
FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMODYNAMICS
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781119634928
Author: Borgnakke
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.64P
A house is cooled by a heat pump driven by an electric motor using the inside as the low−temperature reservoir. The house grains energy in direct proportion to the temperature difference as ˙Qgain=K(TH−TL) . Determine the minimum electric power to drive the heat pump as a function of the two temperatures
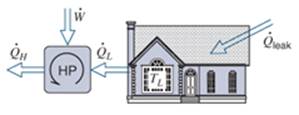
Figure P5.64
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The wheel is rotating with an angular velocity ωω.Determine the velocity of the collar A for the given values of θθ and ϕϕ.
Given:
θ=30∘θ=30∘
ϕ=60∘ϕ=60∘
ω=8 rad/sω=8rad/s
rA=500 mmrA=500mm
rB=150 mmrB=150mm
solve it
moment at A
and Fx then Fy
Determine the speed and acceleration of the mechanism if it has a constant angular velocity of 50 rad/sec counterclockwise from 02
Chapter 5 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMODYNAMICS
Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.1PCh. 5 - A windowmounted air conditioner removes 3.5kJ from...Ch. 5 - R410A enters the evaporator (the cold beat...Ch. 5 - A large heat pump should upgrade 4MW of heat at...Ch. 5 - A car engine 5g/s fuel (equivalent to addition of...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.37PCh. 5 - R134a fills a 0.1m3 capsule at 20°C, 200kPa. It is...Ch. 5 - Air in a piston/ cylinder goes through a Carnot...Ch. 5 - A heat engine receives 7kW from a 300°C source and...Ch. 5 - Consider the previous problem and assume the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Find the deformation of the beam at the free end.arrow_forwardcan you please help[ me conduct Causal Analysis (FTA) on the scenario attatched: FTA diagram which is a fault tree analysis diagram will be used to gain an overview of the entire path of failure from root cause to the top event (i.e., the swing’s detachment) and to identify interactions between misuse, material decay and inspection errors. Do not use Ai.arrow_forwardcan you please help me perform Visual Inspection and Fractography of the attatched image: Preliminary examination to identify the fracture origin, suspected fatigue striation, and corrosion evidences. Do not use Ai.arrow_forward
- For the beam shown, determine: 1) The beam reactions 2) The cutting force and bending moment diagrams including the relevant values. 3) Draw the deformed of the beam (approximate elastic curve). 4) Determine the equation of the charge w(x) 5) Use the fourth-order differential equation: The y'*'* = - w(x) 6) Find the slope and deflection equations (elastic curve) 7) Indicate the slope and deflection values at the free end ( 0в, в)arrow_forwardFor the beam and loads shown, determine the reaction in A and the bending moment equation. Show procedurearrow_forwardFor the beam and loads shown, determine the reaction in the "roller A" Show Procedurearrow_forward
- 1 F/2 F/2 Collar Nut F/2 1F/2 The figure shows a square thread and nut. The axial load is 1000 lb. The friction coefficients (μ and μ) are 0.15. The collar diameter is 1.75 in. The major diameter is 1.25 in and the pitch is 0.2 in. Answer the following questions. (a) Find the torque required to raise and lower the load. (b) What is the efficiency of the power screw during the lift? (c) Without collar, find if the power screw is self-locked or self- lowered.arrow_forward2 - The figure illustrates the connection of a cylinder head to a pressure vessel using 10 bolts and a confined-gasket scal. The effective sealing diameter is 150 mm. Other dimensions are: A 100, B 200, C300, D = 20, and E = 20, all in millimeters. The cylinder is used to store gas at a static pressure of 6 MPa. ISO class 8.8 bolts with a diameter of 12 mm have been selected. This provides an acceptable bolt spacing. What load factor results from this selection? - B Cylinder head and cylinder is Steel (E=207GPa) (a) Find A and A, when 1 is 30mm. (b) Find k₁ and km (Use α=30°). (c) Determine F₁ for permanent connections. (d) Find the factor of safety for bolts (static loading). (e) When the pressure is cycling between 0 and 8MPa, determine the safety factor (for bolts) using Goodman criterion.arrow_forward3 מון Jin -1 in 600 lbf in in 16 UNC 52 in 2in 3in The figure shows a connection that employs three SAE grade 5 bolts. The members are cold-drawn AISI 1020 steel. On the static load, find the shear loads in the bolt having maximum shear load and find the factor of safety for the bolt. Note: Consider 3 threads after nuts.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781133612315Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob ThompsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781133612315Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob ThompsonPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305578296
Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781133612315
Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Heat Transfer [Conduction, Convection, and Radiation]; Author: Mike Sammartano;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kNZi12OV9Xc;License: Standard youtube license