
1.
Indicate the given adjustments and complete the worksheet for B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Worksheet: Worksheet is an accounting tool that help accountants to record adjustments and up-date balances required to prepare financial statements. Worksheet is a central place where
Indicate the given adjustments and complete the worksheet for B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--.
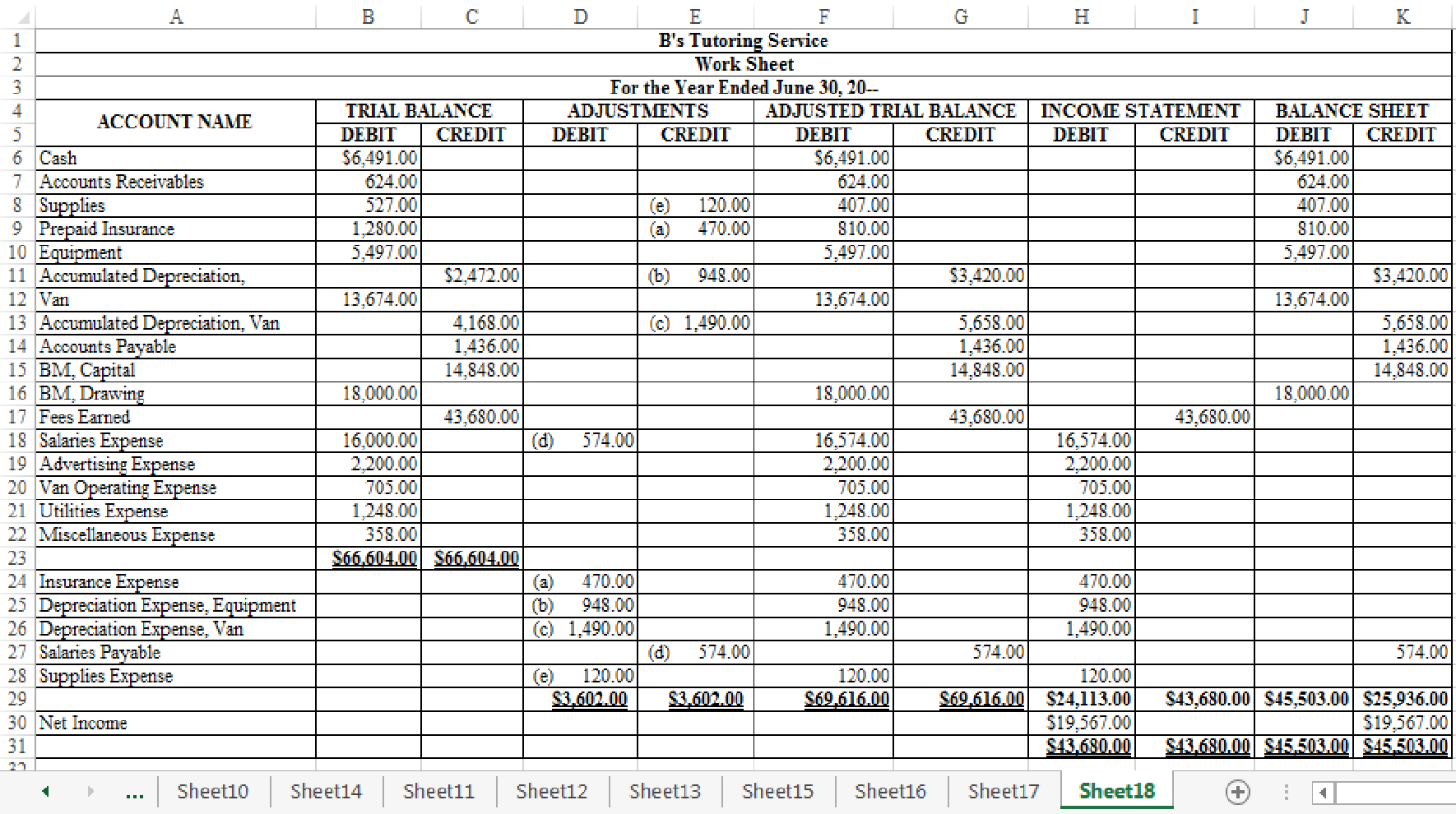
Figure-(1)
2.
Prepare adjusting journal entries for B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Prepare adjusting journal entries for B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--.
Adjusting entry (a) for the prepaid insurance:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| June | 30 | Insurance Expense | 470 | |||
| Prepaid Insurance | 470 | |||||
| (Record part of prepaid insurance expired) | ||||||
Table (1)
Description:
- Insurance Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Prepaid Insurance is an asset account. Since amount of insurance has expired, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Adjusting entry (b) for the
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| June | 30 | Depreciation Expense, Equipment | 948 | |||
| 948 | ||||||
| (Record depreciation expense) | ||||||
Table (2)
Description:
- Depreciation Expense, Equipment is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Accumulated Depreciation, Equipment is a contra-asset account, and contra-asset accounts would have a normal credit balance, hence, the account is credited.
Adjusting entry (c) for the depreciation expense for van:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| June | 30 | Depreciation Expense, Van | 1,490 | |||
| Accumulated Depreciation, Van | 1,490 | |||||
| (Record depreciation expense for van) | ||||||
Table (3)
Description:
- Depreciation Expense, Van is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Accumulated Depreciation, Van is a contra-asset account, and contra-asset accounts would have a normal credit balance, hence, the account is credited.
Adjusting entry (d) for the salaries expense:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| June | 30 | Salaries Expense | 574 | |||
| Salaries Payable | 574 | |||||
| (Record accrued salaries expenses) | ||||||
Table (4)
Description:
- Salaries Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Salaries Payable is a liability account. Since amount of payables has increased, liability decreased, and an increase in liability is credited.
Adjusting entry (e) for the supplies expense:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| June | 30 | Supplies Expense | 120 | |||
| Supplies | 120 | |||||
| (Record part of supplies consumed) | ||||||
Table (5)
Description:
- Supplies Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Supplies is an asset account. Since amount of supplies is used, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
3.
Prepare an income statement for B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--, based on the account balances from worksheet of Part (1).
3.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations, and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare an income statement of B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--.
| B’s Tutoring Service | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the Year Ended June 30, 20-- | ||
| Revenues: | ||
| Fees Earned | $43,680 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Salaries Expense | $16,574 | |
| Advertising Expense | 2,200 | |
| Van Operating Expense | 705 | |
| Utilities Expense | 1,248 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 358 | |
| Insurance Expense | 470 | |
| Depreciation Expense, Equipment | 948 | |
| Depreciation Expense, Van | 1,490 | |
| Supplies Expense | 120 | |
| Total expenses | 24,113 | |
| Net income | $19,567 | |
Table (6)
4.
Prepare a statement of owners’ equity for B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--. (Refer to net income computed in Part (3)).
4.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of owners’ equity: This statement reports the beginning owner’s equity and all the changes which led to ending owners’ equity. Additional capital, net income from income statement is added to, and drawings is deducted from beginning owner’s equity to arrive at the end result, ending owner’s equity.
Prepare a statement of owners’ equity for B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--.
| B’s Tutoring Service | ||
| Statement of Owners’ Equity | ||
| For the Year Ended June 30, 20-- | ||
| BM, Capital, June 1, 20-- | $11,848 | |
| Investment on June 10 | $3,000 | |
| Net income for the year | 19,567 | |
| 22,567 | ||
| Less: Withdrawals for June | 18,000 | |
| Increase in capital | 4,567 | |
| BM, Capital, June 30, 20-- | $16,415 | |
Table (7)
5.
Prepare a balance sheet for B’s Tutoring Service, based on the account balances from work sheet in Part (1), and capital of the owner from the statement of owners’ equity prepared in Part (4).
5.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and owners (owners’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by owners and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity.
Prepare the balance sheet for B’s Tutoring Service as at June 30, 20--.
| B’s Tutoring Service | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| June 30, 20-- | ||
| Assets | ||
| Cash | $6,491 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 624 | |
| Supplies | 407 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 810 | |
| Equipment | $5,497 | |
| Less: Accumulated Depreciation, Equipment | 3,420 | 2,077 |
| Van | 13,674 | |
| Less: Accumulated Depreciation, Van | 5,658 | 8,016 |
| Total Assets | $18,425 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts Payable | $1,436 | |
| Salaries Payable | 574 | |
| Total Liabilities | $2,010 | |
| Owners’ Equity | ||
| BM, Capital | 16,415 | |
| Total Liabilities and Owners’ Equity | $18,425 | |
Table (8)
6.
Prepare closing entries.
6.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries: The journal entries prepared to close the temporary accounts to capital account are referred to as closing entries. The revenue, expense, and drawing accounts are referred to as temporary accounts because the information and figures in these accounts is held temporarily and consequently transferred to permanent account at the end of accounting year.
Steps in closing procedure:
- 1. Close the revenue accounts to Income Summary account.
- 2. Close the expense accounts to Income Summary account.
- 3. Close the Income Summary account and transfer the net income or net loss balance to the Capital account.
- 4. Close the Drawing account to Capital account.
Prepare closing entries.
Step 1: Close the revenue accounts to Income Summary account.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| June | 30 | Fees Earned | 43,680 | |||
| Income Summary | 43,680 | |||||
| (Record closing of revenue to Income Summary account) | ||||||
Table (9)
Description:
- Fees Earned is a revenue account. Revenue account has a normal credit balance. Since revenue is closed to Income Summary account, the account is debited.
- Income Summary is a clearing account which closes revenue, expense, drawings, and net of revenues and expenses to capital accounts. The account is credited to hold the transferred balance from revenue account.
Step 2: Close the expense accounts to Income Summary account.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| Income Summary | 24,113 | |||||
| Salaries Expense | 16,574 | |||||
| Advertising Expense | 2,200 | |||||
| Supplies Expense | 120 | |||||
| Van Operating Expense | 705 | |||||
| Utilities Expense | 1,248 | |||||
| Insurance Expense | 470 | |||||
| Depreciation Expense, Equipment | 948 | |||||
| Depreciation Expense, Van | 1,490 | |||||
| Miscellaneous Expense | 120 | |||||
| (Record closing of expenses to Income Summary account) | ||||||
Table (10)
Description:
- Income Summary is a clearing account which closes revenue, expense, drawings, and net of revenues and expenses to capital accounts. The account is debited to hold the transferred balance from expense accounts.
- Salaries Expense, Advertising Expense, Supplies Expense, Van Operating Expense, Utilities Expense, Insurance Expense, Depreciation Expense-Equipment, Depreciation Expense-Van, and Miscellaneous Expense are expense accounts. Expense account has a normal debit balance. Since expenses are closed to Income Summary account, the accounts are credited.
Step 3: Close the net income to Capital account.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| Income Summary | 19,567 | |||||
| BW, Capital | 19,567 | |||||
| (Record closing of net income to capital account) | ||||||
Table (11)
Description:
- Income Summary is a clearing account which closes revenue, expense, drawings, and net of revenues and expenses to capital accounts. Since net income is closed, the account is reversed, hence, the Income Summary account is debited.
- BM, Capital is a capital account. Since net income is transferred to the account, the value increased, and an increase in capital is credited.
Step 4: Close the Drawing account to Capital account.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| BM, Capital | 18,000 | |||||
| BM, Drawing | 18,000 | |||||
| (Record closing of drawing to capital account) | ||||||
Table (12)
Description:
- BM, Capital is a capital account. Since drawings is transferred to the account, the value decreased, and a decrease in capital is debited.
- BM, Drawing is a capital account. Since drawings is transferred, the account is credited to reverse the previously debited effect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
College Accounting - With Quickbooks 2015 CD and Access
- 5 PTSarrow_forwardPlease given correct answer for General accounting question I need step by step explanationarrow_forwardArmour vacation cabin was destroyed by a wildfire. He had purchased the cabin 14 months ago for $625,000. He received $890,000 from his insurance company to replace the cabin. If he fails to rebuild the cabin or acquire a replacement property in the required time, how much gain must he recognize on this conversion? A. $375,000 B. $160,000 C. $265,000 D. $0 E. None of the above helparrow_forward
- I am looking for the correct answer to this financial accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardResidentside Manufacturing has the following data: direct labor $215,000, direct materials used $185,000, total manufacturing overhead $205,000,and beginning work in process inventory $45,000. Compute the total manufacturing costs and the total cost of work in process.arrow_forwardMC Company made sales to two customers. Both sales were on credit terms of 2/10, n/30. Customer A purchased $30,000 of goods, returned none, and paid in 9 days. Customer B purchased $40,000 of goods, returned, and was given credit for $4,000 of goods and paid in 25 days. What was the net revenue from these two customers?arrow_forward
- Crestview Manufacturing produces a product with a standard direct labor cost of 2.2 hours at $21.75 per hour. During September, 1,850 units were produced using 3,980 hours at $20.25 per hour. The labor quantity variance was $__. No AI ANSWERarrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardFinancial Accountingarrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub


