
1.
Compute the cost per set and the total production cost of the three customer groups of F Company using activity based costing.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Activity Based Costing: Activity based costing is a method of costing adopted by a company. Under this method, the activities in production are identified and the cost of each activity is assigned to all their products and services. An activity based costing can be used to recognize the resources spent by the company on activities that are performed in manufacturing the product or providing a service.
Step 1: Compute the total levels of activity cost drivers of F Company.
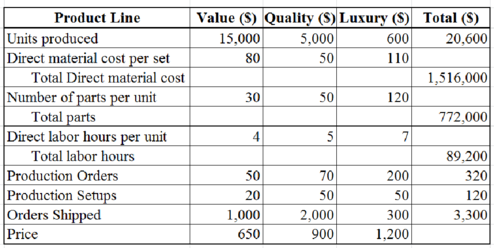
Table (1)
Step 2: Compute total activity rates of F Company.
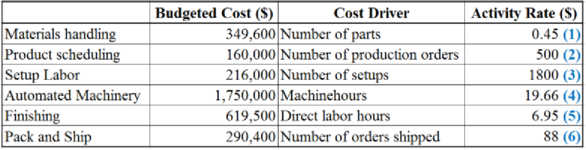
Table (2)
Working Notes:
(1) Compute the activity rate of F Company with respect to number of parts.
(2) Compute the activity rate of F Company with respect to number of production orders.
(3) Compute the activity rate of F Company with respect to number of setups.
(4) Compute the activity rate of F Company with respect to machine hours.
(5) Compute the activity rate of F Company with respect to direct labor hours.
(6) Compute the activity rate of F Company with respect to number of orders shipped.
Step 3:
Compute the unit and total cost of F Company.
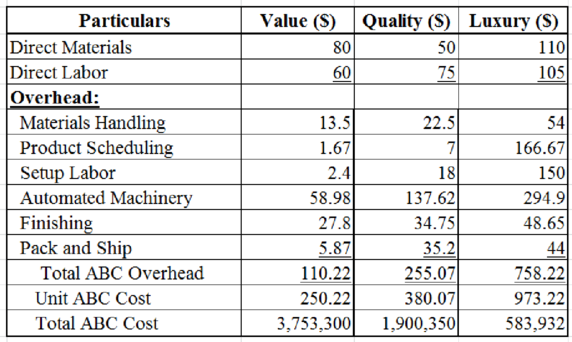
Table (3)
2.
Compute the production cost of each of the three customer groups of F Company using the current volume based approach of the company.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the production cost of each of the three customer groups of F Company using the current volume based approach of the company.
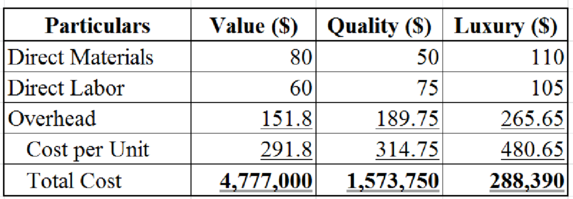
Table (4)
3.
Compute the revised activity rate of F Company and provide information on the costing of products and its strategic planning using the additional information.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the revised activity rate of F Company and provide information on the costing of products and its strategic planning using the additional information.
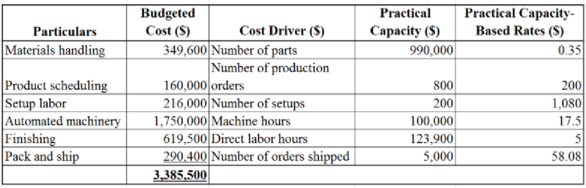
Table (5)
A significant change is observed in the activity rates that were computed in the above requirement. This is due to a notable level of unused capacity in many activities. This additional information can be utilized by the management to compute the activity based costs by using practical capacity rates. The information regarding utilization of capacity can be used to help bring the spending of resources in line with the resource usage. Additional capacity will be required in the luxury segment since the firm has plans of further growth. Therefore, a careful plan will enable them to balance their planned future capacity needs against their current spending on such resources that may allow the reduction of capacities. The potential for overcapacity seems to be highest in the activity of product scheduling and pack and ship.
4.
Provide information on the competitive and strategic issues by comparing both the costing approaches.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the profitability of F Company with respect to their customer group.
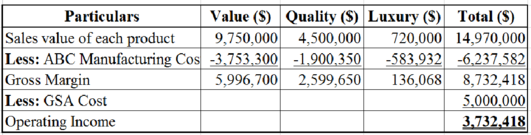
Table (6)
Compute the budgeted activity based cost of F Company.
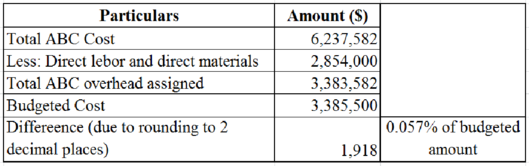
Table (7)
- The results obtained from activity based costing indicate that luxury group is expensive to produce for the company. However, the volume based approach failed to account for the activity usage of the luxury line of products and it resulted in direct under-costing.
- Activity based costing enables the company to understand how their costs will increase along with their increase in producing the luxury line of products. This will help them to understand the manner in which the company will have to adapt their pricing policies accordingly. Using volume based costing can undermine the profitability of the entire firm by underpricing the luxury line. This will happen if the continued use of volume based approach when the sales of the luxury line are increasing.
- From the calculated results, it is concluded that luxury group is marginally profitable out of the three customer groups.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Cost Management: A Strategic Emphasis
- Journal Entries Rocky Mountain Tours Co. is a travel agency. The nine transactions recorded by Rocky Mountain Tours during June 20Y2, its first month of operations, are indicated in the following T accounts: Cash (1) 40,000 (2) 4,000 (7) 13,100 (3) 5,000 (4) 6,175 (6) 6,000 (9) 1,500 Equipment (3) 15,000 Dividends (9) 1,500 Accounts Receivable Accounts Payable Service Revenue (5) 20,500 (7) 13,100 (6) 6,000 (3) 10,000 (5) 20,500 Supplies (2) 4,000 (8) 2,200 Common Stock (1) 40,000 Operating Expenses (4) 6,175 (8) 2,200 Prepare the nine journal entries from which the postings were made. Journal entry explanations may be omitted. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.arrow_forwardInnovative Consulting Co. has the following accounts in its ledger: Cash, Accounts Receivable, Supplies, Office Equipment, Accounts Payable, Common Stock, Retained Earnings, Dividends, Fees Earned, Rent Expense, Advertising Expense, Utilities Expense, Miscellaneous Expense. Journalize the following selected transactions for October 2012 in a two-column journal. Journal entry explanations may be omitted. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. Oct. 1. Paid rent for the month, $2,500. 4. Paid advertising expense, $1,000. 5. Paid cash for supplies, $1,800. 6. Purchased office equipment on account, $11,500. 12. Received cash from customers on account, $7,500. 20. Paid creditor on account, $2,700. 27. Paid cash for miscellaneous expenses, $700. 30. Paid telephone bill for the month, $475. 31. Fees earned and billed to customers for the month, $42,400. 31. Paid electricity bill for the month, $900. 31. Paid dividends, $1,500.arrow_forwardCash Accounts Receivable Supplies Prepaid Insurance Equipment Notes Payable Accounts Payable Debit Balances Credit Balances 20,350 37,000 1,100 200 171,175 36,000 26,000 Common Stock 50,000 Retained Earnings 94,150 Dividends 15,000 Fees Earned 429,850 Wages Expense 270,000 Rent Expense 63,000 Advertising Expense 25,200 Miscellaneous Expense 5,100 608,125 636,000arrow_forward
- On October 1, 20Y6, Jay Crowley established Affordable Realty, which completed the following transactions during the month: Oct. 1 Jay Crowley transferred cash from a personal bank account to an account to be used for the business in exchange for common stock, $40,000. 2 Paid rent on office and equipment for the month, $4,800. 3 Purchased supplies on account, $2,150. 4 Paid creditor on account, $1,100. 10 5 Earned sales commissions, receiving cash, $18,750. 6 Paid automobile expenses (including rental charge) for month, $1,580, and miscellaneous expenses, $800. 7 Paid office salaries, $3,500. 8 Determined that the cost of supplies used was $1,300. 9 Paid dividends, $1,500.arrow_forwardReese, a calendar-year taxpayer, uses the cash method of accounting for her sole proprietorship. In late December, she received a $20,000 bill from her accountant for consulting services related to her small business. Reese can pay the $20,000 bill anytime before January 30 of next year without penalty. Assume Reese’s marginal tax rate is 32 percent this year and will be 37 percent next year, and that she can earn an after-tax rate of return of 12 percent on her investments. a. What is the after-tax cost if she pays the $20,000 bill in December? b. What is the after-tax cost if she pays the $20,000 bill in January 30? Use Exhibit 3.1. (Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Exhibit 3.1 below 4% 5% 6% 7% 8% 9% 10% 11% 12% Year 1 .962 .952 .943 .935 .926 .917 .909 .901 .893 Year 2 .925 .907 .890 .873 .857 .842 .826 .812 .797 Year 3 .889 .864 .840 .816 .794 .772 .751 .731 .712 Year 4 .855 .823 .792 .763 .735 .708 .683 .659 .636 Year 5…arrow_forwardManny, a calendar-year taxpayer, uses the cash method of accounting for his sole proprietorship. In late December he performed $20,000 of legal services for a client. Manny typically requires his clients to pay his bills immediately upon receipt. Assume Manny’s marginal tax rate is 37 percent this year and next year, and that he can earn an after-tax rate of return of 12 percent on his investments. a. What is the after-tax income if Manny sends his client the bill in December? b. What is the after-tax income if Manny sends his client the bill in January? Use Exhibit 3.1. (Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Exhibit 3.1 below 4% 5% 6% 7% 8% 9% 10% 11% 12% Year 1 .962 .952 .943 .935 .926 .917 .909 .901 .893 Year 2 .925 .907 .890 .873 .857 .842 .826 .812 .797 Year 3 .889 .864 .840 .816 .794 .772 .751 .731 .712 Year 4 .855 .823 .792 .763 .735 .708 .683 .659 .636 Year 5 .822 .784 .747 .713 .681 .650 .621 .593 .567 Year 6 .790 .746…arrow_forward
- Rocky Mountain Tours Co. is a travel agency. The nine transactions recorded by Rocky Mountain Tours during June 20Y2, its first month of operations, are indicated in the following T accounts: Cash (1) 40,000 (2) 4,000 (7) 13,100 (3) 5,000 (4) 6,175 (6) 6,000 (9) 1,500 Equipment (3) 15,000 Dividends (9) 1,500 Accounts Receivable Accounts Payable Service Revenue (5) 20,500 (7) 13,100 (6) 6,000 (3) 10,000 (5) 20,500 Supplies (2) 4,000 (8) 2,200 Common Stock (1) 40,000 Operating Expenses (4) 6,175 (8) 2,200 a. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance. List all the accounts in the order of Assets, Liabilities, Stockholders' equity, Revenues, and Expenses. Place the amounts in the proper columns. If an entry is not required in an amount box, leave it blank.arrow_forwardTransactions and T Accounts The following selected transactions were completed during July of the current year: 1. Billed customers for fees earned, $112,700. 2. Purchased supplies on account, $4,500. 3. Received cash from customers on account, $88,220. 4. Paid creditors on account, $3,100. a. Journalize these transactions in a two-column journal, using the appropriate number to identify the transactions. Journal entry explanations may be omitted. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. (1) Accounts Receivable Fees Earned (2) Supplies Accounts Payable (3) Cash Accounts Receivable (4) Accounts Payable Casharrow_forwardIsabel, a calendar-year taxpayer, uses the cash method of accounting for her sole proprietorship. In late December she received a $20,000 bill from her accountant for consulting services related to her small business. Isabel can pay the $20,000 bill anytime before January 30 of next year without penalty. Assume her marginal tax rate is 37 percent this year and next year, and that she can earn an after-tax rate of return of 12 percent on her investments. a. What is the after-tax cost if Isabel pays the $20,000 bill in December? b. What is the after-tax cost if Isabel pays the $20,000 bill in January? Use Exhibit 3.1. (Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.) c. Based on requirements a and b, should Isabel pay the $20,000 bill in December or January? multiple choice December Januaryarrow_forward
- Answer correctly plz otherwise unhearrow_forwardFinancial accountingarrow_forwardWhen privately-held Toys "R" Us filed for bankruptcy in fall 2017, it disclosed that it had $5 billion in debt and was spending about $400 million per year for interest on that debt. Toys "R" Us net debt was $109.0 million in 2005, just before being taken over by private equity buyers in 2005. In that takeover, the company incurred $5.3 billion in debt. Sales revenue in the twelve months before the buyout in 2005 were $11.2 billion. Sales in the twelve months ending October 2017 were $11.1 billion. During the bankruptcy and store closing announcement in March 2018, the Toys "R" Us CEO stated that the company had fallen behind on the general upkeep and condition of its stores, which contributed to the decline in sales. It has also faced intense competition from other retailers, such as Amazon.com and Walmart. Toys "R" Us had had plans during 2017 to invest in technology, upgrade its stores to have toy testing areas, and create other features that would draw customers into the stores,…arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





