
Concept explainers
a.
To calculate: The zeros of the function
a.
Answer to Problem 42PPS
The zeros of the function
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The function
Formula used:
A polynomial of n degree has n zeros, which can be either real or imaginary.
Descartes’ rule of signs states that consider a polynomial
Calculation:
Consider the function
Observe that degree of polynomial is 3, so the functions has 3 zeros which can be either real or imaginary.
Descartes’ rule of signs states that consider a polynomial
So, count the number of times the sign changes between the coefficients of
There is 1 positive real zeros.
Now,
Descartes’ rule of signs states that consider a polynomial
So, count the number of times the sign changes between the coefficients of
There are 2 or 0 negative real zero.
Next, construct a table with possible combinations of real and imaginary zeros.
Recall that the Rational zero theorem states that provided a polynomial
For the provided function leading coefficient is 2 and constant term is 3 Therefore, p is a factor of 3 and q is a factor of 2.
The possible combinations of
Next, construct a table with help of synthetic substitution to compute the value of
As observed three zeros are resulted at
Thus, the zeros of the function
Consider the function
Observe that degree of polynomial is 3, so the functions has 3 zeros which can be either real or imaginary.
Descartes’ rule of signs states that consider a polynomial
So, count the number of times the sign changes between the coefficients of
There are 2 or 0 positive real zeros.
Now,
Descartes’ rule of signs states that consider a polynomial
So, count the number of times the sign changes between the coefficients of
There is 1 negative real zero.
Next, construct a table with possible combinations of real and imaginary zeros.
Recall that the Rational zero theorem states that provided a polynomial
For the provided function leading coefficient is 2 and constant term is 3 Therefore, p is a factor of 3 and q is a factor of 2.
The possible combinations of
Next, construct a table with help of synthetic substitution to compute the value of
As observed three zeros are resulted at
Thus, the zeros of the function
b.
To describe: The function among
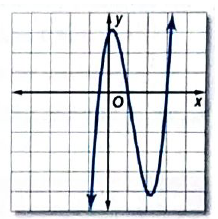
b.
Answer to Problem 42PPS
The function represented by graph is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The functions
Consider the graph provided below,
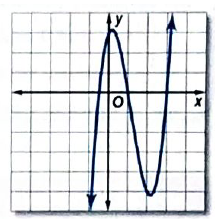
Observe the points at which the graph intersects the x -axis.
Such points are
This means the zeroes of the function depicted by the graph are
From the above calculations the function
Therefore, the graph of the function represented by graph is
Chapter 5 Solutions
Glencoe Algebra 2 Student Edition C2014
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- A research study in the year 2009 found that there were 2760 coyotes in a given region. The coyote population declined at a rate of 5.8% each year. How many fewer coyotes were there in 2024 than in 2015? Explain in at least one sentence how you solved the problem. Show your work. Round your answer to the nearest whole number.arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions related to the following matrix A = 3 ³).arrow_forwardExplain the following termsarrow_forward
- Solve questions by Course Name (Ordinary Differential Equations II 2)arrow_forwardplease Solve questions by Course Name( Ordinary Differential Equations II 2)arrow_forwardInThe Northern Lights are bright flashes of colored light between 50 and 200 miles above Earth. Suppose a flash occurs 150 miles above Earth. What is the measure of arc BD, the portion of Earth from which the flash is visible? (Earth’s radius is approximately 4000 miles.)arrow_forward
- e). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forwardSuppose you flip a fair two-sided coin four times and record the result. a). List the sample space of this experiment. That is, list all possible outcomes that could occur when flipping a fair two-sided coin four total times. Assume the two sides of the coin are Heads (H) and Tails (T).arrow_forwarde). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





