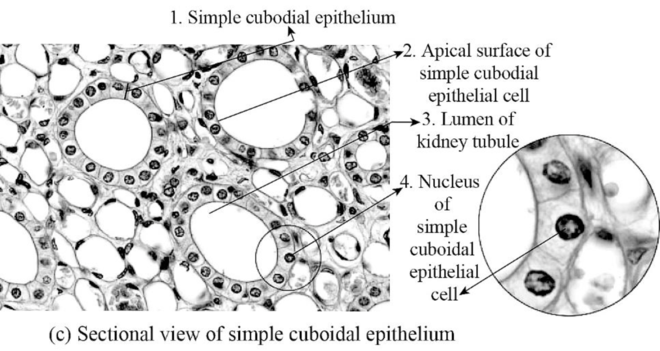
Fig.3: The figure showing simple cuboidal epithelial cell.
Explanation of Solution
Simple cuboidal epithelial cells: The simple cuboidal epithelial cells are a single layer of epithelial cells that are found in the wall of kidney tubules and glands. These epithelial cells have a specific function of absorption and secretion. These epithelial cells absorb substance from outside of the tubules and secret those substances inside the kidney tubules.
(d).
To label: The photomicrographs in figure 6.6.
(d).
Answer to Problem 1.3BGL
Pictorial representation:
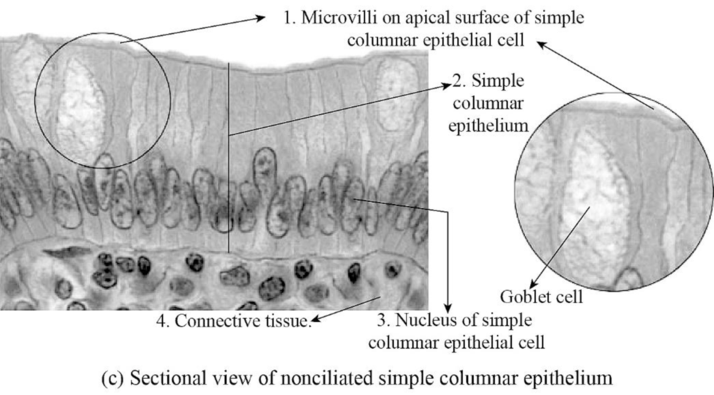
Fig.4: The figure showing simple columnar epithelial cell.
Explanation of Solution
Simple columnar epithelial cells: The simple columnar epithelial cells are a single layer of epithelial cells that are found in the lining of the stomach and intestines. These are special types of cells that are elongated and have microvilli present on them. The columnar epithelial cells have special functions like secreting digestive juices and absorption by increasing the surface area in the small intestine.
(e).
To label: The photomicrographs in figure 6.7.
(e).
Answer to Problem 1.3BGL
Pictorial representation:
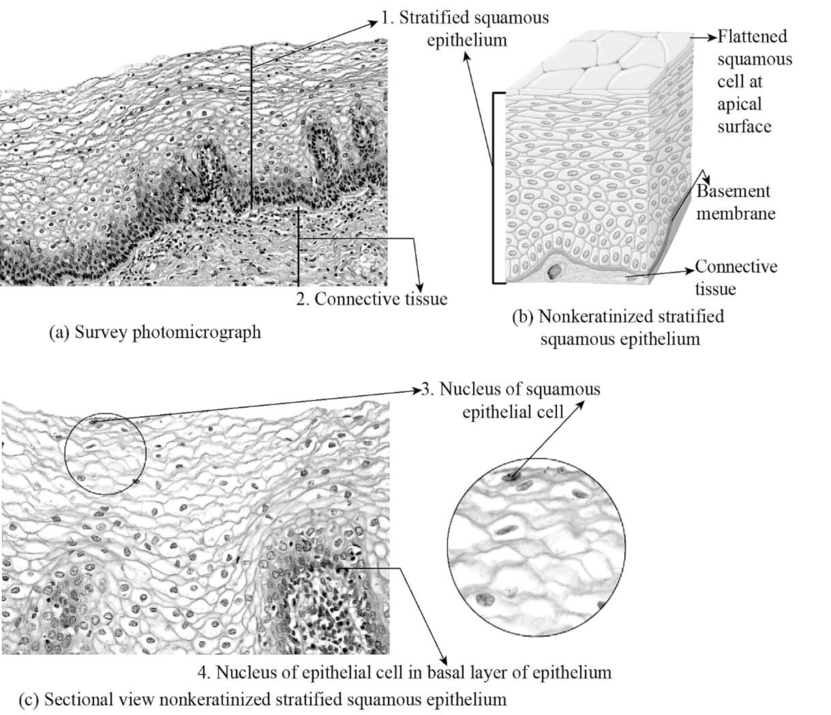
Fig.5: The figure showing stratified squamous epithelial cell.
Explanation of Solution
Stratified squamous epithelium: The stratified squamous epithelium cells are found at areas of lips, esophagus, mouth, vagina, and anus. The stratified epithelium formed by multiple layers of epithelium cells that makes surface area to be thicker, damage resistance, forms a protective barrier against friction and abrasion, and also prevent the entry of pathogens due to their tight adherence of multi-layered cells.
(f).
To label: The photomicrographs in figure 6.8.
(f).
Answer to Problem 1.3BGL
Pictorial representation:
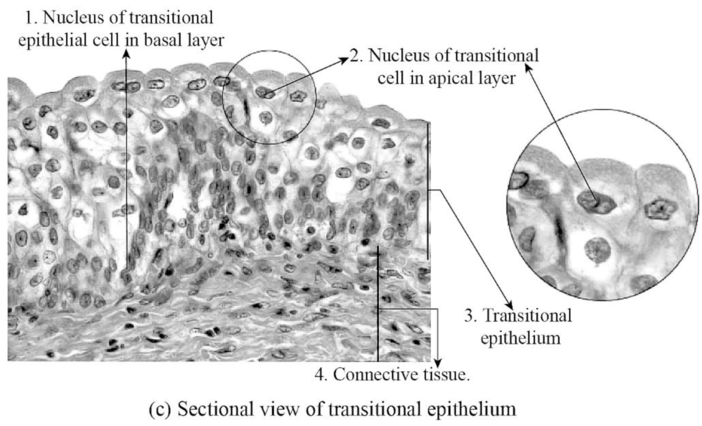
Fig.6: The figure showing transitional epithelial cell.
Explanation of Solution
Transitional epithelium cell: The transitional epithelial cells are one of the types of epithelial cells that has a special function like changing the structure of the cell. The transitional epithelial cells are found in the lining of the urinary bladder, urethra, and ureters. The function of the transitional epithelial cells is to form a protective barrier on the surface of the urinary bladder and also reduces tension.
(g).
To label: The photomicrographs in figure 6.9.
Introduction: The epithelial cell is formed by joining cells that together form layers of epithelial cells in the body. The epithelial cells have important functions like protecting the tissue layers and hence they are always found on the surface of the organs and tissues.
(g).
Answer to Problem 1.3BGL
Pictorial representation:
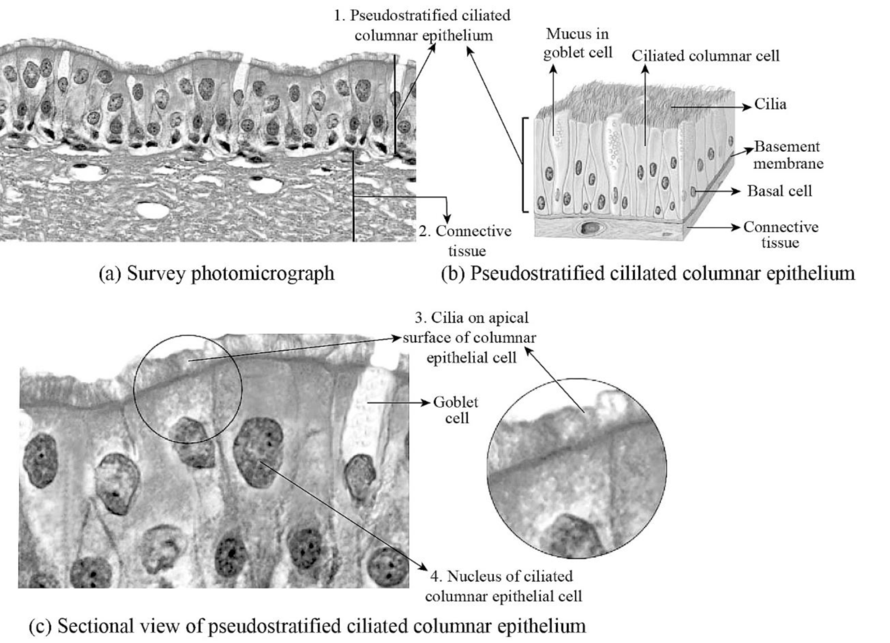
Fig.7: The figure showing pseudostratified epithelial cell.
Explanation of Solution
Pseudostratified epithelium cell: The stratified epithelium formed by multiple layers of epithelium cells that makes surface area to be thicker, damage resistance, forms a protective barrier against friction and abrasion, and also prevent the entry of pathogens. The pseudostratified epithelial cells also look like multilayer epithelium but it is a single-layered thick cell. The pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells found in the nasal cavity lining. The pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells protect the nasal cavity by secretion of mucus to trap the pathogens and dust.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK LABORATORY MANUAL FOR ANATOMY AND P
- Can you described the image? Can you explain the question as well their answer and how to get to an answer to an problem like this?arrow_forwardglg 112 mid unit assignment Identifying melting processesarrow_forwardGive only the mode of inheritance consistent with all three pedigrees and only two reasons that support this, nothing more, (it shouldn't take too long)arrow_forward
- Oarrow_forwardDescribe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
- What are the functions of the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardDescribe the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardPlease help me calculate drug dosage from the following information: Patient weight: 35 pounds, so 15.9 kilograms (got this by dividing 35 pounds by 2.2 kilograms) Drug dose: 0.05mg/kg Drug concentration: 2mg/mLarrow_forward
- A 25-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a 2-day history of fever, chills, severe headache, and confusion. She recently returned from a trip to sub-Saharan Africa, where she did not take malaria prophylaxis. On examination, she is febrile (39.8°C/103.6°F) and hypotensive. Laboratory studies reveal hemoglobin of 8.0 g/dL, platelet count of 50,000/μL, and evidence of hemoglobinuria. A peripheral blood smear shows ring forms and banana-shaped gametocytes. Which of the following Plasmodium species is most likely responsible for her severe symptoms? A. Plasmodium vivax B. Plasmodium ovale C. Plasmodium malariae D. Plasmodium falciparumarrow_forwardStandard Concentration (caffeine) mg/L Absorbance Reading 10 0.322 20 0.697 40 1.535 60 2.520 80 3.100arrow_forwardPlease draw in the missing answer, thank youarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





