
Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences and Social Sciences Plus NEW MyLab Math with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780321947628
Author: Raymond A. Barnett, Michael R. Ziegler, Karl E. Byleen
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.1, Problem 3MP
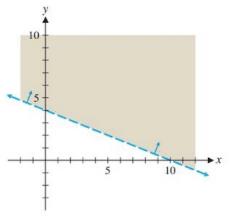
Find the linear inequality whose graph is given in Figure 14. Write the boundary line equation in the form
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
If you are using chatgpt leave it
I will downvote .
Temperature measurements are based on the transfer of heat between the sensor of a measuring device (such as an ordinary thermometer or the gasket of a thermocouple) and the medium whose temperature is to be measured. Once the sensor or thermometer is brought into contact with the medium, the sensor quickly receives (or loses, if warmer) heat and reaches thermal equilibrium with the medium. At that point the medium and the sensor are at the same temperature. The time required for thermal equilibrium to be established can vary from a fraction of a second to several minutes. Due to its small size and high conductivity it can be assumed that the sensor is at a uniform temperature at all times, and Newton's cooling law is applicable. Thermocouples are commonly used to measure the temperature of gas streams. The characteristics of the thermocouple junction and the gas stream are such that λ = hA/mc 0.02s-1. Initially, the thermocouple junction is at a temperature Ti and the gas stream at…
A body of mass m at the top of a 100 m high tower is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 10 m/s. Assume that the air resistance FD acting on the body is proportional to the velocity V, so that FD=kV. Taking g = 9.75 m/s2 and k/m = 5 s, determine: a) what height the body will reach at the top of the tower, b) how long it will take the body to touch the ground, and c) the velocity of the body when it touches the ground.
Chapter 5 Solutions
Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences and Social Sciences Plus NEW MyLab Math with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (13th Edition)
Ch. 5.1 - Graph 6x3y18.Ch. 5.1 - Graph (A) y4 (B) 4x9 (C) 3x2yCh. 5.1 - Find the linear inequality whose graph is given in...Ch. 5.1 - A food vendor at a rock concert sells hot dogs for...Ch. 5.1 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.1 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.1 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.1 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.1 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.1 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...
Ch. 5.1 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.1 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.1 - Graph each inequality in Problems 9-18. yx1Ch. 5.1 - Graph each inequality in Problems 9-18. yx+1Ch. 5.1 - Graph each inequality in Problems 9-18. 3x2y6Ch. 5.1 - Graph each inequality in Problems 9-18. 2x5y10Ch. 5.1 - Graph each inequality in Problems 9-18. x4Ch. 5.1 - Graph each inequality in Problems 9-18. y5Ch. 5.1 - Graph each inequality in Problems 9-18. 6x+4y24Ch. 5.1 - Graph each inequality in Problems 9-18. 4x+8y32Ch. 5.1 - Graph each inequality in Problems 9-18. 5x2yCh. 5.1 - Graph each inequality in Problems 9-18. 6x4yCh. 5.1 - In Problems 19-22, (A) graph the set of points...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 19-22, (A) graph the set of points...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 19-22, (A) graph the set of points...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 19-22, (A) graph the set of points...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 23-28, define the variable and...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 23-28, define the variable and...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 23-28, define the variable and...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 23-28, define the variable and...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 23-28, define the variable and...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 23-28, define the variable and...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 33-38, state the linear inequality...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 33-38, state the linear inequality...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 33-38, state the linear inequality...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 33-38, state the linear inequality...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 33-38, state the linear inequality...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 33-38, state the linear inequality...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 39-44, define two variables and...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 39-44, define two variables and...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 39-44, define two variables and...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 39-44, define two variables and...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 39-44, define two variables and...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 39-44, define two variables and...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 45-54, graph each inequality subject...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 45-54, graph each inequality subject...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 45-54, graph each inequality subject...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 45-54, graph each inequality subject...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 45-54, graph each inequality subject...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 45-54, graph each inequality subject...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 45-54, graph each inequality subject...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 45-54, graph each inequality subject...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 45-54, graph each inequality subject...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 45-54, graph each inequality subject...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 51-62, express your answer as a linear...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 52ECh. 5.1 - In Problems 55-66, express your answer as a linear...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 55-66, express your answer as a linear...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 55-66, express your answer as a linear...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 55-66, express your answer as a linear...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 55-66, express your answer as a linear...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 55-66, express your answer as a linear...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 55-66, express your answer as a linear...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 55-66, express your answer as a linear...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 55-66, express your answer as a linear...Ch. 5.1 - In Problems 55-66, express your answer as a linear...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the following system of linear inequalities...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the following system of linear inequalities...Ch. 5.2 - A manufacturing plant makes two types of...Ch. 5.2 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.2 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.2 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.2 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.2 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.2 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.2 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.2 - For Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Section...Ch. 5.2 - In Problems 9-12, match the solution region of...Ch. 5.2 - In Problems 9-12, match the solution region of...Ch. 5.2 - In Problems 9-12, match the solution region of...Ch. 5.2 - In Problems 9-12, match the solution region of...Ch. 5.2 - In Problems 13-16, solve each system of linear...Ch. 5.2 - In Problems 13-16, solve each system of linear...Ch. 5.2 - In Problems 13-16, solve each system of linear...Ch. 5.2 - In Problems 13-16, solve each system of linear...Ch. 5.2 - In Problems 17-20, match the solution region of...Ch. 5.2 - In Problems 17-20, match the solution region of...Ch. 5.2 - In Problems 17-20, match the solution region of...Ch. 5.2 - In Problems 17-20, match the solution region of...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 29-38 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 29-38 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 29-38 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 29-38 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 29-38 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 29-38 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 29-38 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 29-38 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 29-38 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 29-38 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 39-48 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 39-48 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 39-48 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - \ Solve the systems in Problems 39-48 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 39-48 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 39-48 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 39-48 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 39-48 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 39-48 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Solve the systems in Problems 39-48 graphically...Ch. 5.2 - Problems 49 and 50 introduce an algebraic process...Ch. 5.2 - Problems 49 and 50 introduce an algebraic process...Ch. 5.2 - Water skis. A manufacturing company makes two...Ch. 5.2 - Furniture. A furniture manufacturing company...Ch. 5.2 - Water skis. Refer to Problem 51. The company makes...Ch. 5.2 - Furniture. Refer to Problem 52. The company makes...Ch. 5.2 - Plant food. A farmer can buy two types of plant...Ch. 5.2 - Nutrition. A dietician in a hospital is to arrange...Ch. 5.2 - Psychology. A psychologist uses two types of boxes...Ch. 5.3 - A manufacturing plant makes two types of...Ch. 5.3 - Refer to the feasible region S shown in Figure 3....Ch. 5.3 - In Example 2B we saw that there was no optimal...Ch. 5.3 - (A) Maximize and minimize z=4x+2y subject to the...Ch. 5.3 - A chicken farmer can buy a special food mix A at...Ch. 5.3 - In Problem 1-8, if necessary, review Theorem 1. In...Ch. 5.3 - In Problem 1-8, if necessary, review Theorem 1. In...Ch. 5.3 - In Problem 1-8, if necessary, review Theorem 1. In...Ch. 5.3 - In Problem 1-8, if necessary, review Theorem 1. In...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Theorem 1....Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Theorem 1....Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Theorem 1....Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 1-8, if necessary, review Theorem 1....Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 9-12, graph the constant-profit lines...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 9-12, graph the constant-profit lines...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 9-12, graph the constant-profit lines...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 9-12, graph the constant-profit lines...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 13-16, graph the constant-cost lines...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 13-16, graph the constant-cost lines...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 13-16, graph the constant-cost lines...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 13-16, graph the constant-cost lines...Ch. 5.3 - Solve the linear programming problems stated in...Ch. 5.3 - Solve the linear programming problems stated in...Ch. 5.3 - Solve the linear programming problems stated in...Ch. 5.3 - Solve the linear programming problems stated in...Ch. 5.3 - Solve the linear programming problems stated in...Ch. 5.3 - Solve the linear programming problems stated in...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 23ECh. 5.3 - Solve the linear programming problems stated in...Ch. 5.3 - Solve the linear programming problems stated in...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 26ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 27ECh. 5.3 - Solve the linear programming problems stated in...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 29ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 30ECh. 5.3 - Solve the linear programming problems stated in...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 32ECh. 5.3 - Solve the linear programming problems stated in...Ch. 5.3 - Solve the linear programming problems stated in...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 39 and 40, explain why Theorem 2...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 39 and 40, explain why Theorem 2...Ch. 5.3 - The corner points for the bounded feasible region...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 38ECh. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5.3 - In Problems 49-64, construct a mathematical model...Ch. 5 - Graph each inequality. x2y3Ch. 5 - Graph each inequality. 3y5x30Ch. 5 - Graph the systems in Problems 3-6 and indicate...Ch. 5 - Graph the systems in Problems 3-6 and indicate...Ch. 5 - Graph the systems in Problems 3-6 and indicate...Ch. 5 - Graph the systems in Problems 3-6 and indicate...Ch. 5 - In Exercises 7 and 8, state the linear inequality...Ch. 5 - In Exercises 7 and 8, state the linear inequality...Ch. 5 - Solve the linear programming problems in Problems...Ch. 5 - Solve the linear programming problems in Problems...Ch. 5 - Solve the linear programming problems in Problems...Ch. 5 - Solve the linear programming problems in Problems...Ch. 5 - Solve the linear programming problems in Problems...Ch. 5 - Electronics. A company uses two machines to solder...Ch. 5 - In problems 15 and 16, construct a mathematical...Ch. 5 - In problems 15 and 16, construct a mathematical...
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The solution of the equation
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Surfing College students and surfers Rex Robinson and Sandy Hudson collected data on the self-reported numbers ...
Introductory Statistics
In Exercises 13–16, find the margin of error for the values of c, ?, and n.
16. e = 0.975, ? = 4.6, n = 100
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
In Exercises 5–12, find and sketch the domain for each function.
11.
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Explain the meaning of the term “statistically significant difference” in statistics terminology.
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, subject and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A chemical reaction involving the interaction of two substances A and B to form a new compound X is called a second order reaction. In such cases it is observed that the rate of reaction (or the rate at which the new compound is formed) is proportional to the product of the remaining amounts of the two original substances. If a molecule of A and a molecule of B combine to form a molecule of X (i.e., the reaction equation is A + B ⮕ X), then the differential equation describing this specific reaction can be expressed as: dx/dt = k(a-x)(b-x) where k is a positive constant, a and b are the initial concentrations of the reactants A and B, respectively, and x(t) is the concentration of the new compound at any time t. Assuming that no amount of compound X is present at the start, obtain a relationship for x(t). What happens when t ⮕∞?arrow_forwardConsider a body of mass m dropped from rest at t = 0. The body falls under the influence of gravity, and the air resistance FD opposing the motion is assumed to be proportional to the square of the velocity, so that FD = kV2. Call x the vertical distance and take the positive direction of the x-axis downward, with origin at the initial position of the body. Obtain relationships for the velocity and position of the body as a function of time t.arrow_forwardAssuming that the rate of change of the price P of a certain commodity is proportional to the difference between demand D and supply S at any time t, the differential equations describing the price fluctuations with respect to time can be expressed as: dP/dt = k(D - s) where k is the proportionality constant whose value depends on the specific commodity. Solve the above differential equation by expressing supply and demand as simply linear functions of price in the form S = aP - b and D = e - fParrow_forward
- Find the area of the surface obtained by rotating the circle x² + y² = r² about the line y = r.arrow_forward3) Recall that the power set of a set A is the set of all subsets of A: PA = {S: SC A}. Prove the following proposition. АСВ РАСРВarrow_forwardA sequence X = (xn) is said to be a contractive sequence if there is a constant 0 < C < 1 so that for all n = N. - |Xn+1 − xn| ≤ C|Xn — Xn−1| -arrow_forward
- 3) Find the surface area of z -1≤ y ≤1 = 1 + x + y + x2 over the rectangle −2 ≤ x ≤ 1 and - Solution: TYPE YOUR SOLUTION HERE! ALSO: Generate a plot of the surface in Mathematica and include that plot in your solution!arrow_forward7. Walkabout. Does this graph have an Euler circuit? If so, find one. If not, explain why not.arrow_forwardBelow, let A, B, and C be sets. 1) Prove (AUB) nC = (ANC) U (BNC).arrow_forward
- Q1: find the Reliability of component in the system in fig(1) by minimal cut method. Q2: A component A with constant failure rate 1.5 per 1000 h, B per to 2 in 1000h, A and B in parallel, find the Reliability system? [ by exponential distribution]. Q3: Give an example to find the minimal path and estimate the reliability of this block diagram. Q4: By Tie set method find the Reliability of fig (2) FUZarrow_forwardA sequence X = (xn) is said to be a contractive sequence if there is a constant 0 < C < 1 so that for all n = N. - |Xn+1 − xn| ≤ C|Xn — Xn−1| -arrow_forward1) Suppose continuous random variable X has sample space S = [1, ∞) and a pdf of the form f(x) = Ce-(2-1)/2. What is the expected value of X?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:9780395977224
Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:McDougal Littell

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...
Algebra
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...
Algebra
ISBN:9781680331141
Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt


Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...
Algebra
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:McGraw Hill

Elementary Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:9780998625713
Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-Smith
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University
2.1 Introduction to inequalities; Author: Oli Notes;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D6erN5YTlXE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
GCSE Maths - What are Inequalities? (Inequalities Part 1) #56; Author: Cognito;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e_tY6X5PwWw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Introduction to Inequalities | Inequality Symbols | Testing Solutions for Inequalities; Author: Scam Squad Math;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=paZSN7sV1R8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY