
Long-term contract; revenue recognition over time
• LO5–8, LO5–9
In 2018, the Westgate Construction Company entered into a contract to construct a road for Santa Clara County for $10,000,000. The road was completed in 2020. Information related to the contract is as follows: Westgate recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion.
Required:
1. Calculate the amount of revenue and gross profit to be recognized in each of the three years.
2. Prepare all necessary
3. Prepare a partial
4. Calculate the amount of revenue and gross profit to be recognized in each of the three years assuming the following costs incurred and costs to complete information:
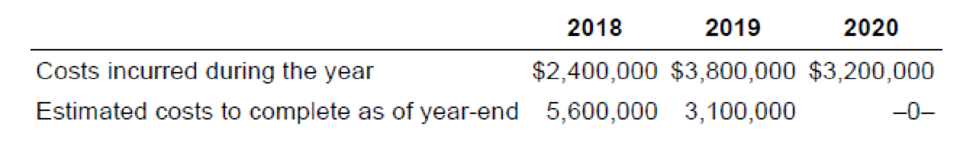
5. Calculate the amount of revenue and gross profit to be recognized in each of the three years assuming the following costs incurred and costs to complete information:
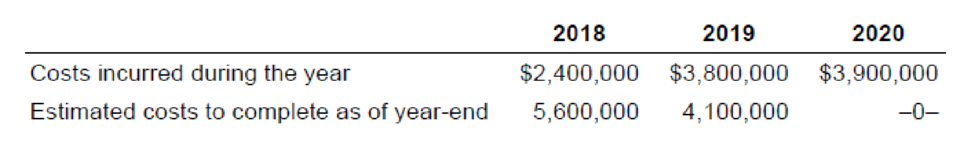
Requirement – 1
Contract
Contract is a written document that creates legal enforcement for buying and selling the property. It is committed by the parties to perform their obligations and enforcing their rights.
Revenue recognized point of long term contract
A long-term contract qualifies for revenue recognition over time. The seller can recognize the revenue as per percentage of the completion of the project, which is recognized by revenue minus cost of completion until date.
If a contract does not meet the performance obligation norm, the seller cannot recognize the revenue till the project complete.
The revenue recognition principle
The revenue recognition principle refers to the revenue that should be recognized in the time period, when the performance obligation (sales or services) of the company is completed.
To determine: The amount of revenue and gross profit or loss to be recognized in 2018, 2019, and 2020.
Explanation of Solution
Recognized revenue
In the year 2018:
Given,
The contract price is $10,000,000
Actual cost to date is $2,400,000
Calculated total estimated cost is $8,000,000(1)
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is $3,000,000.
In the year 2019:
Given,
The contract price is $10,000,000
Actual cost to date is $6,000,000
Calculated total estimated cost is $8,000,000
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is $4,500,000.
In the year 2020:
Given,
Contract price is $10,000,000
Calculated revenue recognition in 2018 is $3,000,000
Calculated revenue recognition in 2019 is $4,500,000
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is$2,500,000.
Recognized gross profit
In the year 2018
Here,
Estimated gross profit in 2018 is $2,000,000 (1)
Total estimated cost is $8,000,000,
Actual cost to date is $2,400,000.
Now, calculate the gross profitrecognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $6,000,000.
In the year 2019
Here,
Estimated gross profit in 2019 is $2,000,000(1)
Total estimated cost is $8,000,000,
Gross profit recognition in 2018 is $6,000,000
Actual cost to date is $6,000,000.
Now, calculate the gross profitrecognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $9,000,000.
In the year 2020
Here,
Estimated gross profit in 2020 is $1,800,000(1)
Gross profit recognition in 2018 is $6,000,000,
Gross profit recognition in 2019 is $9,000,000.
Now, calculate the gross profitrecognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $3,000,000.
Working note:
Calculate the value of gross profit (in millions)
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |||
| Contract price | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | |||
| Actual costs to date | $240 | $600 | $820 | |||
| Estimated costs to complete | $560 | $200 | $0 | |||
| Less: Total estimated cost | $800 | $800 | $820 | |||
| Estimated gross profit | $200 | $200 | $180 | |||
Table (1)
(1)
Requirement – 2
To prepare: The journal entries for the year 2018, 2019 and 2020.
Explanation of Solution
In the year 2018:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Construction in progress | $2,400,000 | |||
| Various accounts | $2,400,000 | |||
| (To record construction cost) |
Table (2)
- Construction in progress is an asset. There is an increase in asset value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Various accounts are revenue. There is an increase in liability value. Therefore, it is credited.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Account receivable | $2,000,000 | |||
| Billings on construction contract | $2,000,000 | |||
| (To record progress billings) |
Table (3)
- Account receivable is an asset. There is an increase in asset value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Billings on construction contract is revenue. There is a decrease in liability value. Therefore, it is debited.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Cash | $1,800,000 | |||
| Account receivable | $1,800,000 | |||
| (To record cash collection) |
Table (4)
- Cash is an asset. There is an increase in asset value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Account receivable is an asset. There is a decrease in asset value. Therefore, it is credited.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Cost of construction | $600,000 | |||
| Construction in progress | $2,400,000 | |||
| Revenue from long-term contracts | $3,000,000 | |||
| (To record gross profit) |
Table (5)
- Cost of constructionis anexpense. There is a decrease in liability value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Construction in progress is an asset. There is an increase in asset value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Revenue from long-term contracts is revenue. There is an increase in liability value. Therefore, it is credited.
In the year 2019:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Construction in progress | $3,600,000 | |||
| Various accounts | $3,600,000 | |||
| (To record construction cost) |
Table (6)
- Construction in progress is an asset. There is an increase in asset value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Various accounts are revenue. There is an increase in liability value. Therefore, it is credited.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Account receivable | $4,000,000 | |||
| Billings on construction contract | $4,000,000 | |||
| (To record progress billings) |
Table (7)
- Account receivable is an asset. There is an increase in asset value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Billings on construction contract is revenue. There is a decrease in liability value. Therefore, it is debited.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Cash | $3,600,000 | |||
| Account receivable | $3,600,000 | |||
| (To record cash collection) |
Table (8)
- Cash is an asset. There is an increase in asset value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Account receivable is an asset. There is a decrease in asset value. Therefore, it is credited.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Cost of construction | $900,000 | |||
| Construction in progress | $3,600,000 | |||
| Revenue from long-term contracts | $4,500,000 | |||
| (To record gross profit) |
Table (9)
- Cost of constructionis anexpense. There is a decrease in liability value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Construction in progress is an asset. There is an increase in asset value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Revenue from long-term contracts is revenue. There is an increase in liability value. Therefore, it is credited.
In the year 2020:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Construction in progress | $2,200,000 | |||
| Various accounts | $2,200,000 | |||
| (To record construction cost) |
Table (10)
- Construction in progress is an asset. There is an increase in asset value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Various accounts are revenue. There is an increase in liability value. Therefore, it is credited.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Account receivable | $4,000,000 | |||
| Billings on construction contract | $4,000,000 | |||
| (To record progress billings) |
Table (11)
- Account receivable is an asset. There is an increase in asset value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Billings on construction contract is revenue. There is a decrease in liability value. Therefore, it is debited.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Cash | $4,600,000 | |||
| Account receivable | $4,600,000 | |||
| (To record cash collection) |
Table (12)
- Cash is an asset. There is an increase in asset value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Account receivable is an asset. There is a decrease in asset value. Therefore, it is credited.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit | Credit |
| Construction in progress | $300,000 | |||
| Cost of construction | $2,200,000 | |||
| Revenue from long-term contracts | $2,500,000 | |||
| (To record gross profit) |
Table (13)
- Construction in progress is an asset. There is an increase in asset value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Cost of constructionis anexpense. There is a decrease in liability value. Therefore, it is debited.
- Revenue from long-term contracts is revenue. There is an increase in liability value. Therefore, it is credited.
Requirement – 3
To prepare: The partial balance sheet for 2018 and 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Partial balance sheet of W Construction Company is as follows:
In the year 2018:
| Assets | 2018 | |
| Account receivables | $200,000 | |
| Construction in progress | $3,000,000 | |
| Less: Billings | ($2,000,000) | |
| Costs in excess of billings | $1,000,000 | |
Table (14)
In the year 2019:
| Assets | 2019 | |
| Account receivables | $600,000 | |
| Construction in progress | $7,500,000 | |
| Less: Billings | ($6,000,000) | |
| Costs in excess of billings | $1,500,000 | |
Table (15)
Requirement – 4
Explanation of Solution
Recognized revenue
In the year 2018:
Given,
The contract price is $10,000,000
Actual cost to date is $2,400,000
Calculated total estimated cost is $8,000,000(1)
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is $3,000,000.
In the year 2019:
Given,
The contract price is $10,000,000
Actual cost to date is $6,200,000
Calculated total estimated cost is $9,300,000
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is $3,666,667.
In the year 2020:
Given,
Contract price is $10,000,000
Calculated revenue recognition in 2018 is $3,000,000
Calculated revenue recognition in 2019 is $3,666,667
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is$3,333,333.
Recognized gross profit
In the year 2018
Here,
Estimated gross profit in 2018 is $2,000,000, (2)
Total estimated cost is $8,000,000,
Actual cost to date is $2,400,000.
Now, calculate the gross profitrecognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $6,000,000.
In the year 2019
Here,
Estimated gross profit in 2019 is $700,000 (2)
Total estimated cost is $9,300,000,
Gross profit recognition in 2018 is $6,000,000
Actual cost to date is $6,200,000.
Now, calculate the gross profitrecognition:
Hence, the calculated gross loss recognition is $133,333.
In the year 2020
Here,
Estimated gross profit in 2020 is $600,000(2)
Gross profit recognition in 2018 is $600,000,
Gross profit recognition in 2019 is -$133,333.
Now, calculate the gross profitrecognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $133,333.
Working note
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Costs incurred during the year | $2,400,000 | $3,800,000 | $3,200,000 |
| Estimated costs to complete as of year-end | $5,600,000 | $3,100,000 |
Calculate the estimated gross profit ($ in millions):
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |||
| Contract price | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | |||
| Actual costs to date | $240 | $620 | $940 | |||
| Estimated costs to complete | $560 | $310 | $0 | |||
| Total estimated cost | $800 | $930 | $940 | |||
| Estimated gross profit | $200 | $70 | $60 | |||
Table (15)
(2)
Requirement – 5
Explanation of Solution
Recognized revenue
In the year 2018:
Given,
The contract price is $10,000,000
Actual cost to date is $2,400,000
Calculated total estimated cost is $8,000,000(1)
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is $3,000,000.
In the year 2019:
Given,
The contract price is $10,000,000
Actual cost to date is $6,200,000
Calculated total estimated cost is $10,300,000
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is $3,019,417.
In the year 2020:
Given,
Contract price is $10,000,000
Calculated revenue recognition in 2018 is $3,000,000
Calculated revenue recognition in 2019 is $3,019,417
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is$3,980,583.
Recognized gross profit
In the year 2018
Here,
Estimated gross profit in 2018 is $2,000,000(3)
Total estimated cost is 8,000,000
Actual cost to date is $2,400,000
Now, calculate the gross profitrecognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $6,000,000.
In the year 2019
Here,
Estimated gross profit in 2019 is -$300,000(3)
Gross profit recognition in 2018 is $6,000,000.
Now, calculate the gross profitrecognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is ($900,000).
In the year 2020
Here,
Estimated gross profit in 2020 is -$100,000 (3)
Gross profit recognition in 2018 is $600,000,
Gross profit recognition in 2019 is -$900,000.
Now, calculate the gross profitrecognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $200,000.
Working note
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Costs incurred during the year | $2,400,000 | $3,800,000 | $3,900,000 |
| Estimated costs to complete as of year-end | $5,600,000 | $4,100,000 |
Calculate the value of estimated gross profit ($ in millions):
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |||
| Contract price | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | |||
| Actual costs to date | $240 | $620 | $1,100 | |||
| Estimated costs to complete | $560 | $410 | $0 | |||
| Less: Total estimated cost | $800 | $1,030 | $1,010 | |||
| Estimated gross profit | $200 | -$30 | -$10 | |||
(3)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Connect Access Card for Intermediate Accounting
- Please explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate explanations.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with the appropriate accounting analysis techniques?arrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this general accounting question with proper steps.arrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this general accounting question using valid accounting techniques?arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forwardCan you explain this general accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forward
