
To check
If 1+ cations of homonuclear diatomic molecules of the second-row elements always have shorter bond lengths than the corresponding neutral molecules.
Answer to Problem 5.111QA
Solution:
The cations of homonuclear diatomic molecules of the second row elements do not have shorter bond lengths than the corresponding neutral molecules.
Explanation of Solution
Bond order and bond length are inversely proportional to each other. When bond order increases the bond length decreases and vice versa. We will find out the bond order of neutral diatomic molecules and their 1+ cations. From that we will check if the bond length of the cation is shorter or not.
From the molecular orbital diagram we can find out number of bonding and antibonding electrons. The formula to calculate bond order is as below.
The molecular orbital diagram for the given molecule with the loss of two electrons forming the corresponding 1+ cation is as shown below. With the help of this diagram we will calculate bond order of each molecule and ion of the second row element.
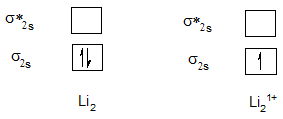
Bond order of Li2 and Li21+.
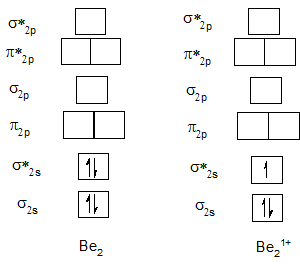
Bond order of Be2 and Be21+.
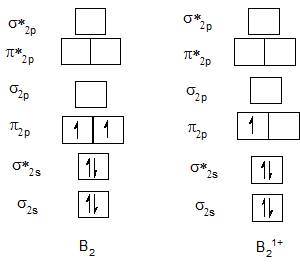
Bond order of B2 and B21+.
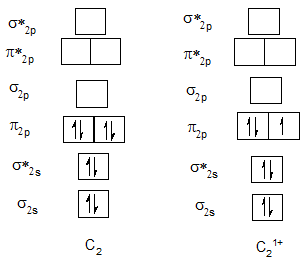
Bond order of C2 and C21+.
Bond order of N2 and N21+.
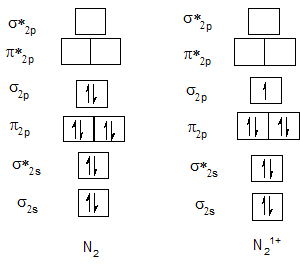
Bond order of O2 and O21+.
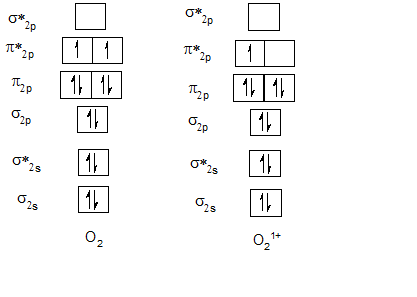
Bond order of F2 and F21+.
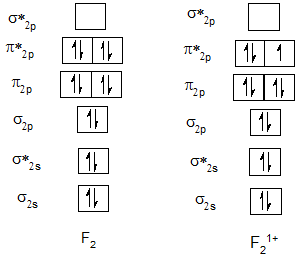
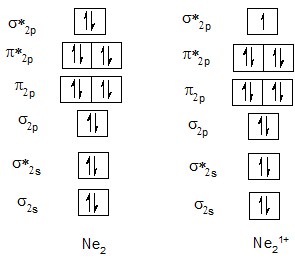
Bond order of Ne2 and Ne21+.
| Neutral diatomic molecule | Bond order of neutral molecule | Molecular cation | Bond order of cation |
| Li2 | 1 | Li21+ | 0.5 |
| Be2 | 0 | Be21+ | 0.5 |
| B2 | 1 | B21+ | 0.5 |
| C2 | 2 | C21+ | 1.5 |
| N2 | 3 | N21+ | 2.5 |
| O2 | 2 | O21+ | 2.5 |
| F2 | 1 | F21+ | 1.5 |
| He2 | 0 | He21+ | 0.5 |
From the bond order of neutral diatomic molecule and bond order of corresponding +1 cation we can say the bond order is not always increasing. Therefore, 1+ cations of homonuclear diatomic molecules of the second-row elements do not always have shorter bond lengths than the corresponding neutral molecules.
Conclusion:
Bond order is inversely proportional to bond length. From bond order of the neutral diatomic molecule and cations we cannot say the bond length is always shorter than neutral atom.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
SMARTWORKS FOR CHEMISTRY: ATOMS FOCUSED
- Please help me solve this reaction.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





