
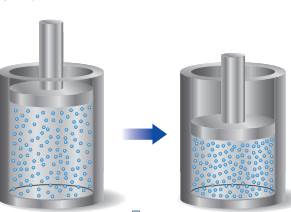
A sample of gas is contained in a cylinder-and-piston arrangement. It undergoes the change in state shown in the drawing. (a) Assume first that the cylinder and piston are perfect thermal insulators that do not allow heat to be transferred. What is the value of q for the state change? What is the sign of w for the state change? What can be said about ?E for the state change?
(b) Now assume that the cylinder and piston are made up of a thermal conductor such as a metal.
During the state change, the cylinder gets warmer to the touch. What is the sign of q for the state change in this case? Describe the difference in the state of the system at the end of the in the two cases. What can you say about the relative values of ?E?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Chemistry: The Central Science, Books a la Carte Edition & Solutions to Red Exercises for Chemistry & Mastering Chemistry with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package
- BeF2 exists as a linear molecule. Which kind of hybrid orbitals does Be use in this compound? Use Orbital Diagrams to show how the orbitals are formed. (6)arrow_forwardPlease answer the questions and provide detailed explanations as well as a drawing to show the signals in the molecule.arrow_forwardPropose an efficient synthesis for the following transformation: EN The transformation above can be performed with some reagent or combination of the reagents listed below. Give the necessary reagents in the correct order, as a string of letters (without spaces or punctuation, such as "EBF"). If there is more than one correct solution, provide just one answer. A. t-BuOK B. Na2Cr2O7, H2SO4, H2O C. NBS, heat F. NaCN D. MeOH E. NaOH G. MeONa H. H2O I. 1) O3; 2) DMSarrow_forward
- Stereochemistry Identifying the enantiomer of a simple organic molecule 1/5 Check the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of t above box under the table. Br ま HO H 0 Molecule 1 Molecule 2 Molecule 3 OH H Br H H" Br OH Br Molecule 4 Br H OH + + OH Molecule 5 Br H OH none of the above Molecule 6 Br H... OHarrow_forwardPlease answer the questions and provide detailed explanations.arrow_forwardQuestion 16 0/1 pts Choose the correct option for the following cycloaddition reaction. C CF3 CF3 CF3 CF3 The reaction is suprafacial/surafacial and forbidden The reaction is antarafacial/antarafacial and forbidden The reaction is antarafacial/antarafacial and allowed The reaction is suprafacial/surafacial and allowedarrow_forward
- 1. Give the structures of the products obtained when the following are heated. Include stereochemistry where relevant. A NO2 + NO2 B + C N=C CEN + { 2. Which compounds would you heat together in order to synthesize the following?arrow_forwardExplain how myo-inositol is different from D-chiro-inositol. use scholarly sources and please hyperlink.arrow_forwardWhat is the molarisuty of a 0.396 m glucose solution if its density is 1.16 g/mL? MM glucose 180.2 /mol.arrow_forward
- Provide the proper IUPAC or common name for the following compound. Dashes, commas, and spaces must be used correctly. Br ......Im OHarrow_forwardCan you please help me solve this problems. The top one is just drawing out the skeletal correct and then the bottom one is just very confusing to me and its quite small in the images. Can you enlarge it and explain it to me please. Thank You much (ME EX1) Prblm #33arrow_forwardI'm trying to memorize VESPR Shapes to solve problems like those. I need help making circles like the second image in blue or using an x- and y-axis plane to memorize these and solve those types of problems, especially the ones given in the top/first image (180, 120, 109.5). Can you help me with this? or is their any other efficient method do soarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





