
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780100460300
Author: SERWAY
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.85AP
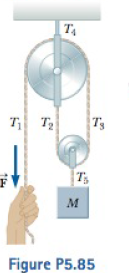
An object of mass M is held in place by an applied force
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Please help by:
Use a free body diagram
Show the equations
State your assumptions
Show your steps
Box your final answer
Thanks!
Please help by:
Use a free body diagram
Show the equations
State your assumptions
Show your steps
Box your final answer
Thanks!
By please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
Ch. 5 - Which of the following statements is correct? (a)...Ch. 5 - An object experiences no acceleration. Which of...Ch. 5 - You push an object, initially at rest, across a...Ch. 5 - Suppose you are talking by interplanetary...Ch. 5 - (i) If a fly collides with the windshield of a...Ch. 5 - You press your physics textbook flat against a...Ch. 5 - Charlie is playing with his daughter Toney in the...Ch. 5 - The driver of a speeding empty truck slams on the...Ch. 5 - In Figure OQ5.2, a locomotive has broken through...Ch. 5 - The third graders are on one side of a schoolyard,...
Ch. 5 - The driver of a speeding truck slams on the brakes...Ch. 5 - An experiment is performed on a puck on a level...Ch. 5 - The manager of a department store is pushing...Ch. 5 - Two objects are connected by a siring that passes...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m is sliding with speed v, at...Ch. 5 - A truck loaded with sand accelerates along a...Ch. 5 - A large crate of mass m is place on the flatbed of...Ch. 5 - If an object is in equilibrium, which of the...Ch. 5 - A crate remains stationary after it has been...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m moves with acceleration a down...Ch. 5 - If you hold a horizontal metal bar several...Ch. 5 - Your hands are wet, and the restroom towel...Ch. 5 - In the motion picture It Happened One Night...Ch. 5 - If a car is traveling due westward with a constant...Ch. 5 - A passenger sitting in the rear of a bus claims...Ch. 5 - A child tosses a ball straight up. She says that...Ch. 5 - A person holds a ball in her hand, (a) Identify...Ch. 5 - A spherical rubber balloon inflated with air is...Ch. 5 - A rubber ball is dropped onto the floor. What...Ch. 5 - Twenty people participate in a tug-of-war. The two...Ch. 5 - Can an object exert a force on itself? Argue for...Ch. 5 - When you push on a box with a 200-N force instead...Ch. 5 - A weight lifter stands on a bathroom scale. He...Ch. 5 - An athlete grips a light rope that passes over a...Ch. 5 - Suppose you are driving a classic car. Why should...Ch. 5 - In Figure CQ5.16, the light, taut, unstretchable...Ch. 5 - Describe two examples in which the force of...Ch. 5 - The mayor of a city reprimands some city employees...Ch. 5 - Give reasons for the answers to each of the...Ch. 5 - Balancing carefully, three boys inch out onto a...Ch. 5 - Identity action-reaction pairs in the following...Ch. 5 - As shown in Figure CQ5.22, student A, a 55-kg...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.23CQCh. 5 - A certain orthodontist uses a wire brace to align...Ch. 5 - If a man weighs 900 N on the Earth, what would he...Ch. 5 - A 3.00-kg object undergoes an acceleration given...Ch. 5 - A certain orthodontist uses a wire brace to align...Ch. 5 - A toy rocket engine is securely fastened to a...Ch. 5 - The average speed of a nitrogen molecule in air is...Ch. 5 - The distinction between mass and weight was...Ch. 5 - (a) A cat with a mass of 850 kg in moving to the...Ch. 5 - Review. The gravitational force exerted on a...Ch. 5 - Review. The gravitational force exerted on a...Ch. 5 - Review. An electron of mass 9. 11 1031 kg has an...Ch. 5 - Besides the gravitational force, a 2.80-kg object...Ch. 5 - One or more external forces, large enough to be...Ch. 5 - A brick of mass M has been placed on a rubber...Ch. 5 - Two forces, F1=(6.00i4.00j)N and...Ch. 5 - The force exerted by the wind on the sails of a...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m is dropped al t = 0 from the...Ch. 5 - A force F applied to an object of mass m1,...Ch. 5 - Two forces F1 and F2 act on a 5.00-kg object....Ch. 5 - You stand on the seat of a chair and then hop off....Ch. 5 - A 15.0-lb block rests on the floor. (a) What force...Ch. 5 - Review. Three forces acting on an object are given...Ch. 5 - A 1 00-kg car is pulling a 300-kg trailer....Ch. 5 - If a single constant force acts on an object that...Ch. 5 - Review. Figure P5.15 shows a worker poling a boata...Ch. 5 - An iron bolt of mass 65.0 g hangs from a string...Ch. 5 - Figure P5.27 shows the horizontal forces acting on...Ch. 5 - The systems shown in Figure P5.28 are in...Ch. 5 - Assume the three blocks portrayed in Figure P5.29...Ch. 5 - A block slides down a frictionless plane having an...Ch. 5 - The distance between two telephone poles is 50.0...Ch. 5 - A 3.00-kg object is moving in a plane, with its x...Ch. 5 - A bag of cement weighing 325 N hangs in...Ch. 5 - A bag of cement whose weight is Fg hangs in...Ch. 5 - Two people pull as hard as they can on horizontal...Ch. 5 - Figure P5.36 shows loads hanging from the ceiling...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m = 1.00 kg is observed to have...Ch. 5 - A setup similar to the one shown in Figure P5.38...Ch. 5 - A simple accelerometer is constructed inside a car...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m1 = 5.00 kg placed on a...Ch. 5 - Figure P5.41 shows the speed of a persons body as...Ch. 5 - Two objects are connected by a light string that...Ch. 5 - Two blocks, each of mass m = 3.50 kg, are hung...Ch. 5 - Two blocks, each of mass m, are hung from the...Ch. 5 - In the system shown in Figure P5.23, a horizontal...Ch. 5 - An object of mass m1 hangs from a string that...Ch. 5 - A block is given an initial velocity of 5.00 m/s...Ch. 5 - A car is stuck in the mud. A tow truck pulls on...Ch. 5 - Two blocks of mass 3.50 kg and 8.00 kg arc...Ch. 5 - In the Atwood machine discussed in Example 5.9 and...Ch. 5 - In Example 5.8, we investigated the apparent...Ch. 5 - Consider a large truck carrying a heavy load, such...Ch. 5 - Review. A rifle bullet with a mass of 12.0 g...Ch. 5 - Review. A car is traveling at 50.0 mi/h on a...Ch. 5 - A 25.0-kg block is initially at rest oil a...Ch. 5 - Why is the following situation impassible? Your...Ch. 5 - To determine the coefficients of friction between...Ch. 5 - Before 1960m people believed that the maximum...Ch. 5 - To meet a U.S. Postal Service requirement,...Ch. 5 - A woman at an airport is towing her 20.0-kg...Ch. 5 - Review. A 3.00-kg block starts from rest at the...Ch. 5 - The person in Figure P5.30 weighs 170 lb. As seen...Ch. 5 - A 9.00-kg hanging object is connected by a light,...Ch. 5 - Three objects are connected on a table as shown in...Ch. 5 - Two blocks connected by a rope of negligible mass...Ch. 5 - A block of mass 3.00 kg is pushed up against a...Ch. 5 - Review. One side of the roof of a house slopes up...Ch. 5 - Review. A Chinook salmon can swim underwater at...Ch. 5 - Review. A magician pulls a tablecloth from under a...Ch. 5 - A 5.00-kg block is placed on top of a 10.0-kg...Ch. 5 - The system shown in Figure P5.49 has an...Ch. 5 - A black aluminum glider floats on a film of air...Ch. 5 - A young woman buys an inexpensive used car stock...Ch. 5 - Why is the following situation impossible? A book...Ch. 5 - Review. A hockey puck struck by a hockey stick is...Ch. 5 - A 1.00-kg glider on a horizontal air track is...Ch. 5 - A frictionless plane is 10.0 m long and inclined...Ch. 5 - A rope with mass mr is attached to a block with...Ch. 5 - Two blocks of masses m1 and m2, are placed on a...Ch. 5 - On a single, light, vertical cable that does not...Ch. 5 - An inventive child named Nick wants to reach an...Ch. 5 - In the situation described in Problem 41 and...Ch. 5 - In Example 5.7, we pushed on two blocks on a...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.84APCh. 5 - An object of mass M is held in place by an applied...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.86APCh. 5 - Objects with masses m, = 10.0 kg and nut = 5.00 kg...Ch. 5 - Consider the three connected objects shown in...Ch. 5 - A crate of weight Fg is pushed by a force P on a...Ch. 5 - A student is asked to measure the acceleration of...Ch. 5 - A flat cushion of mass m is released from rest at...Ch. 5 - In Figure P5.46, the pulleys and pulleys the cord...Ch. 5 - What horizontal force must be applied to a large...Ch. 5 - An 8.40-kg object slides down a fixed,...Ch. 5 - A car accelerates down a hill (Fig. P5.95), going...Ch. 5 - A time-dependent force, F = (8.00i - 4.00/j),...Ch. 5 - The board sandwiched between two other boards in...Ch. 5 - Initially, the system of objects shown in Figure...Ch. 5 - A block of mass 2.20 kg is accelerated across a...Ch. 5 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 5 - Review. A block of mass m = 2.00 kg is released...Ch. 5 - In Figure P5.55, the incline has mass M and is...Ch. 5 - A block of mass m = 2.00 kg rests on the left edge...Ch. 5 - A mobile is formed by supporting four metal...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A collection of electric charges that share a common magnitude q (lower case) has been placed at the corners of a square, and an additional charge with magnitude Q (upper case) is located at the center of that square. The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four unique setups of charges are displayed. By moving one of the direction drawings from near the bottom to the bucket beside each of the setups, indicate the direction of the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q, located near the center, else indicate that the magnitude of the net electric force is zero, if appropriate.arrow_forwardA number of electric charges has been placed at distinct points along a line with separations as indicated. Two charges share a common magnitude, q (lower case), and another charge has magnitude Q(upper case). The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four different configurations of charges are shown. For each, express the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q (upper case) as F⃗E=FE,xî where the positive x direction is towards the right. By repositioning the figures to the area on the right, rank the configurations from the most negative value to the most positive value of FE,x.arrow_forwardFor each part make sure to include sign to represent direction, with up being positive and down being negative. A ball is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 30.5 m/s. A) How high does it rise? y= B) How long does it take to reach its highest point? t= C) How long does it take the ball return to its starting point after it reaches its highest point? t= D) What is its velocity when it returns to the level from which it started? v=arrow_forward
- Four point charges of equal magnitude Q = 55 nC are placed on the corners of a rectangle of sides D1 = 27 cm and D2 = 11cm. The charges on the left side of the rectangle are positive while the charges on the right side of the rectangle are negative. Use a coordinate system where the positive y-direction is up and the positive x-direction is to the right. A. Which of the following represents a free-body diagram for the charge on the lower left hand corner of the rectangle? B. Calculate the horizontal component of the net force, in newtons, on the charge which lies at the lower left corner of the rectangle.Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression.Fx = __________________________________________NC. Calculate the vertical component of the net force, in newtons, on the charge which lies at the lower left corner of the rectangle.Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression.Fy = __________________________________________ND. Calculate the magnitude of the…arrow_forwardPoint charges q1=50.0μC and q2=-35μC are placed d1=1.0m apart, as shown. A. A third charge, q3=25μC, is positioned somewhere along the line that passes through the first two charges, and the net force on q3 is zero. Which statement best describes the position of this third charge?1) Charge q3 is to the right of charge q2. 2) Charge q3 is between charges q1 and q2. 3) Charge q3 is to the left of charge q1. B. What is the distance, in meters, between charges q1 and q3? (Your response to the previous step may be used to simplify your solution.)Give numeric value.d2 = __________________________________________mC. Select option that correctly describes the change in the net force on charge q3 if the magnitude of its charge is increased.1) The magnitude of the net force on charge q3 would still be zero. 2) The effect depends upon the numeric value of charge q3. 3) The net force on charge q3 would be towards q2. 4) The net force on charge q3 would be towards q1. D. Select option that…arrow_forwardThe magnitude of the force between a pair of point charges is proportional to the product of the magnitudes of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of their separation distance. Four distinct charge-pair arrangements are presented. All charges are multiples of a common positive charge, q. All charge separations are multiples of a common length, L. Rank the four arrangements from smallest to greatest magnitude of the electric force.arrow_forward
- A number of electric charges has been placed at distinct points along a line with separations as indicated. Two charges share a common magnitude, q (lower case), and another charge has magnitude Q (upper case). The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four different configurations of charges are shown. For each, express the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q (upper case) as F⃗E=FE,xî where the positive x direction is towards the right. By repositioning the figures to the area on the right, rank the configurations from the most negative value to the most positive value of FE,x.arrow_forwardA collection of electric charges that share a common magnitude q (lower case) has been placed at the corners of a square, and an additional charge with magnitude Q (upper case) is located at the center of that square. The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four unique setups of charges are displayed. By moving one of the direction drawings from near the bottom to the bucket beside each of the setups, indicate the direction of the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q, located near the center, else indicate that the magnitude of the net electric force is zero, if appropriate.arrow_forwardIn Dark Souls 3 you can kill the Ancient Wyvern by dropping on its head from above it. Let’s say you jump off the ledge with an initial velocity of 3.86 mph and spend 1.72 s in the air before hitting the wyvern’s head. Assume the gravity is the same as that of Earth and upwards is the positive direction. Also, 1 mile = 1609 m. A) How high up is the the ledge you jumped from as measured from the wyvern’s head? B) What is your velocity when you hit the wyvern?arrow_forward
- A conducting sphere is mounted on an insulating stand, and initially it is electrically neutral. A student wishes to induce a charge distribution similar to what is shown here. The student may connect the sphere to ground or leave it electrically isolated. The student may also place a charged insulated rod near to the sphere without touching it. Q. The diagrams below indicate different choices for whether or not to include a ground connection as well as the sign of the charge on and the placement of an insulating rod. Choose a diagram that would produce the desired charge distribution. (If there are multiple correct answers, you need to select only one of them.)arrow_forwardA person is making pancakes and tries to flip one in the pan. The person is holding the pan a distance y0 = 1.10 m above the ground when they launch the pancake. The pancake just barely touches the ceiling, which is at a height y = 2.47 m above the ground. A) What must be the initial velocity of the pancake to reach that height? B) This person, shocked that they almost hit the ceiling, does not catch it on the way down and the pancake hits the floor. Assuming up as the positive direction, what is the velocity of the pancake when it hits the floor, ruining breakfast and this person’s day?arrow_forwardOne of Spider-Man’s less talked about powers is that he can jump really high. In the comics Spider-Man can jump upwards 3 stories. A) If Spider-Man leaves the ground at 14.3 m/s, how high can he get? y= B) If Spider-Man jumps directly upwards with the initial velocity used above and then returns to the ground, what total amount of time does he spend airborn? t=arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's Third Law of Motion: Action and Reaction; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y61_VPKH2B4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY