
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(a)
Explanation of Solution
In the marked carbon atom, one s and three p orbital hybridize forming four
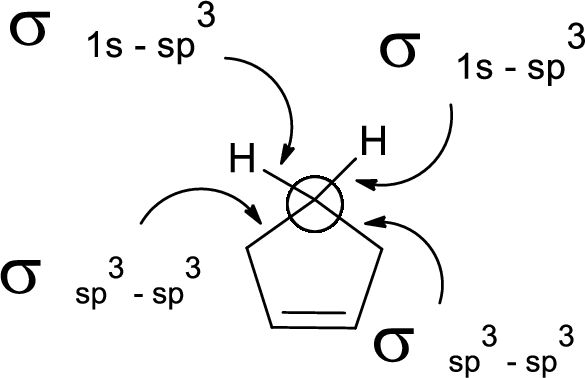
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
(b)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(b)
Explanation of Solution
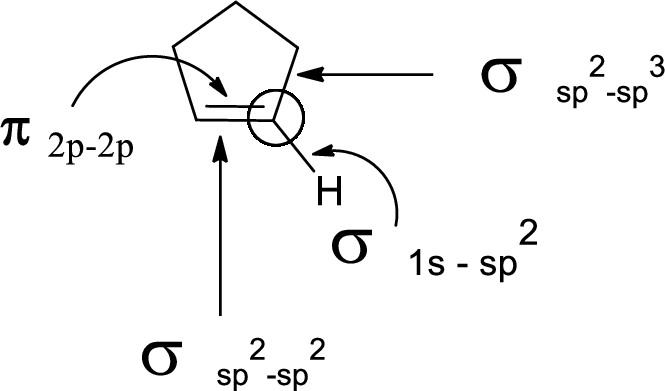
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
(c)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(c)
Explanation of Solution
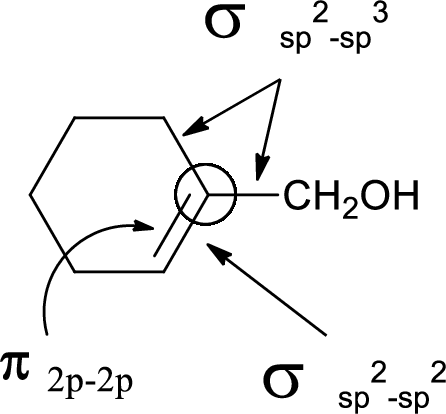
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
(d)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(d)
Explanation of Solution
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
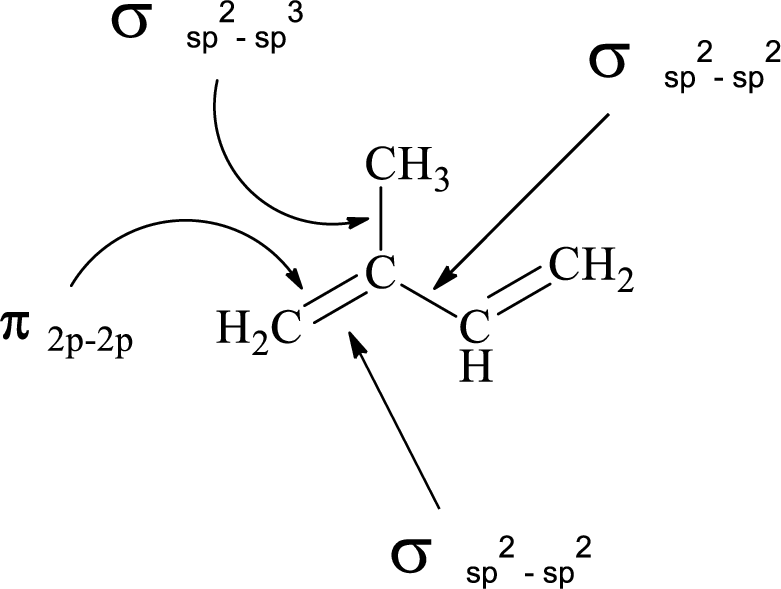
(e)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(e)
Explanation of Solution
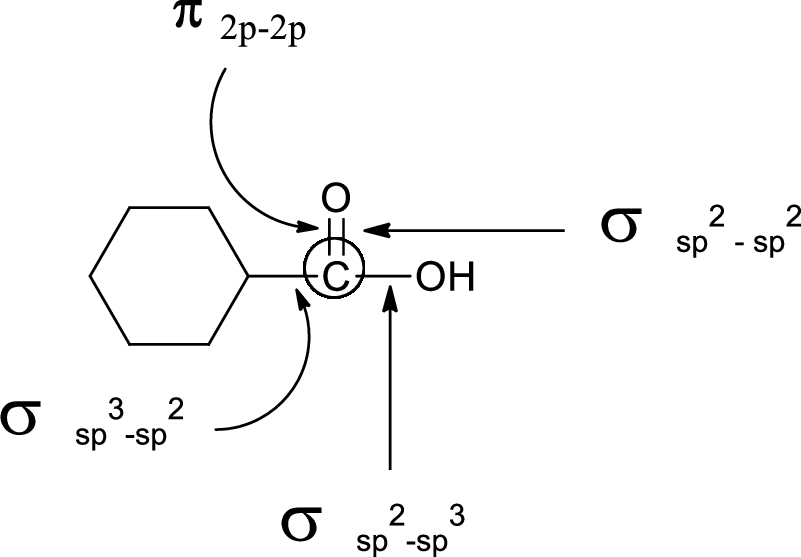
In the marked carbon atom, one s and one p orbital hybridize forming two
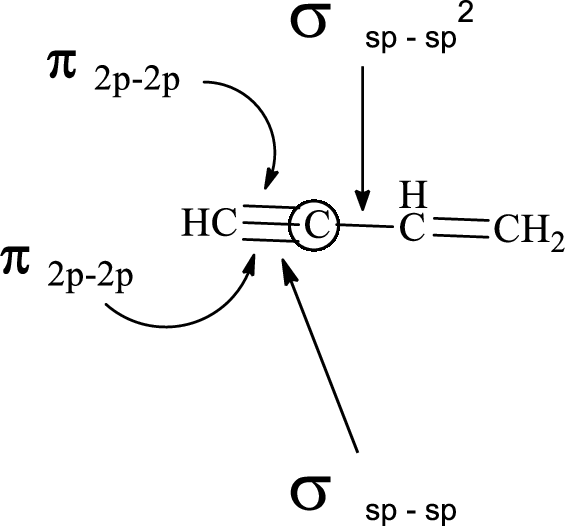
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
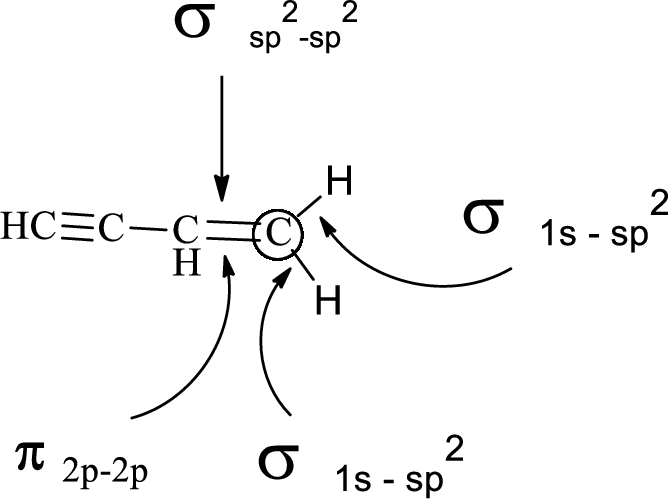
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Choose the major product of the reaction with correct regio- and stereochemistry. Br2 H₂O O "Br Br & O 'Br OH Br 吡 O OH OH Br "OH Brarrow_forwardSelect the major product of the following reaction. & Br (CH)CONa (CH₂),COH 0 OC(CH) O &arrow_forwardDraw the products of the hydrolysis reaction between the ester molecule and water. Determine the products of the following reaction.arrow_forward
- What is the unsaturation number for compounds with the formula C₂H₁₂Cl₂? O õ õ o o 4 3arrow_forwardIndicate the product obtained (formula). F3C. CF3 Br NH2 NH OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forwardWhat are the missing intermediates 1, 2, and 3? Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediates and how they occur.arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax


