
Concept explainers
(a)
To Find:The force of static friction exerted on the car by the runway surface.
The minimum coefficient of static friction necessary for the car to sustain this speed.
(a)
Answer to Problem 90P
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Mass of the car,
Air drag on the car,
Speed of the car,
Formula Used:
Newton’s second law:
Calculation:
The following is the free body diagram of the car as the car travels on the runway.
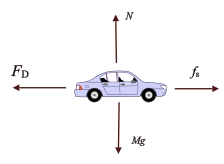
Assume the mass of the car as
Convert the units of the speed of the car from
Speed of the car,
Since, the car is moving with constant velocity, the acceleration of the car is zero.
Net force acting on the car along z axis,
Substitute
Thus, the required static frictional force on the car is
Net force acting on the car along
Rewrite equation
Here
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the required coefficient of static frictional force is
(b)
To Find: The minimum coefficient of static friction necessary for the car to hold the last radius of curvature without skidding.
(b)
Answer to Problem 90P
The radius of the curve at
The radius of the curve at
The required coefficient of friction for the car without skidding is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Mass of the car,
Air drag on the car,
Speed of the car,
Formula Used:
Newton’s second law:
Frictional force
Calculation:
The following is a free body diagram of the car on a circular path.
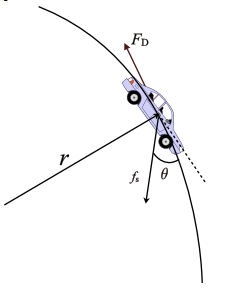
In the above figure,
Apply Newton’s second law to the motion of the car and calculate the net force acting on the car
The radial force acting on the car along x-axis.
Here,
The tangential force acting on the car along x-axis.
Divide equation
Rearrange this equation for
Substitute
Thus, the radius of the curve at
Similarly, use equation
Substitute
Thus, the radius of the curve at
Calculate the minimum coefficient of friction required for the car to hold at radius
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the required coefficient of friction for the car without skidding is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
PHYSICS F/SCI.+ENGRS.,STAND.-W/ACCESS
- An L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forward
- Discuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forwardExplain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forward
- A 0.850-m-long metal bar is pulled to the right at a steady 5.0 m/s perpendicular to a uniform, 0.650-T magnetic field. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 25-Ω, resistor (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. Ignore the resistance of the bar and the rails. Please explain how to find the direction of the induced current.arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted, determine the direction (right, left, or zero) of the current induced to flow through the resistor in the circuit containing the secondary coil. The coils are wrapped around a plastic core. Immediately after the switch is closed, as shown in the figure, (Figure 1) in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? If the switch is then opened, as shown in the figure, in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? I have the answers to the question, but would like to understand the logic behind the answers. Please show steps.arrow_forwardWhen violet light of wavelength 415 nm falls on a single slit, it creates a central diffraction peak that is 8.60 cm wide on a screen that is 2.80 m away. Part A How wide is the slit? ΟΙ ΑΣΦ ? D= 2.7.10-8 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining marrow_forward
- Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forwardCalculate the center of mass of the hollow cone shown below. Clearly specify the origin and the coordinate system you are using. Z r Y h Xarrow_forward12. If all three collisions in the figure below are totally inelastic, which will cause more damage? (think about which collision has a larger amount of kinetic energy dissipated/lost to the environment? I m II III A. I B. II C. III m m v brick wall ע ע 0.5v 2v 0.5m D. I and II E. II and III F. I and III G. I, II and III (all of them) 2marrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





