
Concept explainers
Consider the three connected objects shown in Figure P5.88. Assume first that the inclined plane is friction-less and that the system is in equilibrium. In terms of m, g, and θ, find (a) the mass M and (b) the tensions T, and T2. Now assume that the value of Af is double the value found in part (a). Find (c) the acceleration of each object and (d) the tensions T1 and T2. Next, assume that the coefficient of static friction between m and 2m and the inclined plane is m, and that the system is in equilibrium. Find (e) the maximum value of M and (0 the minimum value of M. (g) Compare the values of T2 when M has its minimum and maximum values.
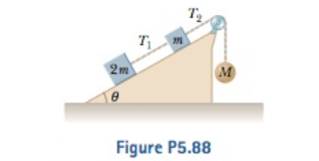
(a)
The expression for the mass of
Answer to Problem 5.88AP
The expression for the mass
Explanation of Solution
The free body diagram of the three connected objects is shown in Figure below,
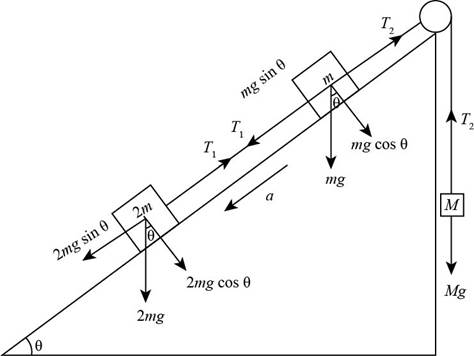
Figure (1)
From Figure (1), the equilibrium forces acts on the object of mass
Here,
From the Newton’s second law of motion, the net force on the object of mass
Here,
Substitute
From Figure (1), the equilibrium forces act on the object of mass
Here,
From the Newton’s second law of motion, the net force on the object of mass
Substitute
Add the equation (1) with equation (2).
From Figure (1), the equilibrium forces act on the object of mass
Here,
Substitute
From the Newton’s second law of motion, the net force on the object of mass
Substitute
The system is in equilibrium so value of the acceleration is zero.
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the expression for the mass
(b)
The expressions for tensions
Answer to Problem 5.88AP
The expression for the tension
Explanation of Solution
From part (a), the expression for the mass of
From part (a), the equilibrium forces act on the object is,
The system is in equilibrium, the value of acceleration is zero so the net force acts on the system is also zero.
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the expression for the tension
From part (a), the equation (2) is,
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the expression for the tension
Conclusion:
Therefore, the expression for the tension
(c)
The acceleration of each object.
Answer to Problem 5.88AP
The acceleration of each object is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The value of mass
From part (a), the expression for the mass when it is double represents as,
From part (a), the equation (1) is,
Rearrange the above equation.
From part (a), the equation (2) is,
Rearrange the above equation.
Substitute
From Figure (1), the equilibrium forces act on the object of mass
Substitute
Subtract the equation (3) from equation (4).
Conclusion:
Therefore, the acceleration of each object is
(d)
The expressions for tensions
Answer to Problem 5.88AP
The expression for the tension
Explanation of Solution
From part (c), the expression for the acceleration is,
From part (c), the equation for tension
Substitute
Thus, the expression for tension
From part (c), the equation (3) is,
Substitute
Thus, the expression for tension
Conclusion:
Therefore, the expression for the tension
(e)
The maximum value of
Answer to Problem 5.88AP
The maximum value of
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The coefficient of static friction between mass
The static friction forces on the masses
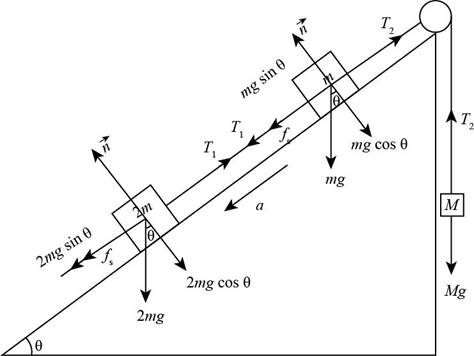
Figure (2)
From the Figure (2), the normal force on the object of mass
The expression for the static friction force on the object of mass
Here,
Substitute
From the Figure (1), the equilibrium forces acts on the object of mass
Substitute
Rearrange the above equation for
Substitute
From the Figure (2), the normal force on the object of mass
Substitute
From the Figure (1), the equilibrium forces acts on the object of mass
Substitute
Add equation (4) with the above equation.
Substitute
The equilibrium forces on the block of mass
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the maximum value of
(f)
The minimum value of
Answer to Problem 5.88AP
The minimum value of
Explanation of Solution
From part (e), the expression of tension
The equilibrium forces acts on block for minimum mass of
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the minimum value of
(g)
The difference between the tension
Answer to Problem 5.88AP
The difference between the tension for maximum and minimum mass is
Explanation of Solution
From part (e), the expression for maximum mass is,
From part (f), the expression for the minimum mass is,
From part (e), the expression for the tension for maximum mass is,
From part (f), the expression for the tension for maximum mass is,
Compare both the above equation.
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the difference between the tension for maximum and minimum mass is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- Using Coulomb's Law, calculate the magnitude of the electrical force between two protons located 1 meter apart from each other. (Give your answer as the number of Newtons but as usual you only need to include the number, not the unit label.)arrow_forwardPart A You want to get an idea of the magnitude of magnetic fields produced by overhead power lines. You estimate that a transmission wire is about 12 m above the ground. The local power company tells you that the line operates at 12 kV and provide a maximum of 60 MW to the local area. Estimate the maximum magnetic field you might experience walking under such a power line, and compare to the Earth's field. [For an ac current, values are rms, and the magnetic field will be changing.] Express your answer using two significant figures. ΟΤΕ ΑΣΦ VAΣ Bmax= Submit Request Answer Part B Compare to the Earth's field of 5.0 x 10-5 T. Express your answer using two significant figures. Ο ΑΣΦ B BEarth ? ? Tarrow_forwardHo propel 9-kN t. Boat 27. An elevator accelerates downward at 2.4 m/s². What force does the elevator's floor exert on a 52-kg passenger?arrow_forward
- 16. 17 A CUIN Starting from rest and undergoing constant acceleration, a 940-kg racing car covers 400 m in 4.95 s. Find the force on the car.arrow_forward----- vertical diste Section 4.6 Newton's Third Law 31. What upward gravitational force does a 5600-kg elephant exert on Earth?arrow_forward64. Two springs have the same unstretched length but different spring constants, k₁ and k₂. (a) If they're connected side by side and stretched a distance x, as shown in Fig. 4.24a, show that the force exerted by the combination is (k₁ + k₂)x. (b) If they're con- nected end to end (Fig. 4.24b) and the combination is stretched a distance x, show that they exert a force k₁k2x/(k₁ + k₂). www (a) FIGURE 4.24 Problem 65 www (b)arrow_forward
- 65. Although we usually write Newton's second law for one-dimensional motion in the form F =ma, which holds when mass is constant, d(mv) a more fundamental version is F = . Consider an object dt whose mass is changing, and use the product rule for derivatives to show that Newton's law then takes the form F dm = ma + v dtarrow_forwardIf a proton is located on the x-axis in some coordinate system at x0 = -3.2 x 10-5 meters, what is the x-component of the Electric Field due to this proton at a position x = +3.2 x 10-5 meters and on the x axis as the y-axis is 0 giving a number of Newtons/Coulomb?arrow_forwardConsider a single square loop of wire of area A carrying a current I in a uniform magnetic field of strength B. The field is pointing directly up the page in the plane of the page. The loop is oriented so that the plane of the loop is perpendicular to the plane of the page (this means that the normal vector for the loop is always in the plane of the page!). In the illustrations below the magnetic field is shown in red and the current through the current loop is shown in blue. The loop starts out in orientation (i) and rotates clockwise, through orientations (ii) through (viii) before returning to (i). (i) Ø I N - - I N - (iii) (iv) (v) (vii) (viii) a) [3 points] For each of the eight configurations, draw in the magnetic dipole moment vector μ of the current loop and indicate whether the torque on the dipole due to the magnetic field is clockwise (CW), counterclockwise (CCW), or zero. In which two orientations will the loop experience the maximum magnitude of torque? [Hint: Use the…arrow_forward
- Please help with calculating the impusle, thanks! Having calculated the impact and rebound velocities of the ping pong ball and the tennis ball calculate the rebounding impulse: 1.Measure the weight of the balls and determine their mass. Tennis ball: 0.57 kg Ping Pong Ball: 0.00246 kg The impulse, I, is equal to the change in momentum, Pf-Pi. Note the sign change, i.e., going down is negative and up is positive. The unit for momentum is kg-m/s. The change is momentum, impulse, is often givens the equivalent unit of N-S, Newton-Secondarrow_forward5. Three blocks, each with mass m, are connected by strings and are pulled to the right along the surface of a frictionless table with a constant force of magnitude F. The tensions in the strings connecting the masses are T1 and T2 as shown. m T1 T2 F m m How does the magnitude of tension T₁ compare to F? A) T₁ = F B) T₁ = (1/2)F C) T₁ = (1/3)F D) T₁ = 2F E) T₁ = 3Farrow_forwardUsing Coulombs Law, what is the magnitude of the electrical force between two protons located 1 meter apart from each other in Newtons?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





