
Concept explainers
a.
To graph: The given function in the given interval and approximate maximum and minimum points (to four decimal places) of the graph.
a.
Answer to Problem 96E
The approximate maximum and minimum points are:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The following function:
The following interval:
Graph:
Sketch the graph using graphing utility.
Step 1: Press WINDOW button to access the Window editor.
Step 2: Press
Step 3: Enter the expression
Step 4: Press GRAPH button to graph the function.
The graph is obtained as:
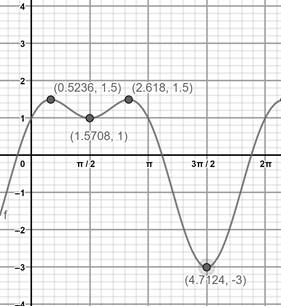
Interpretation:
Using
Maxima:
Minima:
b.
To solve: The given trigonometric equation and verify that the x-coordinates of the maximum and minimum points of
b.
Answer to Problem 96E
The solutions of the trigonometric equation are:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The following equation:
Calculation:
The given equation is solved as:
To verify if the x-coordinates of the maximum and minimum points of
Graph:
Sketch the graph using graphing utility.
Step 1: Press WINDOW button to access the Window editor.
Step 2: Press
Step 3: Enter the expressions
Step 4: Press GRAPH button to graph the function.
The graph is obtained as:
Interpretation:
The x-coordinates of the trigonometric function(
Chapter 5 Solutions
Precalculus with Limits: A Graphing Approach
- A 20 foot ladder rests on level ground; its head (top) is against a vertical wall. The bottom of the ladder begins by being 12 feet from the wall but begins moving away at the rate of 0.1 feet per second. At what rate is the top of the ladder slipping down the wall? You may use a calculator.arrow_forwardExplain the focus and reasons for establishment of 12.4.1(root test) and 12.4.2(ratio test)arrow_forwarduse Integration by Parts to derive 12.6.1arrow_forward
- Explain the relationship between 12.3.6, (case A of 12.3.6) and 12.3.7arrow_forwardExplain the key points and reasons for the establishment of 12.3.2(integral Test)arrow_forwardUse 12.4.2 to determine whether the infinite series on the right side of equation 12.6.5, 12.6.6 and 12.6.7 converges for every real number x.arrow_forward
- use Corollary 12.6.2 and 12.6.3 to derive 12.6.4,12.6.5, 12.6.6 and 12.6.7arrow_forwardExplain the focus and reasons for establishment of 12.5.1(lim(n->infinite) and sigma of k=0 to n)arrow_forwardExplain the focus and reasons for establishment of 12.5.3 about alternating series. and explain the reason why (sigma k=1 to infinite)(-1)k+1/k = 1/1 - 1/2 + 1/3 - 1/4 + .... converges.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





