
Student Solutions Manual for Zumdahl/Zumdahl/DeCoste?s Chemistry, 10th Edition
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957510
Author: ZUMDAHL, Steven S.; Zumdahl, Susan A.; DeCoste, Donald J.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 130CP
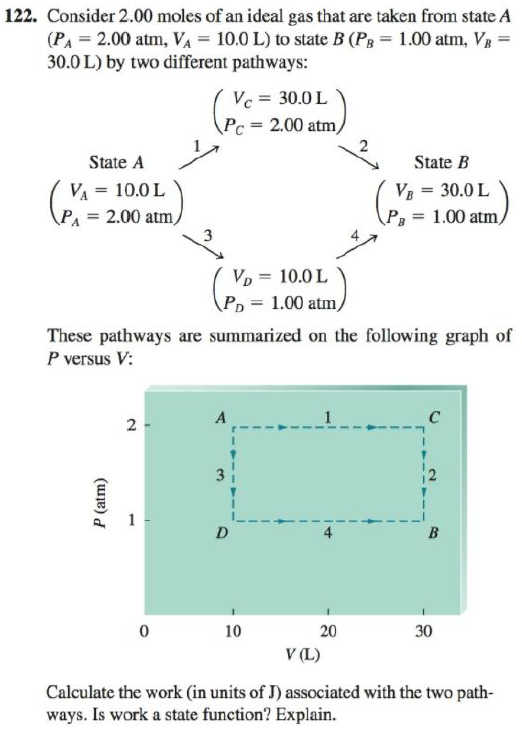
Consider 2.00 moles of an ideal gas that are taken from state A (PA = 2.00 atm, vA = 10.0 L) to state B (PB = 1.00 attn, VB = 30.0 L) by two different pathways:
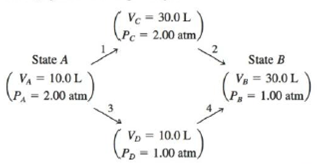
These pathways are summarized on the following graph of P versus V:
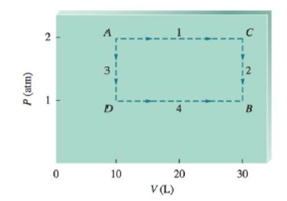
Calculate the work (in units of J) associated with the two pathways. Is work a state function? Explain.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Seee the attached ima
Please see the attached image.
Please see the attached image.
Chapter 6 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual for Zumdahl/Zumdahl/DeCoste?s Chemistry, 10th Edition
Ch. 6 - Define the following terms: potential energy,...Ch. 6 - Consider the following potential energy diagrams...Ch. 6 - What is the first law of thermodynamics? How can a...Ch. 6 - When a gas expands, what is the sign of w? Why?...Ch. 6 - What is the heat gained/released at constant...Ch. 6 - High-quality audio amplifiers generate large...Ch. 6 - Explain how calorimetry works to calculate H or E...Ch. 6 - What is Hesss law? When a reaction is reversed,...Ch. 6 - Define the standard enthalpy of formation. What...Ch. 6 - Objects placed together eventually reach the same...
Ch. 6 - What is meant by the term lower in energy? Which...Ch. 6 - A fire is started in a fireplace by striking a...Ch. 6 - Liquid water turns to ice. Is this process...Ch. 6 - Consider the following statements: ''Heat is a...Ch. 6 - Consider 5.5 L of a gas at a pressure of 3.0 atm...Ch. 6 - Consider 5.5 L of a gas at a pressure of 3.0 atm...Ch. 6 - What if energy was not conserved? How would this...Ch. 6 - Hesss law is really just another statement of the...Ch. 6 - In the equation w = P V, why is there a negative...Ch. 6 - Consider an airplane trip from Chicago, Illinois,...Ch. 6 - How is average bond strength related to relative...Ch. 6 - Assuming gasoline is pure C8H18(l), predict the...Ch. 6 - What is the difference between H and E?Ch. 6 - The enthalpy change for the reaction...Ch. 6 - Explain why oceanfront areas generally have...Ch. 6 - The equation for the fermentation of glucose to...Ch. 6 - Explain why H is obtained directly from coffee-cup...Ch. 6 - The enthalpy of combustion of CH4(g) when H2O (1)...Ch. 6 - The enthalpy change for a reaction is a state...Ch. 6 - Standard enthalpies of formation are relative...Ch. 6 - The combustion of methane can be represented as...Ch. 6 - Why is it a good idea to rinse your thermos bottle...Ch. 6 - Prob. 26QCh. 6 - What is incomplete combustion of fossil fuels? Why...Ch. 6 - Explain the advantages and disadvantages of...Ch. 6 - Prob. 29ECh. 6 - Which has the greater kinetic energy, an object...Ch. 6 - Consider the following diagram when answering the...Ch. 6 - A gas absorbs 45 kJ of heat and does 29 kJ of...Ch. 6 - Calculate E for each of the following. a. q = 47...Ch. 6 - A system undergoes a process consisting of the...Ch. 6 - If the internal energy of a thermodynamic system...Ch. 6 - Calculate the internal energy change for each of...Ch. 6 - A sample of an ideal gas at 15.0 atm and 10.0 L is...Ch. 6 - A piston performs work of 210. L atm on the...Ch. 6 - Consider a mixture of air and gasoline vapor in a...Ch. 6 - As a system increases in volume, it absorbs 52.5 J...Ch. 6 - A balloon filled with 39.1 moles of helium has a...Ch. 6 - One mole of H2O(g) at 1.00 atm and 100.C occupies...Ch. 6 - One of the components of polluted air is NO. It is...Ch. 6 - The reaction SO3(g)+H2O(l)H2SO4(aq) is the last...Ch. 6 - Are the following processes exothermic or...Ch. 6 - Are the following processes exothermic or...Ch. 6 - The overall reaction in a commercial heat pack can...Ch. 6 - Consider the following reaction:...Ch. 6 - Consider the combustion of propane:...Ch. 6 - Consider the following reaction:...Ch. 6 - For the process H2O(l) H2O(g) at 298 K and 1.0...Ch. 6 - For the following reactions at constant pressure,...Ch. 6 - Consider the substances in Table 7-1. Which...Ch. 6 - The specific heat capacity of silver is 0.24 J/Cg....Ch. 6 - A 500-g sample of one of the substances listed in...Ch. 6 - It takes 585 J of energy to raise the temperature...Ch. 6 - A 30.0-g sample of water at 280. K is mixed with...Ch. 6 - A biology experiment requires the preparation of a...Ch. 6 - A 5.00-g sample of aluminum pellets (specific heat...Ch. 6 - Hydrogen gives off 120. J/g of energy when burned...Ch. 6 - A 150.0-g sample of a metal at75.0C is added to...Ch. 6 - A 110.-g sample of copper (specific heat capacity...Ch. 6 - In a coffee-cup calorimeter, 50.0 mL of 0.100 M...Ch. 6 - In a coffee-cup calorimeter, 100.0 mL of 1.0 M...Ch. 6 - A coffee-cup calorimeter initially contains 125 g...Ch. 6 - In a coffee-cup calorimeter, 1.60 g NH4NO3 is...Ch. 6 - Consider the dissolution of CaCl2:...Ch. 6 - Consider the reaction...Ch. 6 - Quinone is an important type of molecule that is...Ch. 6 - The energy content of food is typically determined...Ch. 6 - The heat capacity of a bomb calorimeter was...Ch. 6 - The combustion of 0.1584 g benzoic acid increases...Ch. 6 - The enthalpy of combustion of solid carbon to form...Ch. 6 - Combustion reactions involve reacting a substance...Ch. 6 - Given the following data calculate H for the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 78ECh. 6 - The bombardier beetle uses an explosive discharge...Ch. 6 - Calculate H for the reaction...Ch. 6 - Given the following data...Ch. 6 - Given the following data...Ch. 6 - Give the definition of the standard enthalpy of...Ch. 6 - Write reactions for which the enthalpy change will...Ch. 6 - Use the values ofHf in Appendix 4 to calculate H...Ch. 6 - Use the values of Hf in Appendix 4 to calculate H...Ch. 6 - The Ostwald process for the commercial production...Ch. 6 - Calculate H for each of the following reactions...Ch. 6 - The reusable booster rockets of the space shuttle...Ch. 6 - The space shuttle Orbiter utilizes the oxidation...Ch. 6 - Consider the reaction...Ch. 6 - The standard enthalpy of combustion of ethene gas,...Ch. 6 - Water gas is produced from the reaction of steam...Ch. 6 - Syngas can be burned directly or converted to...Ch. 6 - Ethanol (C2H5OH) has been proposed as an...Ch. 6 - Methanol (CH3OH) has also been proposed as an...Ch. 6 - Some automobiles and buses have been equipped to...Ch. 6 - Acetylene (C2H2) and butane (C4H10) are gaseous...Ch. 6 - Prob. 99ECh. 6 - The complete combustion of acetylene, C2H2(g),...Ch. 6 - It has been determined that the body can generate...Ch. 6 - One way to lose weight is to exercise! Walking...Ch. 6 - Three gas-phase reactions were run in a...Ch. 6 - Nitrogen gas reacts with hydrogen gas to form...Ch. 6 - Combustion of table sugar produces CO2(g) and H2O(...Ch. 6 - Prob. 106AECh. 6 - A serving size of six cookies contains 4 g of fat,...Ch. 6 - Calculate H for the reaction...Ch. 6 - The enthalpy of neutralization for the reaction of...Ch. 6 - Given the following data: NO2(g) NO(g) + O(g)H =...Ch. 6 - If a student performs an endothermic reaction in a...Ch. 6 - In a bomb calorimeter, the reaction vessel is...Ch. 6 - The bomb calorimeter in Exercise 102 is filled...Ch. 6 - Consider the two space shuttle fuel reactions in...Ch. 6 - Consider the following equations:...Ch. 6 - Given the following data...Ch. 6 - At 298 K, the standard enthalpies of formation for...Ch. 6 - Using the following data, calculate the standard...Ch. 6 - A sample of nickel is heated to 99.8C and placed...Ch. 6 - Given: 2Cu2O(s) + O2(g) 4CuO(s)H = 288 kJ Cu2O(s)...Ch. 6 - Calculate H for each of the following reactions,...Ch. 6 - Consider a balloon filled with helium at the...Ch. 6 - In which of the following systems is(are) work...Ch. 6 - Which of the following processes are exothermic?...Ch. 6 - Consider the reaction...Ch. 6 - A swimming pool, 10.0 m by 4.0 m, is filled with...Ch. 6 - In a coffee-cup calorimeter, 150.0 mL of 0.50 M...Ch. 6 - Calculate H for the reaction...Ch. 6 - Which of the following substances have an enthalpy...Ch. 6 - Consider 2.00 moles of an ideal gas that are taken...Ch. 6 - For the process H2O(l)H2O(g) at 298 K and 1.0 atm,...Ch. 6 - The sun supplies energy at a rate of about 1.0...Ch. 6 - The best solar panels currently available are...Ch. 6 - On Easter Sunday, April 3, 1983, nitric acid...Ch. 6 - A piece of chocolate cake contains about 400...Ch. 6 - The standard enthalpies of formation for S(g),...Ch. 6 - You have a l.00-mole sample of water at 30.C and...Ch. 6 - A 500.0-g sample of an element at 195C is dropped...Ch. 6 - When 1.00 L of 2.00 M Na2SO4 solution at 30.0c is...Ch. 6 - The preparation of NO2(g) from N2(g) and O2(g) is...Ch. 6 - Nitromethane, CH3NO2, can be used as a fuel. When...Ch. 6 - A cubic piece of uranium metal (specific heat...Ch. 6 - A gaseous hydrocarbon reacts completely with...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- V Biological Macromolecules Drawing the Haworth projection of an aldose from its Fischer projection Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H C=O HO H HO H H OH CH₂OH Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forward
- 8 00 6 = 10 10 Decide whether each of the molecules in the table below is stable, in the exact form in which it is drawn, at pH = 11. If you decide at least one molecule is not stable, then redraw one of the unstable molecules in its stable form below the table. (If more than unstable, you can pick any of them to redraw.) Check OH stable HO stable Ounstable unstable O OH stable unstable OH 80 F6 F5 stable Ounstable X Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C ཀྭ་ A F7 매 F8 F9 4 F10arrow_forwardJust try completing it and it should be straightforward according to the professor and TAs.arrow_forwardThe grading is not on correctness, so if you can just get to the correct answers without perfectionism that would be great. They care about the steps and reasoning and that you did something. I asked for an extension, but was denied the extension.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning


General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Laws of Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Gibbs Free Energy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N1BxHgsoOw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY