
Concept explainers
The following four structures are naturally occurring optically active compounds. Star (*) the asymmetric carbon atoms in these structures.
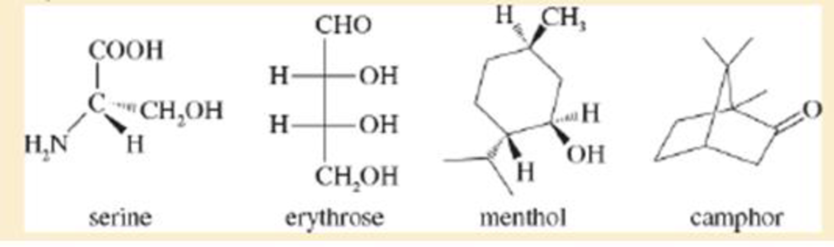
Interpretation: The asymmetric carbon atoms in the given structures are to be marked by star.
Concept introduction: A chiral carbon atom is attached to four different atoms or group of atoms and shows a tetrahedral geometry. The mirror image of a chiral compound is non-super imposable. The two different forms in which a single chiral carbon can exist are referred as enantiomers. The number of enantiomers of a molecule depends on the number of chiral centers.
To determine: The asymmetric carbon atoms in the given structures marked by star.
Answer to Problem 5.25SP
The asymmetric carbon atoms in the given structure have been marked by star.
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is serine. It is attached to
The asymmetric carbon atom present in it is marked by star as shown below.
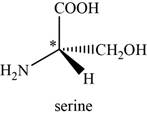
Figure 1
The given compound is erythrose. There are two chiral centres present in it.
The asymmetric carbon atoms present in it are marked by star as shown below.
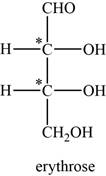
Figure 2
The given compound is menthol. There are three chiral centres present in it.
The asymmetric carbon atoms present in it are marked by star as shown below.
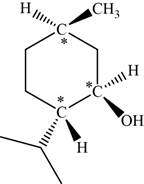
Figure 3
The given compound is camphor. There are two chiral centres present in it.
The asymmetric carbon atoms present in it are marked by star as shown below.
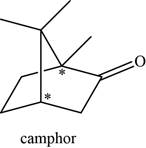
Figure 4
The asymmetric carbon atoms in the given structure have been marked by star.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Pearson eText Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
MARINE BIOLOGY
Organic Chemistry
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- Some of the theories used to describe interface structure can be distinguished by:1. the measured potential difference.2. the distribution of ions in solution.3. the calculation of charge density.4. the external Helmoltz plane.arrow_forwardWhen talking about the acidity of carboxylic acids, is it the same thing to say higher or stronger acidity?arrow_forwardUsing the following two half-reactions, determine the pH range in which $NO_2^-\ (aq)$ cannot be found as the predominant chemical species in water.* $NO_3^-(aq)+10H^+(aq)+8e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+3H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=14.88$* $NO_2^-(aq)+8H^+(aq)+6e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+2H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=15.08$arrow_forward
- Indicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting D-Galactose with hydroxylamine.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div





