
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
A verification whether the molar conductivity follows the Kohlrausch law has to be done. The value of the limiting molar conductivity has to be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Kohlrausch law:
The molar conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution is equal to the sum of the individual conductances of the anions and cations.
(a)
Answer to Problem 5.56P
The limiting molar conductivity is found to be
Explanation of Solution
According to Kohlrausch law, Molar conductivity of a strong electrolyte weakly depends on concentration. On dilution, there is a regular increase in the molar conductivity, due to the decrease in solute-solute interaction.
Molar conductivity can be mathematically represented as
Where,
Substituting the first set of values and cell constant in the above equation and solving for
Similarly, the rest of the calculation can be done as shown above.
It is clear from the table that molar conductivity of a strong electrolyte weakly depends on concentration as all the values came nearly same. Also it shows that on dilution, there is a regular increase in the molar conductivity.
The graph between
Where,
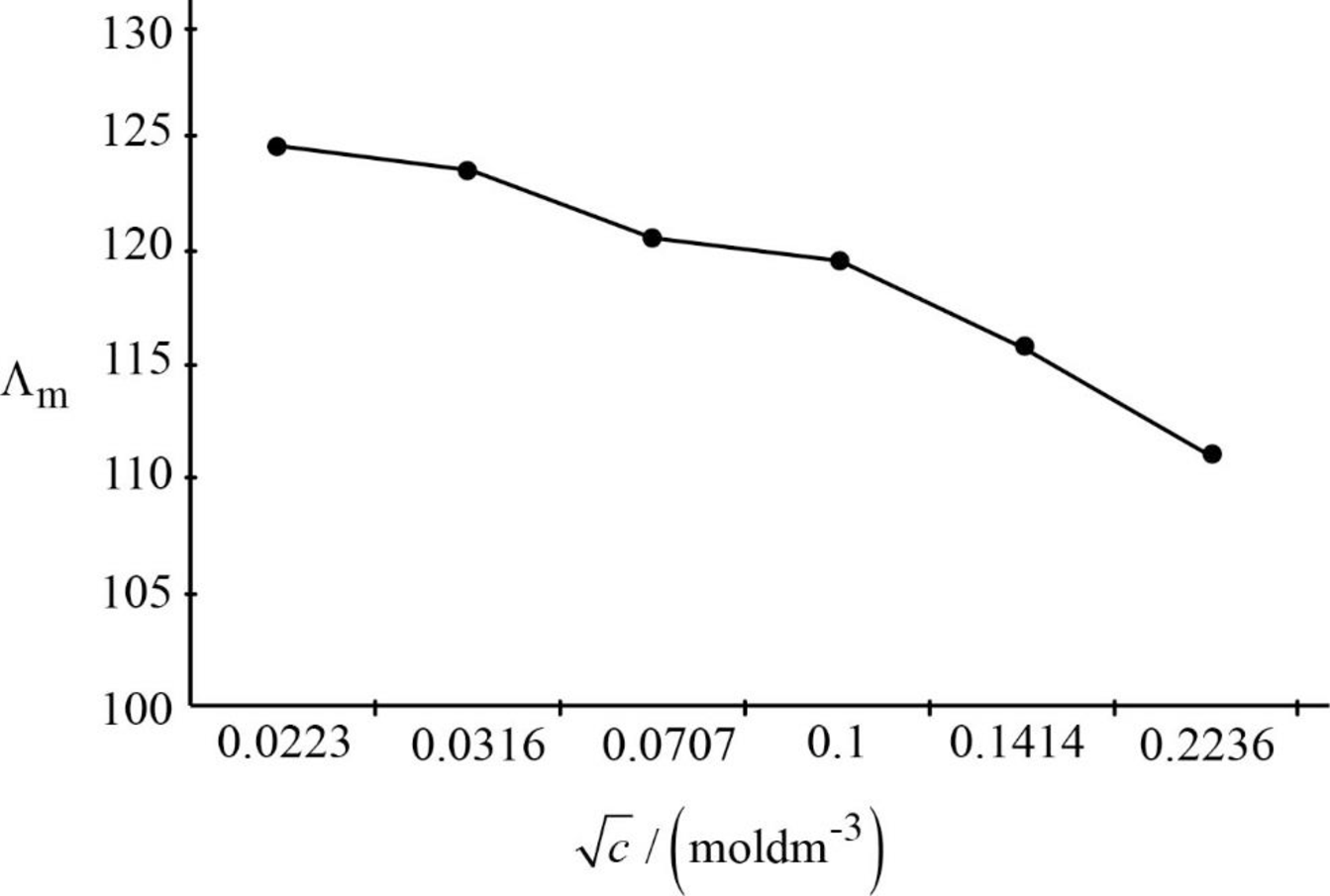
Figure.1
Upon extrapolation the graph, where it will touch on the Y-axis that will be the limiting molar conductivity. Hence, the limiting molar conductivity is around
(b)
Interpretation:
The value of coefficient
Concept Introduction:
Kohlrausch law:
The molar conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution is equal to the sum of the individual conductances of the anions and cations.
(b)
Answer to Problem 5.56P
The value of coefficient
Explanation of Solution
The slope of the graph between
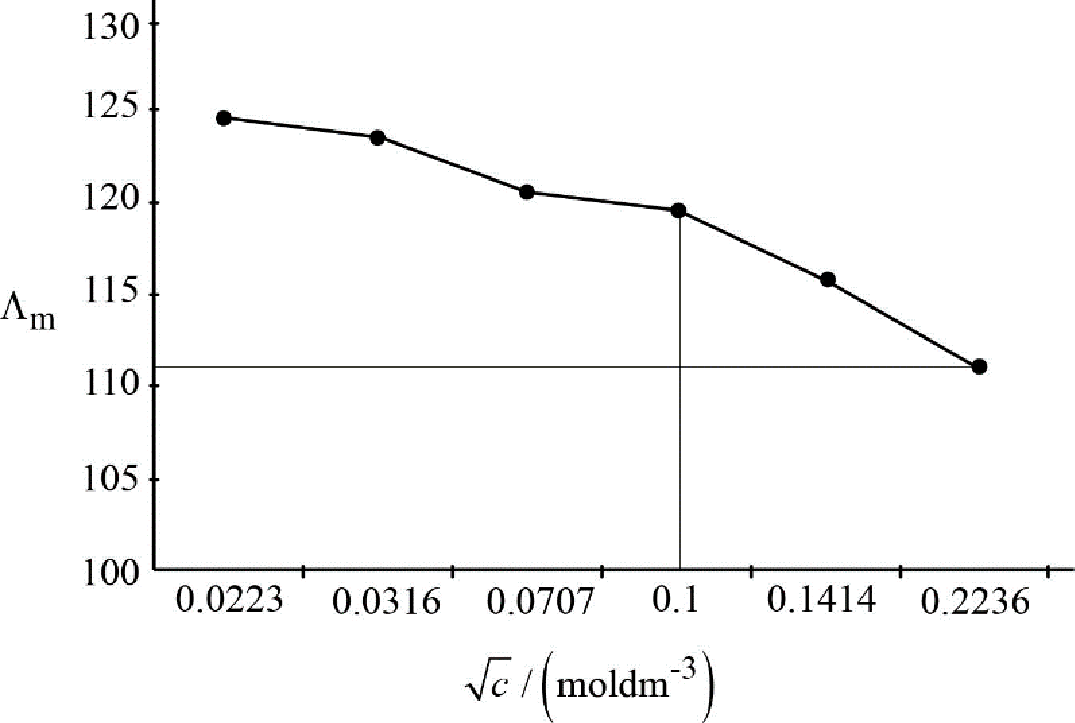
Figure.2
Slope of the graph:
After considering carefully, the unit of
Therefore, the value of coefficient
(c)
Interpretation:
The molar conductivity, conductivity and the resistance of
Concept Introduction:
Kohlrausch law:
The molar conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution is equal to the sum of the individual conductances of the anions and cations.
(c)
Answer to Problem 5.56P
The molar conductivity, conductivity and the resistance of
Explanation of Solution
(I)
Given Data:
The limiting molar conductivity of
Now, molar conductivity
Therefore, the molar conductivity of
(II)
Calculation of conductivity:
Molar conductivity can be mathematically represented as
Where,
Hence, the conductivity can be calculated as
Therefore, the conductivity of
(III)
The conductivity can be further simplified as
Hence, the resistance can be calculated as
Therefore, the resistance of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Elements Of Physical Chemistry
- Please help me Please use https://app.molview.com/ to draw this. I tried, but I couldn't figure out how to do it.arrow_forwardPropose a synthesis of 1-butanamine from the following: (a) a chloroalkane of three carbons (b) a chloroalkane of four carbonsarrow_forwardSelect the stronger base from each pair of compounds. (a) H₂CNH₂ or EtzN (b) CI or NH2 NH2 (c) .Q or EtzN (d) or (e) N or (f) H or Harrow_forward
- 4. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for each of the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a. 2. 1. LDA 3. H3O+ HOarrow_forwardb. H3C CH3 H3O+ ✓ H OHarrow_forward2. Provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the following syntheses. More than one step is required in some cases. a. CH3arrow_forward
- Identify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forwardInstructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





