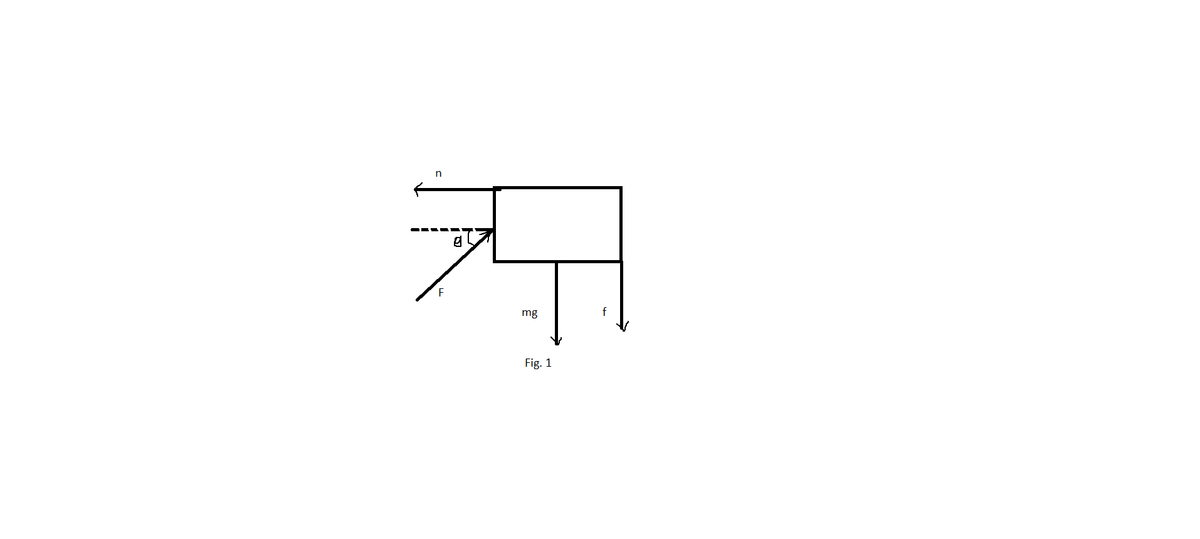
A 5.0-kg block is pushed 3.0 m up a vertical wall with constant speed by a constant force of magnitude F applied at an angle of θ = 30° with the horizontal, as shown in Figure P5.80. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and wall is 0.30, determine the work done by (a) , (b) the force of gravity, and (c) the normal force between block and wall. (d) By how much does the gravitational potential energy increase during the block’s motion?FIGURE P5.80
A 5.0-kg block is pushed 3.0 m up a vertical wall with constant speed by a constant force of magnitude F applied at an angle of θ = 30° with the horizontal, as shown in Figure P5.80. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and wall is 0.30, determine the work done by (a) , (b) the force of gravity, and (c) the normal force between block and wall. (d) By how much does the gravitational potential energy increase during the block’s motion?FIGURE P5.80
Related questions
Question
A 5.0-kg block is pushed 3.0 m up a vertical wall with constant speed by a constant force of magnitude F applied at an angle of θ = 30° with the horizontal, as shown in Figure P5.80. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and wall is 0.30, determine the work done by (a) , (b) the force of gravity, and (c) the normal force between block and wall. (d) By how much does the gravitational potential energy increase during the block’s motion?
FIGURE P5.80
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step 2
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images
