
Elementary Statistics 2nd Edition
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781259724275
Author: William Navidi, Barry Monk
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.1, Problem 21E
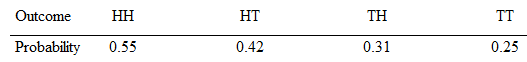
In Exercises 21-24, assume that a coin is tossed twice. The coin may not be fair. The
Is the following a
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
NC Current Students - North Ce X | NC Canvas Login Links - North ( X
Final Exam Comprehensive x Cengage Learning
x
WASTAT - Final Exam - STAT
→
C
webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/submit?dep=36055360&tags=autosave#question3659890_9
Part (b)
Draw a scatter plot of the ordered pairs.
N
Life
Expectancy
Life
Expectancy
80
70
600
50
40
30
20
10
Year of
1950
1970 1990
2010 Birth
O
Life
Expectancy
Part (c)
800
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
1950
1970 1990
W
ALT
林
$
#
4
R
J7
Year of
2010 Birth
F6
4+
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
Year of
1950 1970 1990
2010 Birth
Life
Expectancy
Ox
800
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
Year of
1950 1970 1990 2010 Birth
hp
P.B.
KA
&
7
80
% 5
H
A
B
F10
711
N
M
K
744
PRT SC
ALT
CTRL
Harvard University
California Institute of Technology
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Stanford University
Princeton University
University of Cambridge
University of Oxford
University of California, Berkeley
Imperial College London
Yale University
University of California, Los Angeles
University of Chicago
Johns Hopkins University
Cornell University
ETH Zurich
University of Michigan
University of Toronto
Columbia University
University of Pennsylvania
Carnegie Mellon University
University of Hong Kong
University College London
University of Washington
Duke University
Northwestern University
University of Tokyo
Georgia Institute of Technology
Pohang University of Science and Technology
University of California, Santa Barbara
University of British Columbia
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
University of California, San Diego
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
National University of Singapore
McGill…
Name
Harvard University
California Institute of Technology
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Stanford University
Princeton University
University of Cambridge
University of Oxford
University of California, Berkeley
Imperial College London
Yale University
University of California, Los Angeles
University of Chicago
Johns Hopkins University
Cornell University
ETH Zurich
University of Michigan
University of Toronto
Columbia University
University of Pennsylvania
Carnegie Mellon University
University of Hong Kong
University College London
University of Washington
Duke University
Northwestern University
University of Tokyo
Georgia Institute of Technology
Pohang University of Science and Technology
University of California, Santa Barbara
University of British Columbia
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
University of California, San Diego
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
National University of Singapore…
Chapter 5 Solutions
Elementary Statistics 2nd Edition
Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 5-8, fill in each blank with the...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 5-8, fill in each blank with the...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 5-8, fill in each blank with the...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 5-8, fill in each blank with the...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 9-12, determine whether the statement...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 9--12, determine whether the...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 9-12, determine whether the statement...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 12ECh. 5.1 - In Exercises 13-18, assume that a fair die is...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 13-18, assume that a fair die is...
Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 13-18, assume that a fair die is...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 13-18, assume that a fair die is...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 13-18, assume that a fair die is...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 13-18, assume that a fair die is...Ch. 5.1 - A fair coin has probability 0.5 of coming up...Ch. 5.1 - Roulette wheels in Nevada have 38 pockets. They...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 21-24, assume that a coin is tossed...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 21-24, assume that a coin is tossed...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 21-24, assume that a coin is tossed...Ch. 5.1 - In Exercises 21-24, assume that a coin is tossed...Ch. 5.1 - How probable is it? Someone computes the...Ch. 5.1 - Do you know SpongeBob? According to a survey by...Ch. 5.1 - Who will you vote for? In a survey of 500 likely...Ch. 5.1 - Job satisfaction: In a poll conducted by the...Ch. 5.1 - True-false exam: A section of an exam contains...Ch. 5.1 - A coin flip: A coil is tossed twee times. The...Ch. 5.1 - Empirical Method: A coin is tossed 400 times and...Ch. 5.1 - Empirical Method: A die is rolled 600 times. On 85...Ch. 5.1 - Pitching: During a recent season, pitcher Clayton...Ch. 5.1 - More Pitching: During a recent season, pitcher Jon...Ch. 5.1 - Risky drivers: An automobile insurance company...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 36ECh. 5.1 - Roulette: A Nevada roulette wheel has 38 pockets....Ch. 5.1 - More roulette: Refer to Exercise 37. What is the...Ch. 5.1 - Get an education: The General Social Survey asked...Ch. 5.1 - How many kids? The General Social Survey asked...Ch. 5.1 - Hospital visits: According to Agency for...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 42ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 43ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 44ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 45ECh. 5.1 - Find the probability: What is the probability that...Ch. 5.1 - Find the probability: What is the probability that...Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 48ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 49ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 50ECh. 5.1 - Prob. 51ECh. 5.2 - In Exercises 5-8, fill in each blank with the...Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 5-8, fill in each blank with the...Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 5-8, fill in each blank with the...Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 5-8, fill in each blank with the...Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 9-12, determine whether the statement...Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 9-12, determine whether the statement...Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 9-12, determine whether the statement...Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 9-12, determine whether the statement...Ch. 5.2 - If P(A)=0.75,P(B)=0.4, and P(AandB)=0.25, and...Ch. 5.2 - If P(A)=0.45,P(B)=0.7, and P(AandB)=0.65, find...Ch. 5.2 - If P(A)=0.2,P(B)=0.5, and A and B are mutually...Ch. 5.2 - If P(A)=0.7,P(B)=0.1, and A and B are mutually...Ch. 5.2 - If P(A)=0.3,P(B)=0.4, and P(A and B =0.7, are A...Ch. 5.2 - If P(A)=0.5,P(B)=0.4, and P(A and B =0.8, are A...Ch. 5.2 - If P(A)=0.35, find P(AC).Ch. 5.2 - If P(B)=0.6, find P(BC).Ch. 5.2 - If P(AC)=0.27, find P(A).Ch. 5.2 - If P(BC)=0.64, find P(B).Ch. 5.2 - If P(A)=0, find P(AC).Ch. 5.2 - If P(A)=P(AC), find P(A).Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 25-30, determine whether events A and...Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 25-30, determine whether events A and...Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 25-30, determine whether events A and...Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 25-30, determine whether events A and...Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 25-30, determine whether events A and...Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 25-30, determine whether events A and...Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 31 and 32, find the complements of...Ch. 5.2 - In Exercises 31 and 32, find the complements of...Ch. 5.2 - Traffic lights: A commuter passes through two...Ch. 5.2 - Dice: Two fair dice are rolled. The first die is...Ch. 5.2 - Car repairs: Let E be the event that a new car...Ch. 5.2 - Sick computers: Let V be the event that a computer...Ch. 5.2 - Computer purchases: Out of 800 large purchases...Ch. 5.2 - Visit your local library: On a recent Saturday. a...Ch. 5.2 - How are your grades? In a recent semester at a...Ch. 5.2 - Statistics grades: In a statistics class of 30...Ch. 5.2 - Sick children: There are 25 students in Mrs. Bushs...Ch. 5.2 - Flawed parts: On a certain day, a foundry...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 43ECh. 5.2 - The following table presents the number of reports...Ch. 5.2 - Add probabilities? In a certain community, 28% of...Ch. 5.2 - Add probabilities? According to the National...Ch. 5.2 - Prob. 47ECh. 5.2 - Prob. 48ECh. 5.3 - In Exercises 7-10, fill in each blank with the...Ch. 5.3 - In Exercises 7-10, fill in each blank with the...Ch. 5.3 - In Exercises 7-10, fill in each blank with the...Ch. 5.3 - In Exercises 7-10, fill in each blank with the...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 11ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 12ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 13ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 14ECh. 5.3 - Let A and B be events with P(A)=0.4,P(B)=0.7, and...Ch. 5.3 - Let A and B be events with P(A)=0.6,P(B)=0.4, and...Ch. 5.3 - Let A and B be events with P(A)=0.2 and P(B)=0.9....Ch. 5.3 - Let A and B be events with P(A)=0.5 and P(B)=0.7....Ch. 5.3 - Let A and B be events with P(A)=0.8,P(B)=0.1, and...Ch. 5.3 - Let A and B be events with P(A)=0.3,P(B)=0.5, and...Ch. 5.3 - Let A, B, and C be independent events with...Ch. 5.3 - Let A, B, and C be independent events with...Ch. 5.3 - A fair is tossed four times. What is the...Ch. 5.3 - A fair coin is tossed four times. What is the...Ch. 5.3 - A fair die is rolled three times. What is the...Ch. 5.3 - A fair die is rolled three times. What is the...Ch. 5.3 - In Exercises 27-30, assume that a student is...Ch. 5.3 - In Exercises 27-30, assume that a student is...Ch. 5.3 - In Exercises 27-30, assume that a student is...Ch. 5.3 - In Exercises 27-30, assume that a student is...Ch. 5.3 - Let A and B be events with P(A)=0.25,P(B)=0.4, and...Ch. 5.3 - Let A and B be events with P(A)=0.6,P(B)=0.9, and...Ch. 5.3 - Let A and B be events with P(A)=0.4,P(B)=0.5, and...Ch. 5.3 - Let A and B be events with P(A)=0.5,P(B)=0.3, and...Ch. 5.3 - A fair die is rolled three times. What is the...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 36ECh. 5.3 - Job interview: Seven people, named Anna, Bob,...Ch. 5.3 - Shuffle: Charles has songs on a playlist. Each...Ch. 5.3 - Lets eat: A fast-food restaurant chain has 600...Ch. 5.3 - U.S. senators: The following table displays the...Ch. 5.3 - Genetics: A geneticist is studying two genes. Each...Ch. 5.3 - Quality control: A population of 600 semiconductor...Ch. 5.3 - Stay in school: In a recent school year in the...Ch. 5.3 - Management: The Bureau of Labor Statistics...Ch. 5.3 - GED: In a certain school. the probability that a...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 46ECh. 5.3 - New car: At a certain car dealership, the...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 48ECh. 5.3 - Target practice: Laura and Philip each fire one...Ch. 5.3 - Bowling: Sarah and Thomas are going bowling. The...Ch. 5.3 - Defective components: A lot of 10 components...Ch. 5.3 - More defective components: A lot of 1000...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 53ECh. 5.3 - Multiply probabilities? A traffic light at an...Ch. 5.3 - Lottery: Every day: Jorge buys a lottery ticket....Ch. 5.3 - Car warranty: The a certain make of car will need...Ch. 5.3 - Tic-tac-toe: In the game of tic-tac-toe, fall...Ch. 5.3 - Enter your PIN: The technology consulting company...Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 59ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 60ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 61ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 62ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 63ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 64ECh. 5.3 - Prob. 65ECh. 5.4 - In Exercises 7 and 8, fill in the blank with the...Ch. 5.4 - In Exercises 7 and 8, fill in the blank with the...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 9ECh. 5.4 - Exercises 9 and 10, determine whether the...Ch. 5.4 - In Exercises 11-16, evaluate the factorial. 9!Ch. 5.4 - In Exercises 11-16, evaluate the factorial. 5!Ch. 5.4 - In Exercises 11-16, evaluate the factorial. 0!Ch. 5.4 - In Exercises 11-16, evaluate the factorial. 12!Ch. 5.4 - In Exercises 11-16, evaluate the factorial. 1!Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 16ECh. 5.4 - In Exercises 17-22, evaluate the permutation. 7P3Ch. 5.4 - In Exercises 17-22, evaluate the permutation. 8P1Ch. 5.4 - In Exercises 17-22, evaluate the permutation....Ch. 5.4 - In Exercises 17-22, evaluate the permutation. 5P4Ch. 5.4 - In Exercises 17-22, evaluate the permutation. 20P0Ch. 5.4 - In Exercises 17-22, evaluate the permutation. 45P5Ch. 5.4 - In Exercises 23-28, evaluate the combination. 9C5Ch. 5.4 - In Exercises 23-28, evaluate the combination. 7C1Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 25ECh. 5.4 - Prob. 26ECh. 5.4 - In Exercises 23-28, evaluate the combination. 12C0Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 28ECh. 5.4 - Pizza time: A local pizza parlor is offering a...Ch. 5.4 - Books: Josephine has chemistry books, three...Ch. 5.4 - Playing the horses: In horseracing, one can make a...Ch. 5.4 - Ice cream: A certain ice cream parlor offers 15...Ch. 5.4 - License plates: In a certain state, license plates...Ch. 5.4 - Committee: The Student Council at a certain school...Ch. 5.4 - Day and night shifts: A company has hired 12 new...Ch. 5.4 - Keep your password safe: A computer password...Ch. 5.4 - Its in your genes: Hunan genetic material ONA) is...Ch. 5.4 - Choosing officers: A committee consists of 10...Ch. 5.4 - Texas hold'em, In the game of Texas hold'em, a...Ch. 5.4 - Blackjack: In single-deck casino blackjack the...Ch. 5.4 - Lottery: In the Georgia Fantasy 5 Lottery, balls...Ch. 5.4 - Prob. 42ECh. 5.4 - Prob. 43ECh. 5 - Fill in the blank: The probability that a fair...Ch. 5 - Prob. 2CQCh. 5 - State each of the following rules: General...Ch. 5 - Prob. 4CQCh. 5 - Prob. 5CQCh. 5 - In a group of 100 teenagers, 61 received their...Ch. 5 - A certain has 100 households. Forty-eight...Ch. 5 - Prob. 8CQCh. 5 - Prob. 9CQCh. 5 - Prob. 10CQCh. 5 - Prob. 11CQCh. 5 - Prob. 12CQCh. 5 - Prob. 13CQCh. 5 - Prob. 14CQCh. 5 - Prob. 15CQCh. 5 - Prob. 1RECh. 5 - Prob. 2RECh. 5 - Statistics, anyone? Let S be the event that a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 4RECh. 5 - Prob. 5RECh. 5 - Prob. 6RECh. 5 - Defective parts: A process manufactures...Ch. 5 - Music to my ears: Jeri is listening to songs on a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 9RECh. 5 - Heart attack: The following table presents the...Ch. 5 - Rainy weekend: Sally is planning to go away for...Ch. 5 - Prob. 12RECh. 5 - Required courses: Refer to Exercise 12. Assume the...Ch. 5 - Bookshelf: Bart has books: a novel, a biography, a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 15RECh. 5 - Prob. 1WAICh. 5 - Prob. 2WAICh. 5 - Prob. 3WAICh. 5 - Prob. 4WAICh. 5 - Sometimes events are in the form at least a given...Ch. 5 - Prob. 6WAICh. 5 - Prob. 7WAICh. 5 - Prob. 8WAICh. 5 - The following table is a life table, reproduced...Ch. 5 - Prob. 2CSCh. 5 - Prob. 3CSCh. 5 - The following table is a life table, reproduced...Ch. 5 - The following table is a life table, reproduced...Ch. 5 - Prob. 6CSCh. 5 - Prob. 7CSCh. 5 - In Exercise 1-5, we computed the probability that...Ch. 5 - Prob. 9CS
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A company found that the daily sales revenue of its flagship product follows a normal distribution with a mean of $4500 and a standard deviation of $450. The company defines a "high-sales day" that is, any day with sales exceeding $4800. please provide a step by step on how to get the answers in excel Q: What percentage of days can the company expect to have "high-sales days" or sales greater than $4800? Q: What is the sales revenue threshold for the bottom 10% of days? (please note that 10% refers to the probability/area under bell curve towards the lower tail of bell curve) Provide answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forwardFind the critical value for a left-tailed test using the F distribution with a 0.025, degrees of freedom in the numerator=12, and degrees of freedom in the denominator = 50. A portion of the table of critical values of the F-distribution is provided. Click the icon to view the partial table of critical values of the F-distribution. What is the critical value? (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardA retail store manager claims that the average daily sales of the store are $1,500. You aim to test whether the actual average daily sales differ significantly from this claimed value. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value. Showing the calculation is a must. If calculation is missing,so please provide a step by step on the answers Numerical answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you


 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL



College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...
Algebra
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Mod-01 Lec-01 Discrete probability distributions (Part 1); Author: nptelhrd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6x1pL9Yov1k;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Discrete Probability Distributions; Author: Learn Something;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m9U4UelWLFs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Probability Distribution Functions (PMF, PDF, CDF); Author: zedstatistics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YXLVjCKVP7U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Discrete Distributions: Binomial, Poisson and Hypergeometric | Statistics for Data Science; Author: Dr. Bharatendra Rai;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lHhyy4JMigg;License: Standard Youtube License