
Concept explainers
(a)
The maximum force which is applied so that there is no relative motion between block and bracket.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Mass of the block is
Mass of the bracket is
Value of the static friction is
Value of the kinetic friction is
Formula used:
Draw free body diagram of block and bracket.
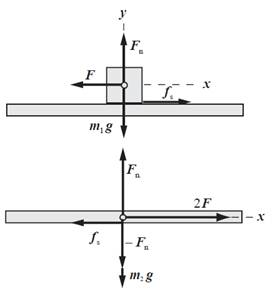
Write expression for net force in x -direction on block.
Substitute
Here,
Substitute
Here,
Rearrange above expression for
Write expression for net force in x -direction on block.
Substitute
Here,
Substitute
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the maximum force is
(a)
The maximum force which is applied so that there is no relative motion between block and bracket.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Mass of the block is
Mass of the bracket is
Value of the static friction is
Value of the kinetic friction is
Formula used:
Draw free body diagram of block and bracket.
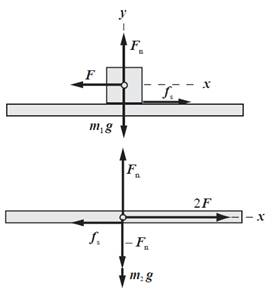
Write expression for net force in x -direction on block.
Substitute
Substitute
Rearrange above expression for
Write expression for net force in x -direction on block.
Substitute
Substitute
Calculation:
Substitute
Conclusion:
The acceleration of the block is equal to the acceleration of the bracket. Thus, the acceleration of the bracket is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
PHYSICS F/SCI.+ENGRS.,STAND.-W/ACCESS
- Two conductors having net charges of +14.0 µC and -14.0 µC have a potential difference of 14.0 V between them. (a) Determine the capacitance of the system. F (b) What is the potential difference between the two conductors if the charges on each are increased to +196.0 µC and -196.0 µC? Varrow_forwardPlease see the attached image and answer the set of questions with proof.arrow_forwardHow, Please type the whole transcript correctly using comma and periods as needed. I have uploaded the picture of a video on YouTube. Thanks,arrow_forward
- A spectra is a graph that has amplitude on the Y-axis and frequency on the X-axis. A harmonic spectra simply draws a vertical line at each frequency that a harmonic would be produced. The height of the line indicates the amplitude at which that harmonic would be produced. If the Fo of a sound is 125 Hz, please sketch a spectra (amplitude on the Y axis, frequency on the X axis) of the harmonic series up to the 4th harmonic. Include actual values on Y and X axis.arrow_forwardSketch a sign wave depicting 3 seconds of wave activity for a 5 Hz tone.arrow_forwardSketch a sine wave depicting 3 seconds of wave activity for a 5 Hz tone.arrow_forward
- The drawing shows two long, straight wires that are suspended from the ceiling. The mass per unit length of each wire is 0.050 kg/m. Each of the four strings suspending the wires has a length of 1.2 m. When the wires carry identical currents in opposite directions, the angle between the strings holding the two wires is 20°. (a) Draw the free-body diagram showing the forces that act on the right wire with respect to the x axis. Account for each of the strings separately. (b) What is the current in each wire? 1.2 m 20° I -20° 1.2 marrow_forwardplease solve thisarrow_forwardplease solve everything in detailarrow_forward
- 6). What is the magnitude of the potential difference across the 20-02 resistor? 10 Ω 11 V - -Imm 20 Ω 10 Ω 5.00 10 Ω a. 3.2 V b. 7.8 V C. 11 V d. 5.0 V e. 8.6 Varrow_forward2). How much energy is stored in the 50-μF capacitor when Va - V₁ = 22V? 25 µF b 25 µF 50 µFarrow_forward9). A series RC circuit has a time constant of 1.0 s. The battery has a voltage of 50 V and the maximum current just after closing the switch is 500 mA. The capacitor is initially uncharged. What is the charge on the capacitor 2.0 s after the switch is closed? R 50 V a. 0.43 C b. 0 66 C c. 0.86 C d. 0.99 C Carrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





