
Concept explainers
Interpretation of Regression Results: Multiple Choice
Cortez Company is planning to introduce a new product that will sell for $96 per unit. The following
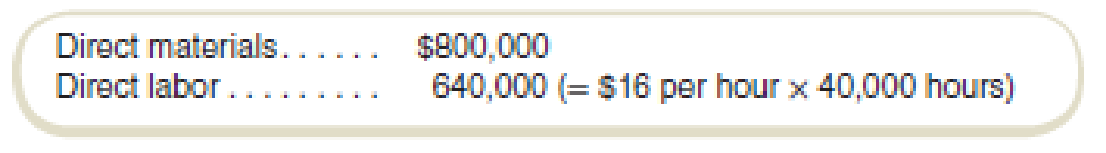
Manufacturing

Required
- a. What percentage of the variation in overhead costs is explained by the independent variable?
- (1) 84.8%.
- (2) 45.0%.
- (3) 92.1%.
- (4) 8.48%.
- (5) Some other amount.
- b. What is the total overhead cost for an estimated activity level of 50,000 direct labor-hours?
- (1) $120,000.
- (2) $370,000.
- (3) $250,000.
- (4) $320,000.
- (5) Some other amount.
- c. How much is the variable manufacturing cost per unit, using the variable overhead estimated by the regression (assuming that direct materials and direct labor are variable costs)?
- (1) $88.00.
- (2) $82.00.
- (3) $86.80.
- (4) $72.00.
- (5) Some other amount.
- d. What is the expected contribution margin per unit to be earned during the first year on 20,000 units of the new product? (Assume that all marketing and administrative costs are fixed.)
- (1) $96.00
- (2) $24.00
- (3) $56.00
- (4) $14.00
- (5) Some other amount.
- e. What is the manufacturing cost equation implied by these results?
- (1) Total cost = $640,000 + ($5.00 × Number of units).
- (2) Total cost = $120,000 + ($86.80 × Number of units).
- (3) Total cost = $120,000 + ($72.00 × Number of units).
- (4) Some other equation.
a.
Identify the appropriate answer for the given statement from the given choices.
Answer to Problem 45E
Option (1) The percentage of the variation in overhead costs is 84.8%.
Explanation of Solution
Regression analysis:
Regression analysis is used to show the relationship between the cost and the activity. It is used to estimate the cost at various level of activity.
The most important step in the calculation of regression analysis is to establish a logical relationship between the cost and the activity. The activity (independent variable) is placed on the right-hand side and the cost (dependent variable) is placed on the left-hand side of the graph.
Percentage of the variation in overhead costs is explained by the independent variable:
The percentage of the variation in overhead costs is 84.8% as per the value of R2.
Justification for the correct and incorrect answer:
(1)
84.8%: This is the correct figure as the value is equal to the value of R2.
(2)
45.0%: This is an incorrect figure as the value is not matching with the value of R2.
(3)
92.1%: This is an incorrect figure as the value is not matching with the correct value of 84.8%.
(4)
$14.00: This is an incorrect figure as the value is not matching with the value of R2.
(5)
Some other amount: This is an incorrect option as the value is 84.8% is given above in the option.
b.
Identify the appropriate answer for the given statement from the given choices.
Answer to Problem 45E
Option (2) The total overhead cost is $370,000.
Explanation of Solution
Total overhead cost:
Total overhead cost is the total cost of the given overhead. It consists of fixed cost and variable cost.
Calculate the total overhead cost:
Thus, the total overhead cost is $370,000.
Justification for the correct and incorrect answer:
(1)
$120,000: This is an incorrect figure as it is not matching with the total overhead cost of $370,000.
(2)
$370,000: This is the correct figure as the total overhead cost is $370,000.
(3)
$250,000: This is an incorrect figure as the value is not matching with the correct value of $370,000.
(4)
$320,000: This is an incorrect figure as the value of total overhead cost is $370,000
(5)
Some other amount: This is an incorrect option as the value is $370,000 is given in the above options.
c.
Identify the appropriate answer for the given statement from the given choices.
Answer to Problem 45E
Option (2) The variable manufacturing cost per unit is $82.
Explanation of Solution
Variable manufacturing cost:
Variable manufacturing cost is the cost of production that varies with the change in the volume of the production.
Calculate the variable manufacturing cost per unit:
Thus, the variable manufacturing cost is $82.
Working note 1:
Calculate the labor cost per unit:
Working note 2:
Calculate the total labor hours:

Justification for the correct and incorrect answer:
(1)
$88.00: This is incorrect figure is not as per the above calculation of 40,000 direct hours.
(2)
$82.00: This is the correct figure as the figure is matching with the calculated figure of $82
(3)
$86.60: This is an incorrect figure as the value is not matching with the correct value of $82.
(4)
$72.00: This is an incorrect figure as the value is $82.00.
(5)
Some other amount: This is an incorrect option as the value is $82.00 is given above option.
d.
Identify the appropriate answer for the given statement from the given choices.
Answer to Problem 45E
Option (4). The expected contribution margin is $14.00.
Explanation of Solution
Contribution margin:
The surplus of sales price over the variable expenses is known as the contribution margin. It is computed by deducting the variable expenses from the sales revenue. The contribution margin income statement is made to record the contribution margin.
Calculate the estimated contribution margin:
Thus, the estimated contribution margin is $14.
Justification for the correct and incorrect answer:
(1)
$96.00: This is an incorrect figure as it is not as per the above-calculated value of $14.
(2)
$24.00: This is an incorrect figure as per the figure is not matching the calculated figure of $14.
(3)
$56.00: This is an incorrect figure as the value is not matching with the correct value of above-calculated figure $56.
(4)
$14.00: This is the correct figure as per the above calculation.
(5)
Some other amount: This is an incorrect option as the value is $14 is given in the above options.
e.
Identify the appropriate answer for the given statement from the given choices.
Answer to Problem 45E
Option (4) The manufacturing cost equation is:
Explanation of Solution
Cost equation:
Cost equation is a mathematical representation of the cost estimation at various level of activity. It is used by defining the fixed cost, and variable cost per unit. The variable cost per unit is multiplied by the given variable to calculate the relative cost.
Calculate the manufacturing cost equation:
Thus, the manufacturing cost equation is:
Justification for the correct and incorrect answer:
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Some other equation: This is the correct figure as the correct answer is not given in any of the above options.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF...(LL)-W/ACCESS>CUSTOM<
- Provide correct answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardChapter 15 Homework 13 Saved Help Save & Exit Submit Part 1 of 2 0.83 points eBook Ask Required information Use the following information to answer questions. (Algo) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Information on Kwon Manufacturing's activities for its first month of operations follows: a. Purchased $100,800 of raw materials on credit. b. Materials requisitions show the following materials used for the month. Job 201 Job 202 Total direct materials Indirect materials Total materials used $ 49,000 24,400 73,400 9,420 $ 82,820 c. Time tickets show the following labor used for the month. Print References Job 201 $ 40,000 Job 202 13,400 Total direct labor 53,400 25,000 $ 78,400 Indirect labor Total labor used d. Applied overhead to Job 201 and to Job 202 using a predetermined overhead rate of 80% of direct materials cost. e. Transferred Job 201 to Finished Goods Inventory. f. Sold Job 201 for $166,160 on credit. g. Incurred the following actual other…arrow_forwardquesrion 2arrow_forward
- Anti-Pandemic Pharma Co. Ltd. reports the following information in its income statement: Sales = $5,250,000; Costs = $2, 173,000; Other expenses = $187,400; Depreciation expense = $79,000; Interest expense= $53,555; Taxes $76,000; Dividends $69,000. $136,700 worth of new shares were also issued during the year and long-term debt worth $65,300 was redeemed. a) Compute the cash flow from assets b) Compute the net change in working capital (325 marks)arrow_forwardQS 15-18 (Algo) Computing and recording over- or underapplied overhead LO P4 A company applies overhead at a rate of 170% of direct labor cost. Actual overhead cost for the current period is $1,081,900, and direct labor cost is $627,000. 1. Compute the under- or overapplied overhead. 2. Prepare the journal entry to close over- or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Compute the under- or overapplied overhead.arrow_forwardQuestion 6 During 2019, Bitsincoins Corporation had EBIT of $100,000, a change in net fixed assets of $400,000, an increase in net current assets of $100,000, an increase in spontaneous current liabilities of $400,000, a depreciation expense of $50,000, and a tax rate of 30%. Based on this information, what is Bitsincoin's free cash flow? (3 marks)arrow_forward
- Question 4 Waterfront Inc. wishes to borrow on a short-term basis without reducing its current ratio below 1.25. At present its current assets and current liabilities are $1,600 and $1,000 respectively. How much can Waterfront Inc. borrow? (5 marks)arrow_forwarddiscus extensivery source of bussines finances requaments not less than 4 pages font size 12 spacing 1.5 roman times references must be less thhan 5arrow_forwardCalculate stricklers cash conversion cycle?arrow_forward
 Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning



