
Concept explainers
1.
Introduction:
Inventory is a record of finished goods of a company which they can sell to the customer, work in progress which can be transformed into finish goods and raw material which is a means of production. Inventory is also classified as a current asset in the
To calculate: Cost assigned to ending inventory and cost of goods sold using FIFO method.
1.
Answer to Problem 4PSB
Cost of goods available for is $249,300 and number of units available for sale is 680
Explanation of Solution
Cost of goods available for sale and number of units available for sale is as follows:
| Date | Particular | Units | Per unit cost | Total cost |
| 1st May | Opening inventory | 150 | 300 | 45000 |
| 6th May | Purchase | 350 | 350 | 122500 |
| 17th May | Purchase | 80 | 450 | 36000 |
| 25th May | purchase | 100 | 458 | 45800 |
| Total | 680 | 249,300 | ||
Thus, cost of goods available for is $249,300 and number of units available for sale is 680
Thus the cost assigned to ending inventory under FIFO method is $88800.
2.
Introduction:
Inventory is a record of finished goods of a company which they can sell to the customer, work in progress which can be transformed into finish goods and raw material which is a means of production. Inventory is also classified as a current asset in the balance sheet and it is valued by FIFO LIFO and weighted average method.
To calculate: Cost assigned to ending inventory and cost of goods sold using FIFO method.
2.
Answer to Problem 4PSB
The number of units in ending inventory is 200 units
Explanation of Solution
The number of units in closing inventory is as follows:
The number of units in ending inventory is 200 units
3.
Introduction:
Inventory is a record of finished goods of a company which they can sell to the customer, work in progress which can be transformed into finish goods and raw material which is a means of production. Inventory is also classified as a current asset in the balance sheet and it is valued by FIFO LIFO and weighted average method.
To compute: Cost assigned to ending inventory and cost of goods sold using LIFO method.
3.
Answer to Problem 4PSB
Cost assigned to ending inventory under FIFO method is $88800, under LIFO method is $62500, using weighted average method is $75600, using specific identification method is $$74,500
Explanation of Solution
- Cost assigned under FIFO method:
- LIFO method:
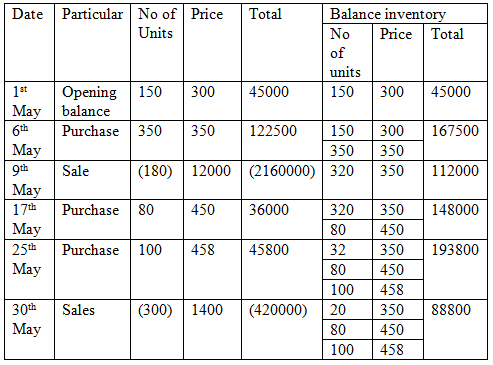
Thus the cost assigned to ending inventory under FIFO method is $88800.
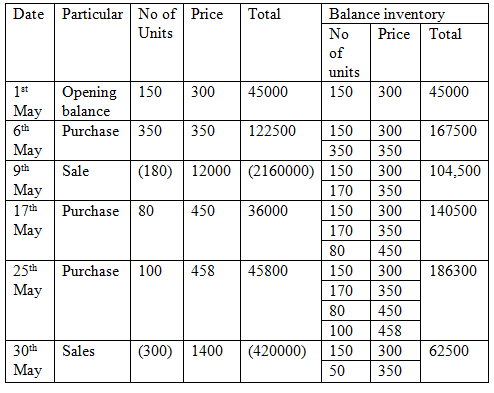
Thus the cost assigned to ending inventory under LIFO method is $62500.
- Calculating the assigned amount of ending inventory according to weighted average method:
- Cost assigned to total inventory using specific identification method:
| Date | Particular | Unit | Cost per unit | Total | Balance inventory | ||
| Units | Cost per unit | Total cost | |||||
| 1st May | Opening balance | 150 | 300 | 45000 | 150 | 300 | 45000 |
| 6th may | Purchase | 350 | 350 | 122500 | 500 | 335 | 167500 |
| 9th may | Sales | 180 | 335 | 60300 | 320 | 335 | 107200 |
| 17th may | Purchase | 80 | 450 | 3600 | 400 | 358 | 143200 |
| 25th may | Purchase | 100 | 458 | 45800 | 500 | 378 | 189000 |
| 30th may | Sales | 300 | 378 | 113400 | 200 | 378 | 75600 |
Thus, cost assigned to ending inventory using weighted average method is $75600
Using specific identification method closing inventory will consist
| Particular | Units | Per unit ($) | Amount ($) |
| Opening Inventory | 70 | 300 | 21000 |
| 6th May | 50 | 350 | 17500 |
| 17th May | 80 | 450 | 36000 |
| Total | $74,500 |
Thus, cost assigned to ending inventory using specific identification method is $$74,500
4.
Introduction:
Inventory is a record of finished goods of a company which they can sell to the customer, work in progress which can be transformed into finish goods and raw material which is a means of production. Inventory is also classified as a current asset in the balance sheet and it is valued by FIFO LIFO and weighted average method.
To compute: The gross profit earn by the company is cost assigned to ending inventory for the company A using FIFO,LIFO and weighted average and specific identification.
4.
Answer to Problem 4PSB
Gross using FIFO methods is $636000 , using LIFO method is $449200, using weighted average method is $460024, and specific identification method is $461200.
Explanation of Solution
Gross profit earn by the company:
Cost of Goods sold:
For FIFO method
For LIFO methods
For weighted average method:
For specific identification:
| Particular | FIFO method | LIFO method | Weighted average method | Specific identification method |
| Total Sales | $636000 | $636000 | $636000 | $636000 |
| Cost of goods sold | $160500 | $186800 | $173700 | $174800 |
| Total | $475,500 | $449200 | $462300 | $461200 |
Thus, gross using FIFO methods is $636000 , using LIFO method is $449200, using the weighted average method is $460024, and specific identification method is $461200.
5.
Introduction:
Inventory is a record of finished goods of a company which they can sell to the customer, work in progress which can be transformed into finish goods and raw material which is a means of production. Inventory is also classified as a current asset in the balance sheet and it is valued by FIFO LIFO and weighted average method.
To compute: The gross profit earn by the company is cost assigned to ending inventory for the company A using FIFO,LIFO and weighted average and specific identification.
5.
Answer to Problem 4PSB
The manager will prefer FIFO method for costing inventory as gross profit is highest in FIFO method so using this method manager will earn more bonuses.
Explanation of Solution
FIFO method yield $475,500 gross profit which highest among other methods. So, the manager will prefer FIFO method for costing inventory as gross profit is highest in the FIFO method so using this method manager will earn more bonuses.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Financial Accounting: Information for Decisions
- Please explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate explanations.arrow_forwardThe total manufacturing costs incurred for the year are $320,000. The overhead cost was 58% of the direct labor cost, and the direct material cost was $42,000. Direct labor cost was _.arrow_forwardStevenson has 250 kilos of metal in the beginning inventory and wants to have 180 kilos In the ending inventory.arrow_forward
- For the year ended December 31, 2020, Malek Inc. earned an ROI of 12.5%. Sales for the year were $25 million, and the average asset turnover was 4.0. Average stockholders' equity was $3.5 million. Required: a. Calculate Malek Inc.'s margin and net income. b. Calculate Malek Inc.'s return on equity.arrow_forwardWhite Co. incurs a cost of $17 per pound to produce Product X, which it sells for $25 per pound. The company can further process Product X to produce Product Y. Product Y would sell for $31 per pound and would require an additional cost of $15 per pound to be produced. The differential cost of producing Product Y is: a. $15 per pound b. $26 per pound c. $13 per pound d. $10 per pound correct answerarrow_forwardQuick answer of this accountingarrow_forward
- Ash Merchandising Company expects to purchase $88,000 of materials in July and $120,000 of materials in August. Three-quarters of all purchases are paid for in the month of purchase, and the other one-fourth are paid for in the month following the month of purchase. How much will August's cash disbursements for materials purchases be?arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting question using standard accounting techniques.arrow_forwardWhat is the labor rate variance for the month ?arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,  Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub





