
Concept explainers
(a)
The time taken by the runaway ski to slide down a 250-m long slope when the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and the snow is 0.100.
Answer to Problem 81QAP
The time taken by the runaway ski to slide down a 250-m long slope when the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and the snow is 0.100 is 8.12 s.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The length of the ski slope
The angle made by the slope to the horizontal
Initial speed of the ski
Coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and snow
Formula used:
A free body diagram of the ski is drawn to analyze its motion.
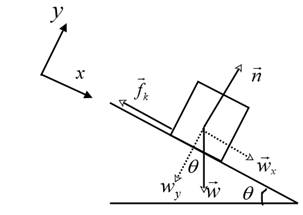
Assume a coordinate system, with the +x directed downwards along the incline and +y directed upwards, perpendicular to the incline. The weight
Resolve the weight
The ski is in equilibrium along the y direction.
Therefore,
Therefore, using equation (1),
The force of kinetic friction and the normal force are related according to the following equation:
From equation (2)
Write the force equation along the +x direction.
Use the values of wx and fk from equations (2) and (3) in the expression,
Simplify and write an expression for ax.
Use the following equation of motion to obtain the value of the time t.
Calculation:
Substitute the values of the variables in equation (4) and calculate the value of the acceleration.
Use the calculated value of ax and the values of v0 and
Solve the quadratic equation.
Taking the positive root,
Conclusion:
The time taken by the runaway ski to slide down a 250-m long slope when the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and the snow is 0.100 is 8.12 s.
(b)
The time taken by the runaway ski to slide down a 250-m long slope when the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and the snow is 0.150.
Answer to Problem 81QAP
The time taken by the runaway ski to slide down a 250-m long slope when the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and the snow is 0.150 is 8.39 s.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The length of the ski slope
The angle made by the slope to the horizontal
Initial speed of the ski
Coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and snow
Formula used:
The acceleration of the ski down the slope is given by
The time taken to reach the bottom of the slope is calculated using the expression,
Calculation:
Substitute the values of the variables in equation for acceleration and calculate the value of the acceleration.
Use the calculated value of ax and the values of v0 and
Solve the quadratic equation.
Taking the positive root,
Conclusion:
The time taken by the runaway ski to slide down a 250-m long slope when the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and the snow is 0.150 is 8.39 s.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS LL W/ 6 MONTH ACCESS
- In simplest way, For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. a) y = x 2 + 16 x + 39 b) y = 5 x2 - 50 x - 120arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step Write each quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = - 4( x + 6)2 + 36arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. 1) y = - 2 x2 - 28 x + 64 2) y = 6 x2 + 36 x - 42arrow_forward
- Write each relation in standard form a)y = 5(x + 10)2 + 7 b)y = 9(x - 8)2 - 4arrow_forwardIn simplest form and step by step Write the quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = 3(x - 1)2 - 147arrow_forwardStep by step instructions The path of a soccer ball can be modelled by the relation h = - 0.1 d 2 + 0.5 d + 0.6, where h is the ball’s height and d is the horizontal distance from the kicker. a) Find the zeros of the relation.arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage


 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill




