
a.
ToDraw:An acute
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given:The relation among three points of concurrency in a triangle.
An acute triangle whose all three
Below is figure of acute triangle.
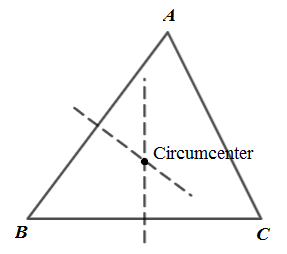
Circumcenter: It is point of intersection of perpendicular bisector of each sides. As shown in below figure.
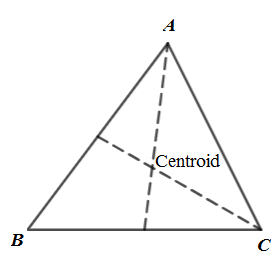
Centroid: It is intersection of medians of triangle. As shown in below figure.
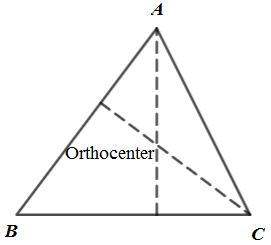
Orthocenter: It is intersetion point of altitudes of a triangle.
b.
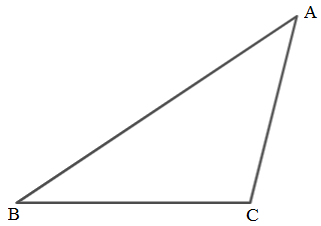
To Draw: An obstude triangle and find the circumcenter, centroid and orthocenter.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Given:The relation among three points of concurrency in a triangle.
An obtude triangle whose one angle is obtuse. An obtude angle is greater than
Below is figure of obtuse triangle.
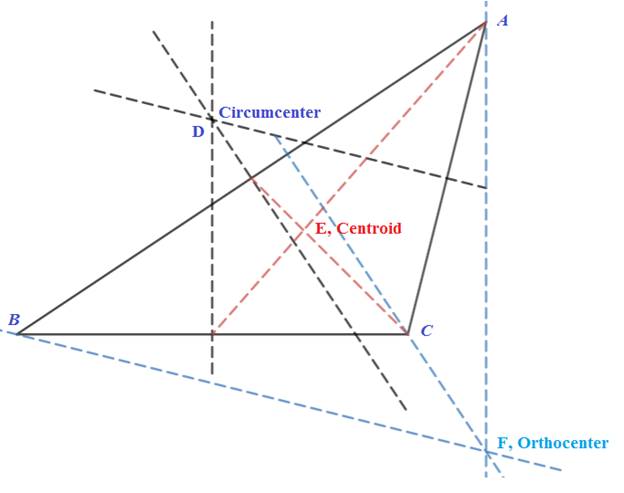
Circumcenter: It is point of intersection of perpendicular bisector of each sides. As shown in below figure.
Centroid: It is intersection of medians of triangle. As shown in below figure.
Orthocenter: It is intersetion point of altitudes of a triangle.
c.
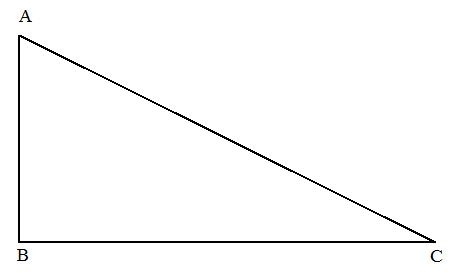
To Draw:Anright triangle and find the circumcenter, centroid and orthocenter.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Given:The relation among three points of concurrency in a triangle.
An right triangle whose one angle is right.
Below is figure of right triangle.
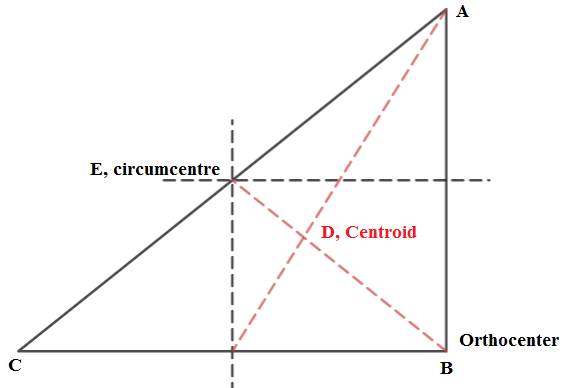
Circumcenter: It is point of intersection of perpendicular bisector of each sides. As shown in below figure.
Centroid: It is intersection of medians of triangle. As shown in below figure.
Orthocenter: It is intersetion point of altitudes of a triangle.
d.
To explain:The conjecture of all three centers.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Given:The relation among three points of concurrency in a triangle.
Circumcenter: It is point of intersection of perpendicular bisector of each sides. As shown in below figure.
Centroid: It is intersection of medians of triangle. As shown in below figure.
Orthocenter: It is intersetion point of altitudes of a triangle.
In acute triangle all three centre lie inside the triangle.
In obtuse triangle orthocenter and circumcenter lie outside the triangle. Centroid lie inside the triangle.
In right triangle circumcenter lie on hypotenuse and orthocenter is opposite vertex of hypotenuse of triangle. Centroid lie inside the triangle.
Chapter 5 Solutions
Glencoe Geometry Student Edition C2014
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- A. 90.6 square meters B. 91.4 square meters C. 92.5 square meters D. 93.7 square metersarrow_forwardAn ice cream cone is 10cm deep and 4cm across the opening of the cone. Two sphere-shaped scoops of ice cream, which also have diameters of 4cm, are placed on top of the cone. Use π≈3.14 and round your answers to the nearest hundredth.a) What is the volume of the cone? cubic centimetersb) What is the total volume of the two sphere-shaped scoops of ice cream? cubic centimetersarrow_forwardFind mSWarrow_forward
- Select all solids for which the formula V = Bh applies. A. a triangular prism B. a triangular pyramid C. a square pyramid D. a rectangular prism E. a cone F. a cylinderarrow_forwardThis is my h/w ,Required to find the region of shaded sector ,I don't really know how to deal with this tasks ,so if someone could help me to understand them it would be awesome,and sorry for my poor Englisharrow_forward△DEF△DEF has vertices D(0, 2) and F(6, 2). If △DEF△DEF has an area of 12 square units, select all the possible coordinates for E.arrow_forward
- In quadrilateral QRST, m<R=60, m<T=90, QR=RS, ST=8, TQ=8 How long is the longer diagonal of QRST? Find the ratio of RT to QS.arrow_forward13:26 ... ← Robert F. Blitzer - Thinkin... 0,04 61 KB/d 目 polygons to create a fraudulent tessellation with discrepancies that are too subtle for the eye to notice. In Exercises 45-46, you will use mathematics, not your eyes, to observe the irregularities. B A 45. Find the sum of the angle measures at vertex A. Then explain why the tessellation is a fake. 46. Find the sum of the angle measures at vertex B. Then explain why the tessellation is a fake. =et at If se Fic SECTION 10.3 Polygons, Perimeter, and Tessellations 645 61. I find it helpful to think of a polygon's perimeter as the length of its boundary. 62. If a polygon is not regular, I can determine the sum of the measures of its angles, but not the measure of any one of its angles. 63. I used floor tiles in the shape of regular pentagons to completely cover my kitchen floor. In Exercises 64-65, write an algebraic expression that represents the perimeter of the figure shown. is be 64. le a b C 2/ If se nyarrow_forwardSchoology → C Cportsk12.com bookmarks Sis Grades and Attendance Al Detector - the Original Al Che X GPTZero + portsmouth.schoology.com/common-assessment-delivery/start/7747152192?action=onresume&submissionId=1600790102 New Tab Home | Schoology Quadrilateral Quiz English If WXYZ is a square, and WY = 32, find XY. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. Z XY = R X Y POSSIBLE POINTS: 5 2 of 20 48 21 1 2 345678910 Next ▸ Δ ㄖㄨ All Bookmarks Schoology Help Center | PRIVACY POLICY | Terms of Use PowerSchool ©2025arrow_forward
- om nearest tenth if necessary. milsum 3. છે. 9.3mm 3mm A 78-43-92 4-3) 11.7 of 72.04-11.7-= lygons 7.8 mi 60.94 blants" 9 om 6. 4.15-7 16- 32m 1.8m 4.5m % ose 4.5m as to 65m 14 represents 5 square meters.arrow_forwardThe diagonals of rhombus ABCD intersect at E. Given that BAC=53 degrees, DE=8, and EC=6 find AEarrow_forwardVolume of Dubai Cayan Towerarrow_forward
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

