
CALCULUS FULL TEXT W/ACCESS >CI<
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305770430
Author: Stewart
Publisher: CENGAGE C
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.1, Problem 53E
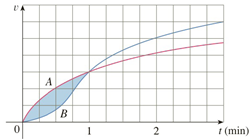
Two cars, A and B, start side by side and accelerate from rest. The figure shows the graphs of their velocity functions.
(a) Which car is ahead after one minute? Explain.
(b) What is the meaning of the area of the shaded region?
(c) Which car is ahead after two minutes? Explain.
(d) Estimate the time at which the cars are again side by side.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
3.1 Limits
1. If lim f(x)=-6 and lim f(x)=5, then lim f(x). Explain your choice.
x+3°
x+3*
x+3
(a) Is 5
(c) Does not exist
(b) is 6
(d) is infinite
1 pts
Let F and G be vector fields such that ▼ × F(0, 0, 0) = (0.76, -9.78, 3.29), G(0, 0, 0) = (−3.99, 6.15, 2.94), and
G is irrotational. Then sin(5V (F × G)) at (0, 0, 0) is
Question 1
-0.246
0.072
-0.934
0.478
-0.914
-0.855
0.710
0.262
.
2. Answer the following questions.
(A) [50%] Given the vector field F(x, y, z) = (x²y, e", yz²), verify the differential identity
Vx (VF) V(V •F) - V²F
(B) [50%] Remark. You are confined to use the differential identities.
Let u and v be scalar fields, and F be a vector field given by
F = (Vu) x (Vv)
(i) Show that F is solenoidal (or incompressible).
(ii) Show that
G =
(uvv – vVu)
is a vector potential for F.
Chapter 5 Solutions
CALCULUS FULL TEXT W/ACCESS >CI<
Ch. 5.1 - Find the area of the shaded region.Ch. 5.1 - Find the area of the shaded region.Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 3ECh. 5.1 - Find the area of the shaded region.Ch. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves....Ch. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves....Ch. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves....Ch. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves....Ch. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves....Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 10E
Ch. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves....Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 12ECh. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 14ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 15ECh. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and...Ch. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and...Ch. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 19ECh. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 21ECh. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and...Ch. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and...Ch. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and...Ch. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 26ECh. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and...Ch. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 29ECh. 5.1 - Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 31ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 32ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 33ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 34ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 35ECh. 5.1 - Evaluate the integral and interpret it as the area...Ch. 5.1 - Use a graph to find approximate x-coordinates of...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 38ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 39ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 40ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 41ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 42ECh. 5.1 - Graph the region between the curves and use your...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 44ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 45ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 46ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 47ECh. 5.1 - The widths in meters of a kidney-shaped swimming...Ch. 5.1 - A cross-section of an airplane wing is shown....Ch. 5.1 - If the birth rate of a population is...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 51ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 52ECh. 5.1 - Two cars, A and B, start side by side and...Ch. 5.1 - The figure shows graphs of the marginal revenue...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 55ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 56ECh. 5.1 - Find the number b such that the line y=b divides...Ch. 5.1 - a Find the number a such that the line x=a bisects...Ch. 5.1 - Find the values of c such that the area of the...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 60ECh. 5.1 - Sketch the region bounded by the given curves and...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 62ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 63ECh. 5.1 - For what values of m do the line y=mx and the...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 3ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 4ECh. 5.2 - Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 6ECh. 5.2 - Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 8ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 9ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 10ECh. 5.2 - Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 16ECh. 5.2 - Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating...Ch. 5.2 - Refer to the figure and find the volume generated...Ch. 5.2 - Refer to the figure and find the volume generated...Ch. 5.2 - Refer to the figure and find the volume generated...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 22ECh. 5.2 - Refer to the figure and find the volume generated...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 24ECh. 5.2 - Refer to the figure and find the volume generated...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 26ECh. 5.2 - Refer to the figure and find the volume generated...Ch. 5.2 - Refer to the figure and find the volume generated...Ch. 5.2 - Refer to the figure and find the volume generated...Ch. 5.2 - Refer to the figure and find the volume generated...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 31ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 32ECh. 5.2 - Set up an integral for the volume of the solid...Ch. 5.2 - Set up an integral for the volume of the solid...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 35ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 36ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 37ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 38ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 39ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 40ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 41ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 42ECh. 5.2 - A CAT scan produces equally spaced cross-sectional...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 44ECh. 5.2 - a If the region shown in the figure is rotated...Ch. 5.2 - a A model for the shape of a birds egg is obtained...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of the described solid S. A right...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of the described solid S. A...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of the described solid S. A cap of...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of the described solid S. A...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of the described solid S. A...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of the described solid S. A...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of described solid S. A...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of described solid S. The base of...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 55ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 56ECh. 5.2 - Find the volume of the described solid S. The base...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 58ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 59ECh. 5.2 - Find the volume of the described solid S. The base...Ch. 5.2 - Find the volume of the described solid S. The...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 62ECh. 5.2 - a Set up an integral for the volume of a solid...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 64ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 65ECh. 5.2 - Find the volume common to two circular cylinders,...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 67ECh. 5.2 - A bowl is shaped like a hemisphere with diameter...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 69ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 70ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 71ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 72ECh. 5.3 - Let S be the solid obtained by rotating the region...Ch. 5.3 - Let S be the solid obtained by rotating the region...Ch. 5.3 - Use the method of cylindrical shells to find the...Ch. 5.3 - Use the method of cylindrical shells to find the...Ch. 5.3 - Use the method of cylindrical shells to find the...Ch. 5.3 - Use the method of cylindrical shells to find the...Ch. 5.3 - Use the method of cylindrical shells to find the...Ch. 5.3 - Let V be the volume of the solid obtained by...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 9ECh. 5.3 - Use the method of cylindrical shells to find the...Ch. 5.3 - Use the method of cylindrical shells to find the...Ch. 5.3 - Use the method of cylindrical shells to find the...Ch. 5.3 - Use the method of cylindrical shells to find the...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 14ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 15ECh. 5.3 - Use the method of cylindrical shells to find the...Ch. 5.3 - Use the method of cylindrical shells to find the...Ch. 5.3 - Use the method of cylindrical shells to find the...Ch. 5.3 - Use the method of cylindrical shells to find the...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 20ECh. 5.3 - a Set up an integral for the volume of the solid...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 22ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 23ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 24ECh. 5.3 - a Set up an integral for the volume of the solid...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 26ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 27ECh. 5.3 - If the region shown in the figure is rotated about...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 29ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 30ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 31ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 32ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 33ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 34ECh. 5.3 - Use a computer algebra system to find the exact...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 36ECh. 5.3 - The region bounded by the given curves is rotated...Ch. 5.3 - The region bounded by the given curves is rotated...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 39ECh. 5.3 - The region bounded by the given curves is rotated...Ch. 5.3 - The region bounded by the given curves is rotated...Ch. 5.3 - The region bounded by the given curves is rotated...Ch. 5.3 - The region bounded by the given curves is rotated...Ch. 5.3 - Let T be the triangular region with vertices...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 45ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 46ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 47ECh. 5.3 - Suppose you make napkin rings by drilling holes...Ch. 5.4 - A 360-lb gorilla climbs a tree to a height of 20...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 2ECh. 5.4 - Prob. 3ECh. 5.4 - Prob. 4ECh. 5.4 - Prob. 5ECh. 5.4 - The table shows values of a force function f(x)...Ch. 5.4 - A force of 10 lb is required to hold a spring...Ch. 5.4 - A spring has a natural length of 40 cm. If a 60-N...Ch. 5.4 - Suppose that 2 J of work is needed to stretch a...Ch. 5.4 - If the work required to stretch a spring 1 ft...Ch. 5.4 - A spring has natural length 20 cm. Compare the...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 12ECh. 5.4 - Prob. 13ECh. 5.4 - Show how to approximate the required work by a...Ch. 5.4 - Show how to approximate the required work by a...Ch. 5.4 - Show how to approximate the required work by a...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 17ECh. 5.4 - Show how to approximate the required work by a...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 19ECh. 5.4 - Prob. 20ECh. 5.4 - Show how to approximate the required work by a...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 22ECh. 5.4 - A tank is full of water. Find the work required to...Ch. 5.4 - A tank is full of water. Find the work required to...Ch. 5.4 - A tank is full of water. Find the work required to...Ch. 5.4 - A tank is full of water. Find the work required to...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 27ECh. 5.4 - Prob. 28ECh. 5.4 - Prob. 29ECh. 5.4 - In a steam engine the pressure P and volume V of...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 31ECh. 5.4 - Prob. 32ECh. 5.4 - Prob. 33ECh. 5.4 - The Great Pyramid of King Khufu was built of...Ch. 5.5 - Find the average value of the function on the...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 2ECh. 5.5 - Prob. 3ECh. 5.5 - Prob. 4ECh. 5.5 - Find the average value of the function on the...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 6ECh. 5.5 - Find the average value of the function on the...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 8ECh. 5.5 - a Find the average value of f on the given...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 10ECh. 5.5 - a Find the average value of f on the given...Ch. 5.5 - a Find the average value of f on the given...Ch. 5.5 - If f is continuous and 13f(x)dx=8, show that f...Ch. 5.5 - Find the numbers b such that the average value of...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 15ECh. 5.5 - The velocity graph of an accelerating car is...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 17ECh. 5.5 - The velocity v of blood that flows in a blood...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 19ECh. 5.5 - If a freely falling body starts from rest, then...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 21ECh. 5.5 - Use the diagram to show that if f is concave...Ch. 5.5 - Prove that Mean value Theorem for Integrals by...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 24ECh. 5.R - a Draw two typical curves y=f(x) and y=g(x) where...Ch. 5.R - Prob. 2CCCh. 5.R - a Suppose S is a solid with known cross-sectional...Ch. 5.R - a What is the volume of a cylindrical shell? b...Ch. 5.R - Suppose that you push a book across a 6-meter-long...Ch. 5.R - Prob. 6CCCh. 5.R - Prob. 1ECh. 5.R - Prob. 2ECh. 5.R - Prob. 3ECh. 5.R - Prob. 4ECh. 5.R - Prob. 5ECh. 5.R - Prob. 6ECh. 5.R - Prob. 7ECh. 5.R - Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating...Ch. 5.R - Prob. 9ECh. 5.R - Prob. 10ECh. 5.R - Prob. 11ECh. 5.R - Set up, but do not evaluate, an integral for the...Ch. 5.R - Prob. 13ECh. 5.R - Prob. 14ECh. 5.R - Prob. 15ECh. 5.R - Let be the region in the first quadrant bounded...Ch. 5.R - Let be the region bounded by the curves...Ch. 5.R - Let be the region bounded by the curves y=1x2 and...Ch. 5.R - Prob. 19ECh. 5.R - Prob. 20ECh. 5.R - Prob. 21ECh. 5.R - Prob. 22ECh. 5.R - The base of a solid is a circular disk with radius...Ch. 5.R - The base of a solid is the region bounded by the...Ch. 5.R - The height of a monument is 20 m. A horizontal...Ch. 5.R - a The base of a solid is a square with vertices...Ch. 5.R - Prob. 27ECh. 5.R - Prob. 28ECh. 5.R - A tank full of water has the shape of a paraboloid...Ch. 5.R - A steel tank has the shape of a circular cylinder...Ch. 5.R - Prob. 31ECh. 5.R - Prob. 32ECh. 5.R - Prob. 33ECh. 5.R - Prob. 34ECh. 5.P - a Find a positive continuous function f such that...Ch. 5.P - There is a line through the origin that divides...Ch. 5.P - The figure shows a horizontal line y=c...Ch. 5.P - A cylindrical glass of radius r and height L is...Ch. 5.P - a Show that the volume of a segment of height h of...Ch. 5.P - Archimedes Principle states that the buoyant force...Ch. 5.P - Prob. 7PCh. 5.P - A sphere of radius 1 overlaps a smaller sphere of...Ch. 5.P - The figure shows a curve C with the property that,...Ch. 5.P - A paper drinking cup filled with water has the...Ch. 5.P - A clepsydra, or water clock, is a glass container...Ch. 5.P - A cylindrical container of radius r and height L...Ch. 5.P - Suppose the graph of a cubic polynomial intersects...Ch. 5.P - Suppose we are planning to make a taco from a...Ch. 5.P - Prob. 15P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A driver is traveling along a straight road when a buffalo runs into the street. This driver has a reaction time of 0.75 seconds. When the driver sees the buffalo he is traveling at 44 ft/s, his car can decelerate at 2 ft/s^2 when the brakes are applied. What is the stopping distance between when the driver first saw the buffalo, to when the car stops.arrow_forwardTopic 2 Evaluate S x dx, using u-substitution. Then find the integral using 1-x2 trigonometric substitution. Discuss the results! Topic 3 Explain what an elementary anti-derivative is. Then consider the following ex integrals: fed dx x 1 Sdx In x Joseph Liouville proved that the first integral does not have an elementary anti- derivative Use this fact to prove that the second integral does not have an elementary anti-derivative. (hint: use an appropriate u-substitution!)arrow_forward1. Given the vector field F(x, y, z) = -xi, verify the relation 1 V.F(0,0,0) = lim 0+ volume inside Se ff F• Nds SE where SE is the surface enclosing a cube centred at the origin and having edges of length 2€. Then, determine if the origin is sink or source.arrow_forward
- 4 3 2 -5 4-3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 12 23 -4 The function graphed above is: Increasing on the interval(s) Decreasing on the interval(s)arrow_forwardQuestion 4 The plot below represents the function f(x) 8 7 3 pts O -4-3-2-1 6 5 4 3 2 + 1 2 3 5 -2+ Evaluate f(3) f(3) = Solve f(x) = 3 x= Question 5arrow_forwardQuestion 14 6+ 5 4 3 2 -8-2 2 3 4 5 6 + 2 3 4 -5 -6 The graph above is a transformation of the function f(x) = |x| Write an equation for the function graphed above g(x) =arrow_forward
- Question 8 Use the graph of f to evaluate the following: 6 f(x) 5 4 3 2 1 -1 1 2 3 4 5 -1 t The average rate of change of f from 4 to 5 = Question 9 10 ☑ 4parrow_forwardQuestion 15 ✓ 6 pts 1 Details The function shown below is f(x). We are interested in the transformed function g(x) = 3f(2x) - 1 a) Describe all the transformations g(x) has made to f(x) (shifts, stretches, etc). b) NEATLY sketch the transformed function g(x) and upload your graph as a PDF document below. You may use graph paper if you want. Be sure to label your vertical and horizontal scales so that I can tell how big your function is. 1- 0 2 3 4 -1- Choose File No file chosen Question 16 0 pts 1 Detailsarrow_forwardhelparrow_forward
- Question 2 Let F be a solenoidal vector field, suppose V × F = (-8xy + 12z², −9x² + 4y² + 9z², 6y²), and let (P,Q,R) = V²F(.725, —.283, 1.73). Then the value of sin(2P) + sin(3Q) + sin(4R) is -2.024 1.391 0.186 -0.994 -2.053 -0.647 -0.588 -1.851 1 ptsarrow_forward1 pts Let F and G be vector fields such that ▼ × F(0, 0, 0) = (0.76, -9.78, 3.29), G(0, 0, 0) = (−3.99, 6.15, 2.94), and G is irrotational. Then sin(5V (F × G)) at (0, 0, 0) is Question 1 -0.246 0.072 -0.934 0.478 -0.914 -0.855 0.710 0.262 .arrow_forwardanswerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Cengage
Surface Area Of A Sphere | Geometry | Math | Letstute; Author: Let'stute;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T_DBkFnr4NM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY