
Concept explainers
a.
Find the
a.
Answer to Problem 37E
The probability that exactly 6 of the adults have hypertension is 0.1472.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
It was found that 30% of the adults have hypertension. A random sample of 25 adults is considered.
Define the random variable X as the number of adults who have hypertension. Here, a random sample (n) of 25 adults is taken. Each adult is independent of the other. Also, there are two possible outcomes, the adult have hypertension or not (success or failure). It was found that 30% of the adults have hypertension. Thus, the probability of success (p) is 0.30. Hence, X follows binomial distribution.
The probability of obtaining x successes in n independent trails of a binomial experiment is,
Where, p is the probability of success.
Substitute
The probability that exactly 6 of them have hypertension is,
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the probability using MINITAB software is given below:
- Choose Calc > Probability Distributions > Binomial Distribution.
- Choose Probability.
- Enter Number of trials as 25 and
Event probability as 0.30. - In Input constant, enter 6.
- Click OK.
The output using the Minitab software is given below:
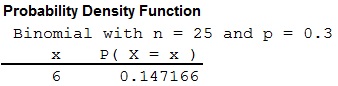
From the Minitab output, the probability value is approximately 0.1472.
Thus, the probability that exactly 6 of the adults have hypertension is 0.1472.
b.
Find the probability that more than 8 of the adults have hypertension.
b.
Answer to Problem 37E
The probability that more than 8 of the adults have hypertension is 0.3231.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The probability that more than 8 of the adults have hypertension is obtained as shown below:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the probability
- Choose Calc > Probability Distributions > Binomial Distribution.
- Choose Cumulative Probability.
- Enter Number of trials as 25 and Event probability as 0.30.
- In Input constant, enter 8.
- Click OK.
The output using the Minitab software is given below:

From the Minitab output, the probability value is approximately 0.6769. Substituting the value, the required probability becomes,
Thus, the probability that more than 8 of the adults have hypertension is 0.3231.
c.
Find the probability that fewer than 4 of the adults have hypertension.
c.
Answer to Problem 37E
The probability that fewer than 4 of the adults have hypertension is 0.0332.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The probability that fewer than 4 of the adults have hypertension is obtained as shown below:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the probability
- Choose Calc > Probability Distributions > Binomial Distribution.
- Choose Cumulative Probability.
- Enter Number of trials as 25 and Event probability as 0.30.
- In Input constant, enter 3.
- Click OK.
The output using the Minitab software is given below:

From the Minitab output, the probability value is approximately 0.0332.
Thus, the probability that fewer than 4 of the adults have hypertension is 0.0332.
d.
Check whether it is unusual if more than 10 of the adults have hypertension.
d.
Answer to Problem 37E
No, it is not unusual if more than 10 of the adults have hypertension.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Unusual:
If the probability of an event is less than 0.05 then the event is called unusual.
The probability that more than 10 of the adults have hypertension is obtained as shown below:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the probability
- Choose Calc > Probability Distributions > Binomial Distribution.
- Choose Cumulative Probability.
- Enter Number of trials as 25 and Event probability as 0.30.
- In Input constant, enter 10.
- Click OK.
The output using the Minitab software is given below:

From the Minitab output, the probability value is 0.9022. The required probability is,
Here, the probability of the event is not less than 0.05. Thus, the event that more than10 of the adults have hypertension is not unusual.
e.
Find the mean number of adults who have hypertension in a sample of 25 adults.
e.
Answer to Problem 37E
The mean number of adults who have hypertension in a sample of 25 adults is 7.5.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
A binomial experiment with n independent trials and a probability of success p has mean,
Substitute the values 25 for n and 0.30 for p,
The mean is,
Thus, the mean number of adults who have hypertension in a sample of 25 adults is 7.5.
f.
Find the standard deviation of the number adults who have hypertension in a sample of 25 adults.
f.
Answer to Problem 37E
The standard deviation of the number adults who have hypertension in a sample of 25 adults is 2.2913.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
A binomial experiment with n independent trials and a probability of success p has standard deviation,
Substitute the values 25 for n and 0.30 for p,
Thus, the standard deviation of the number adults who have hypertension in a sample of 25 adults is 2.2913.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ESSENT. STAT ACCESS CARD
- State and prove the Morton's inequality Theorem 1.1 (Markov's inequality) Suppose that E|X|" 0, and let x > 0. Then, E|X|" P(|X|> x) ≤ x"arrow_forward(iii) If, in addition, X1, X2, ... Xn are identically distributed, then P(S|>x) ≤2 exp{-tx+nt²o}}.arrow_forward5. State space models Consider the model T₁ = Tt−1 + €t S₁ = 0.8S-4+ Nt Y₁ = T₁ + S₁ + V₂ where (+) Y₁,..., Y. ~ WN(0,σ²), nt ~ WN(0,σ2), and (V) ~ WN(0,0). We observe data a. Write the model in the standard (matrix) form of a linear Gaussian state space model. b. Does lim+++∞ Var (St - St|n) exist? If so, what is its value? c. Does lim∞ Var(T₁ — Ît\n) exist? If so, what is its value?arrow_forward
- Let X represent the full height of a certain species of tree. Assume that X has a normal probability distribution with mean 203.8 ft and standard deviation 43.8 ft. You intend to measure a random sample of n = 211trees. The bell curve below represents the distribution of these sample means. The scale on the horizontal axis (each tick mark) is one standard error of the sampling distribution. Complete the indicated boxes, correct to two decimal places. Image attached. I filled in the yellow boxes and am not sure why they are wrong. There are 3 yellow boxes filled in with values 206.82; 209.84; 212.86.arrow_forwardCould you please answer this question using excel.Thanksarrow_forwardQuestions An insurance company's cumulative incurred claims for the last 5 accident years are given in the following table: Development Year Accident Year 0 2018 1 2 3 4 245 267 274 289 292 2019 255 276 288 294 2020 265 283 292 2021 263 278 2022 271 It can be assumed that claims are fully run off after 4 years. The premiums received for each year are: Accident Year Premium 2018 306 2019 312 2020 318 2021 326 2022 330 You do not need to make any allowance for inflation. 1. (a) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the basic chain ladder method. (b) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the Bornhuetter-Ferguson method. 2. Comment on the differences in the reserves produced by the methods in Part 1.arrow_forward
- Calculate the correlation coefficient r, letting Row 1 represent the x-values and Row 2 the y-values. Then calculate it again, letting Row 2 represent the x-values and Row 1 the y-values. What effect does switching the variables have on r? Row 1 Row 2 13 149 25 36 41 60 62 78 S 205 122 195 173 133 197 24 Calculate the correlation coefficient r, letting Row 1 represent the x-values and Row 2 the y-values. r=0.164 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) S 24arrow_forwardThe number of initial public offerings of stock issued in a 10-year period and the total proceeds of these offerings (in millions) are shown in the table. The equation of the regression line is y = 47.109x+18,628.54. Complete parts a and b. 455 679 499 496 378 68 157 58 200 17,942|29,215 43,338 30,221 67,266 67,461 22,066 11,190 30,707| 27,569 Issues, x Proceeds, 421 y (a) Find the coefficient of determination and interpret the result. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardQuestions An insurance company's cumulative incurred claims for the last 5 accident years are given in the following table: Development Year Accident Year 0 2018 1 2 3 4 245 267 274 289 292 2019 255 276 288 294 2020 265 283 292 2021 263 278 2022 271 It can be assumed that claims are fully run off after 4 years. The premiums received for each year are: Accident Year Premium 2018 306 2019 312 2020 318 2021 326 2022 330 You do not need to make any allowance for inflation. 1. (a) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the basic chain ladder method. (b) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the Bornhuetter-Ferguson method. 2. Comment on the differences in the reserves produced by the methods in Part 1.arrow_forward
- Use the accompanying Grade Point Averages data to find 80%,85%, and 99%confidence intervals for the mean GPA. view the Grade Point Averages data. Gender College GPAFemale Arts and Sciences 3.21Male Engineering 3.87Female Health Science 3.85Male Engineering 3.20Female Nursing 3.40Male Engineering 3.01Female Nursing 3.48Female Nursing 3.26Female Arts and Sciences 3.50Male Engineering 3.00Female Arts and Sciences 3.13Female Nursing 3.34Female Nursing 3.67Female Education 3.45Female Engineering 3.17Female Health Science 3.28Female Nursing 3.25Male Engineering 3.72Female Arts and Sciences 2.68Female Nursing 3.40Female Health Science 3.76Female Arts and Sciences 3.72Female Education 3.44Female Arts and Sciences 3.61Female Education 3.29Female Nursing 3.20Female Education 3.80Female Business 3.26Male…arrow_forwardBusiness Discussarrow_forwardCould you please answer this question using excel. For 1a) I got 84.75 and for part 1b) I got 85.33 and was wondering if you could check if my answers were correct. Thanksarrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





