
Concept explainers
1.
Compute the activity based costs that must be assigned to each branch of Incorporation M.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Activity Based Costing:
Activity based costing is a method of costing adopted by a company. Under this method, the activities in production are identified and the cost of each activity is assigned to all their products and services. An activity based costing can be used to recognize the resources spent by the company on activities that are performed in manufacturing the product or providing a service.
Compute the relative use of the cost driver by each office of Incorporation M:
| Timesheet entries | City CO | City CI | City D | Total |
| Direct labor cost | 37.61% | 31.19% | 31.20% | 100.00% |
| Timesheet entries | 45.11% | 28.57% | 26.32% | 100.00% |
| Vendor Invoices | 44.93% | 37.44% | 17.62% | 100.00% |
| Client invoices | 52.13% | 39.36% | 8.51% | 100.00% |
| Employees | 34.33% | 38.81% | 26.87% | 100.00% |
| New hires | 42.11% | 21.05% | 36.84% | 100.00% |
| Insurance claims filed | 34.33% | 38.81% | 26.87% | 100.00% |
| Proposals | 39.22% | 49.02% | 11.76% | 100.00% |
| Contracted sales | 48.07% | 36.88% | 15.05% | 100.00% |
| Projects shipped | 39.13% | 49.01% | 11.86% | 100.00% |
| Purchase orders | 41.54% | 33.85% | 24.62% | 100.00% |
| Copies duplicated | 43.48% | 39.13% | 17.39% | 100.00% |
| Blueprints | 45.24% | 36.19% | 18.56% | 100.00% |
Table (1)
Compute the activity based costs that must be assigned to each branch of Incorporation M.
| Activity-based | |||||
| (in thousands) | |||||
| Cost Driver | City CO | City CI | City D | Total | |
| General administration | Direct labor cost | $153.82 | $127.56 | $127.60 | $409 |
| Project costing | Timesheet entries | $21.65 | $13.71 | $12.63 | $48 |
| Accounts payable/receiving | Vendor Invoices | $62.46 | $52.05 | $24.49 | $139 |
| Client invoices | $24.50 | $18.50 | $4.00 | $47 | |
| Payroll/Mail sort and delivery | Employees | $10.30 | $11.64 | $8.06 | $30 |
| Personnel recruiting | New hires | $16.00 | $8.00 | $14.00 | $38 |
| Employee insurance processing | Insurance claims filed | $4.81 | $5.43 | $3.76 | $14 |
| Proposals | Proposals | $54.51 | $68.14 | $16.35 | $139 |
| Sales meetings/Sales aids | Contracted sales | $97.10 | $74.49 | $30.40 | $202 |
| Shipping | Projects shipped | $9.39 | $11.76 | $2.85 | $24 |
| Ordering | Purchase orders | $19.94 | $16.25 | $11.82 | $48 |
| Duplicating costs | Copies duplicated | $20.00 | $18.00 | $8.00 | $46 |
| Blueprinting | Blueprints | $34.84 | $27.87 | $14.29 | $77 |
| Total | $529.32 | $453.40 | $278.25 | $1,261 | |
Table (2)
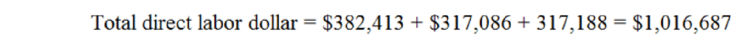
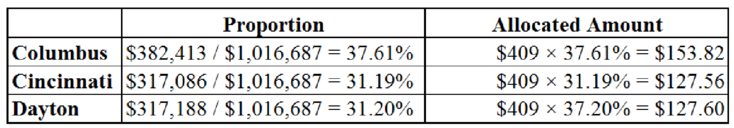
Table (3)
2.
Compute the contribution margin of each branch of Incorporation M.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the contribution margin of each branch of Incorporation M.
| Contribution of Each Branch | ||||
| (in thousands) | ||||
| City CO | City CI | City D | Total | |
| Sales | $1,500 | $1,419 | $1,067 | $3,986 |
| Less: Direct labor | $382 | $317 | $317 | $1,016 |
| Direct materials | $281 | $421 | $185 | $887 |
| Direct overhead | $180 | $270 | $177 | $627 |
| Contribution margin | $657 | $411 | $388 | $1,456 |
Table (4)
3.
Compute the profitability of each branch of Incorporation M.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the profitability of each branch of Incorporation M.
| City CO | City CI | City D | Total | |
| Sales | $1,500 | $1,419 | $1,067 | $3,986 |
| Less: Direct labor | $382 | $317 | $317 | $1,016 |
| Direct materials | $281 | $421 | $185 | $887 |
| Direct overhead | $180 | $270 | $177 | $627 |
| Contribution margin | $657 | $411 | $388 | $1,456 |
| Activity-based overhead | $529 | $453 | $278 | $0 |
| Operating income | $128 | ($42) | $110 | $1,456 |
Table (5)
4.
Provide information on the concern of the management regarding the volume based cost techniques that are currently being used.
4.
Explanation of Solution
The overhead cost are normally aggregated in pools and are allocated to products and other cost objects depending on their volume measures. Therefore, the cost object proportionately shares those costs required for production. The product cost will be determined incorrectly if the overhead costs differ in accordance with variables rather than volume.
From the computed results, the profitability of Cincinnati and Dayton office is employing different direct tracing and activity based costing under their current approach. The prevailing marketing strategy promotes an inaccurate location and strategic planning that may be subject to assumptions associated with profitability.
The results also points to the fact that activity based costs are applicable to service organizations as well as manufacturing organizations. Therefore, the better the information on profitability of cost object, better the chances of keeping the organization profitable.
The process of identifying activities and allocating the costs from the general ledger to the activities is a time consuming and a costly process. This is due to the fact that extensive interviews with functional mangers are normally required for this phase.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Cost Management: A Strategic Emphasis

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





