
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is same or different enantiomer of the shown original molecule is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Isomers are molecules having same connectivity. Enantiomers are nonsuperimposable mirror images. If the molecules can be interconverted by one or more single bond rotation, then they are said to be the same enantiomer or identical molecules. If the molecules are not able to interconvert, then they are enantiomers of each other.
Answer to Problem 5.37P
The given molecule is not same enantiomer as the original one.
Explanation of Solution
The given original enantiomer is:
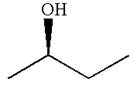
The molecule which is to be compared is:
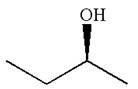
The given molecule is the non superimposable mirror image of THE original molecule.
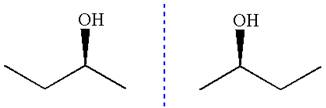
These molecules cannot be interconverted by single bond rotation. Hence, the given molecule is not same enantiomer as the original one.
The molecule is not a same enantiomer as the original molecule is determined on the basis of capability of interconversion by single bond rotation.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is same or different enantiomer of the shown original molecule is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Isomers are the molecules having same connectivity. Enantiomers are nonsuperimposable mirror images. If the molecules can be interconverted by one or more single bond rotation, then they are said to be same enantiomer or identical molecules. If the molecules are not able to interconvert, then they are enantiomers of each other.
Answer to Problem 5.37P
The given molecule is a same enantiomer as the original one.
Explanation of Solution
The given original enantiomer is:
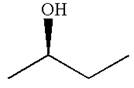
The molecule which is to be compared is:
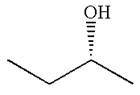
The molecule can be converted to original molecule.
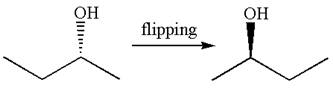
Hence, the given molecule is a same enantiomer as the original one.
The molecule is a same enantiomer as the original molecule is determined on the basis of capability of interconversion by single bond rotation.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is same or different enantiomer of the shown original molecule is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Isomers are the molecules having same connectivity. Enantiomers are nonsuperimposable mirror images. If the molecules can be interconverted by one or more single bond rotation, then they are said to be the same enantiomer or identical molecules. If the molecules are not able to interconvert, then they are enantiomers of each other.
Answer to Problem 5.37P
The given molecule is not a same enantiomer as the original one.
Explanation of Solution
The given original enantiomer is:

The molecule which is to be compared is:
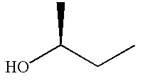
The molecule cannot be converted to the original molecule by single bond rotation.
Hence, the given molecule is not same enantiomer as the original one.
The molecule is not a same enantiomer as original molecule is determined on the basis of capability of interconversion by single bond rotation.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is same or different enantiomer of the shown original molecule is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Isomers are molecules having same connectivity. Enantiomers are nonsuperimposable mirror images. If the molecules can be interconverted by one or more single bond rotation, then they are said to be the same enantiomer or identical molecules. If the molecules are not able to interconvert, then they are enantiomers of each other.
Answer to Problem 5.37P
The given molecule is same enantiomer as the original one.
Explanation of Solution
The given original enantiomer is:
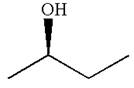
The molecule which is to be compared is:
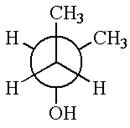
The given Newman projection can be converted to zigzag structure as shown below:
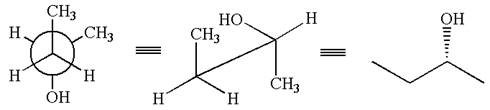
The molecule can be converted to the original molecule.
Hence, the given molecule is same enantiomer as the original one.
The molecule is a same enantiomer as original molecule is determined by converting Newman projection to zigzag structure.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is same or different enantiomer of the shown original molecule is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Isomers are molecules having same connectivity. Enantiomers are nonsuperimposable mirror images. If the molecules can be interconverted by one or more single bond rotation, then they are said to be the same enantiomer or identical molecules. If the molecules are not able to interconvert, then they are enantiomers of each other.
Answer to Problem 5.37P
The given molecule is not a same enantiomer as the original one.
Explanation of Solution
The given original enantiomer is:

The molecule which is to be compared is:
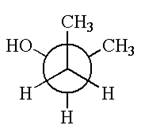
The given Newman projection can be converted to zigzag structure as shown below:
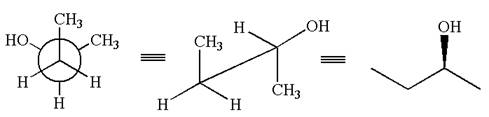
The given molecule is a nonsuperimposable mirror image of the original molecule.
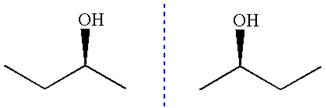
These molecules cannot be interconverted by single bond rotation. Hence, the given molecule is not same enantiomer as the original one.
The molecule is a not the same enantiomer as the original molecule is determined by converting Newman projection to zigzag structure.
(f)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is same or different enantiomer of the shown original molecule it is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Isomers are molecules having same connectivity. Enantiomers are nonsuperimposable mirror images. If the molecules can be interconverted by one or more single bond rotation, then they are said to be same enantiomer or identical molecules. If the molecules are not able to interconvert, then they are enantiomers of each other. In Fischer projection, the horizontal bonds point towards the observer and are denoted as wedge bond in the zigzag structure.
Answer to Problem 5.37P
The given molecule is a same enantiomer as the original one.
Explanation of Solution
The given original enantiomer is:
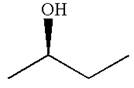
The molecule which is to be compared is:
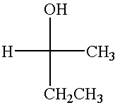
The given Fischer projection can be converted to zigzag structure as shown below:
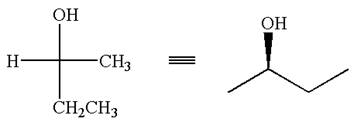
Hence, the given molecule is a same enantiomer as the original one.
The molecule is not a same enantiomer as the original molecule is determined by converting Fischer projection to zigzag structure.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is same or different enantiomer of the shown original molecule is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Isomers are molecules having same connectivity. Enantiomers are nonsuperimposable mirror images. If the molecules can be interconverted by one or more single bond rotation, then they are said to be the same enantiomer or identical molecules. If the molecules are not able to interconvert, then they are enantiomers of each other. In Fischer projection, the horizontal bonds point toward the observer and are denoted as wedge bond in the zigzag structure.
Answer to Problem 5.37P
The given molecule is not a same enantiomer as the original one.
Explanation of Solution
The given original enantiomer is:

The molecule which is to be compared is:
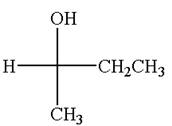
The given Fischer projection can be converted to zigzag structure as shown below:
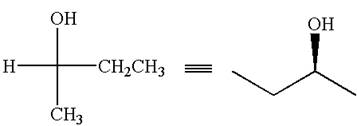
The given molecule is a nonsuperimposable mirror image of the original molecule.
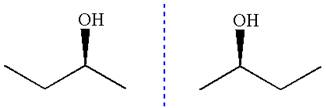
These molecules cannot be interconverted by single bond rotation. Hence, the given molecule is not same enantiomer as the original one.
The molecule is not a same enantiomer as the original molecule is determined by converting Fischer projection to zigzag structure.
(g)
Interpretation:
The given molecule is same or different enantiomer of the shown original molecule it is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Isomers are the molecules having same connectivity. Enantiomers are nonsuperimposable mirror images. If the molecules can be interconverted by one or more single bond rotation, then they are said to be the same enantiomer or identical molecules. If the molecules are not able to interconvert, then they are enantiomers of each other.
Answer to Problem 5.37P
The given molecule is not a same enantiomer as the original one.
Explanation of Solution
The given original enantiomer is:

The molecule which is to be compared is:
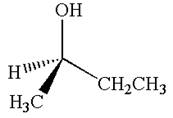
This molecule can be converted to original molecule by single bond rotation.
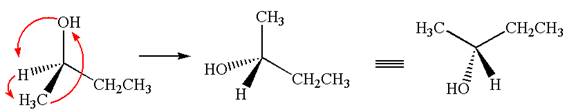
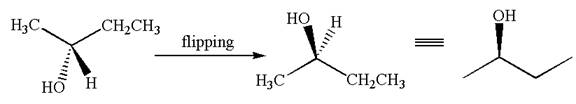
Hence, the given molecule is same enantiomer as the original one.
The molecule is a same enantiomer as the original molecule is determined on the basis of capability of interconversion by single bond rotation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- Which of the following compounds can be synthesized using one reaction from any alkene, as a major product? If it can be synthesized, propose a route, and you may use any other starting materials, reagents and solvents as needed. If you do not think that it can be synthesized as a major product from an alkene, explain in detail why.arrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanism (with arrow pushing)arrow_forwarda) Explain why product 1 is the kinetic product and product 2 is the thermodynamic product. b) Draw the reaction coordinate diagram for the reaction pathway generating each product. c) State the Arrhenius Equation and explain the terms with their physical significance. d) State and explain which reaction pathway has a higher rate constant. What happens to the rate constant if the temperature has increased?arrow_forward
- Part 1. Draw monomer units of the following products and draw their reaction mechanism 1) Bakelite like polymer Using: Resorcinol + NaOH + Formalin 2) Polyester fiber Using a) pthalic anhydride + anhydrous sodium acetate + ethylene glycol B)pthalic anhydride + anhydrous sodium acetate + glycerol 3) Temporary cross-linked polymer Using: 4% polyvinyl alcohol+ methyl red + 4% sodium boratearrow_forwardUsing the table of Reactants and Products provided provide the correct letter that corresponds with the Carboxylic acid that is formed in the reaction below. 6 M NaOH Acid-workup WRITE THE CORRECT LETTER ONLY DO NOT WRITE EXTRA WORDS OR PHRASES A) Pool of Reagents for Part B CI B) OH C) E) CI J) racemic F) K) OH N) OH P) G) OH D) HO H) L) M) HO Q) R) CI Aarrow_forwardIn the table below, the exact chemical structures for Methyl salicylate can be represented by the letter WRITE THE CORRECT LETTER ONLY DO NOT WRITE EXTRA WORDS OR PHRASES CI B) A) E) Cl racemic F) J) CI K) N) OH P) Pool of Reagents for Part B OH OH G) L) OH D) HO H) M) HO Q) R) CIarrow_forward
- Draw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardPart I. a) Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl - 1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forward3. The explosive decomposition of 2 mole of TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene) is shown below: Assume the C(s) is soot-basically atomic carbon (although it isn't actually atomic carbon in real life). 2 CH3 H NO2 NO2 3N2 (g)+7CO (g) + 5H₂O (g) + 7C (s) H a. Use bond dissociation energies to calculate how much AU is for this reaction in kJ/mol.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

