
Concept explainers
(a)
The value of angle E and angle F in the given figure.
Answer to Problem 27A
The angle E and angle F are equal to
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given value angle 1 is
The given value angle 2 is
Given figure is
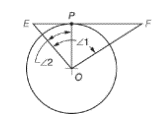
Calculation:
The point P on the circle is the tangent point. Thus, the straight-line EF becomes tangent to the circle. The line joining center and the tangent point is perpendicular to the tangent. In other words, the angle EPO or the angle OPF is 90o.
In triangle OPE,
The value of angle E is
Now, let us calculate the value of angle F. The value of angle F can be calculated by considering triangle OPF.
Now, the angle
The value of angle F is
Now, the angle E and angle F are equal to
Conclusion:
Thus, the angle E and angle F are equal to
(b)
The value of angle E and angle F in the given figure.
Answer to Problem 27A
The angle E and angle F are equal to
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given value angle 1 is
The given value angle 2 is
Given figure is
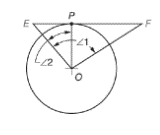
Calculation:
The point P on the circle is the tangent point. Thus, the straight-line EF becomes tangent to the circle. The line joining center and the tangent point is perpendicular to the tangent. In other words, the angle EPO or the angle OPF is 90o.
In triangle OPE,
The value of angle E is
Now, let us calculate the value of angle F. The value of angle F can be calculated by considering triangle OPF.
Now, the angle
The value of angle F is
Now, the angle E and angle F are equal to
Conclusion:
Thus, the angle E and angle F are equal to
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 55 Solutions
EBK MATHEMATICS FOR MACHINE TECHNOLOGY
- ם Hwk 25 Hwk 25 - (MA 244-03) (SP25) || X Answered: [) Hwk 25 Hwk 28 - (X + https://www.webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/last?dep=36606604 3. [1.14/4 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES LARLINALG8 6.4.013. Let B = {(1, 3), (-2, -2)} and B' = {(−12, 0), (-4, 4)} be bases for R², and let 42 - [13] A = 30 be the matrix for T: R² R² relative to B. (a) Find the transition matrix P from B' to B. 6 4 P = 9 4 (b) Use the matrices P and A to find [v] B and [T(V)] B, where [v]B[31]. 26 [V] B = -> 65 234 [T(V)]B= -> 274 (c) Find P-1 and A' (the matrix for T relative to B'). -1/3 1/3 - p-1 = -> 3/4 -1/2 ↓ ↑ -1 -1.3 A' = 12 8 ↓ ↑ (d) Find [T(v)] B' two ways. 4.33 [T(v)]BP-1[T(v)]B = 52 4.33 [T(v)]B' A'[V]B' = 52 目 67% PREVIOUS ANSWERS ill ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHERarrow_forward[) Hwk 25 Hwk 28 - (MA 244-03) (SP25) || X Success Confirmation of Questic X + https://www.webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/submit?dep=36606607&tags=autosave#question 384855 DETAILS MY NOTES LARLINALG8 7.2.001. 1. [-/2.85 Points] Consider the following. -14 60 A = [ -4-5 P = -3 13 -1 -1 (a) Verify that A is diagonalizable by computing P-1AP. P-1AP = 具首 (b) Use the result of part (a) and the theorem below to find the eigenvalues of A. Similar Matrices Have the Same Eigenvalues If A and B are similar n x n matrices, then they have the same eigenvalues. (11, 12) = Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER 2. [-/2.85 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES LARLINALG8 7.2.007. For the matrix A, find (if possible) a nonsingular matrix P such that P-1AP is diagonal. (If not possible, enter IMPOSSIBLE.) P = A = 12 -3 -4 1 Verify that P-1AP is a diagonal matrix with the eigenvalues on the main diagonal. P-1AP = Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWED 80% ill จ ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER ASK YOUR…arrow_forward[) Hwk 25 → C Hwk 27 - (MA 244-03) (SP25) IN X Answered: [) Hwk 25 4. [-/4 Poir X + https://www.webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/submit?dep=36606606&tags=autosave#question3706544_6 3. [-/2.85 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES LARLINALG8 7.1.021. Find the characteristic equation and the eigenvalues (and a basis for each of the corresponding eigenspaces) of the matrix. 2 -2 5 0 3 -2 0-1 2 (a) the characteristic equation (b) the eigenvalues (Enter your answers from smallest to largest.) (1, 2, 13) = ·( ) a basis for each of the corresponding eigenspaces X1 x2 = x3 = Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWER 4. [-/2.85 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES LARLINALG8 7.1.041. Find the eigenvalues of the triangular or diagonal matrix. (Enter your answers as a comma-separated list.) λ= 1 0 1 045 002 Need Help? Read It ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER illarrow_forward
- [) Hwk 25 4. [-/4 Points] Hwk 25 - (MA 244-03) (SP25) || X Answered: Homework#7 | bartle X + https://www.webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/last?dep=36606604 DETAILS MY NOTES LARLINALG8 6.4.019. Use the matrix P to determine if the matrices A and A' are similar. -1 -1 12 9 '-[ ¯ ¯ ], ^ - [ _—2—2 _ ' ], ^' - [ ˜³ −10] P = 1 2 A = -20-11 A' -3-10 6 4 P-1 = Are they similar? Yes, they are similar. No, they are not similar. Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER P-1AP = 5. [-/4 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES LARLINALG8 6.4.023. Suppose A is the matrix for T: R³ - → R³ relative to the standard basis. Find the diagonal matrix A' for T relative to the basis B'. A' = -1 -2 0 A = -1 0 0 ' 0 02 B' = {(−1, 1, 0), (2, 1, 0), (0, 0, 1)} ☐☐☐ ↓ ↑ Need Help? Read It Update available →] - restart now ASK YOUR T Sync and save data { Sign In ill ↑ New tab HT New window N New private window +HP ASK YOUR T Bookmarks History Downloads > > HJ Passwords Add-ons and themes HA Print... HP Save page as... HS…arrow_forwardClarification: 1. f doesn’t have REAL roots2. f is a quadratic, so a≠0arrow_forward[J) Hwk 25 Hwk 25 - (MA 244-03) (SP25) || X Answered: Homework#7 | bartle X + https://www.webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/last?dep=36606604 1. [-/4 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES Find the matrix A' for T relative to the basis B'. LARLINALG8 6.4.003. T: R² → R², T(x, y) = (x + y, 4y), B' = {(−4, 1), (1, −1)} A' = Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWER 2. [-/4 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES LARLINALG8 6.4.007. Find the matrix A' for T relative to the basis B'. T: R³ → R³, T(x, y, z) = (x, y, z), B' = {(0, 1, 1), (1, 0, 1), (1, 1, 0)} A' = ↓ ↑ Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER 具⇧ ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER ill ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER 3. [-/4 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES LARLINALG8 6.4.013. ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHERarrow_forward
- Use Laplace transforms to solve the following heat problem: U₁ = Urr x > 0, t> 0 u(x, 0) = 10c a -X u(0,t) = 0 lim u(x,t) = 0 I7Xarrow_forwarda/ Solve the equation Laplac transfors wt = wxx W (X10)=0 w (o,t) = f (t) lim wexit) = 0 *>° t>o , to t70 848arrow_forwardQ/ Find the Fourier sine and cosine trans forms of f(x) = e-cxarrow_forward
 Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning





